SBI 4UI
advertisement

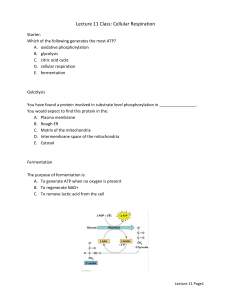
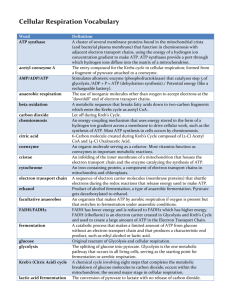
SBI 4UI Metabolism Test Review Key Terms: Coupled reaction Substrate-level phosphorylation ATP NAD+/NADH + H+ FAD/FADH2 Glycolysis Glucose Pyruvate Fermentation Mitochondrial matrix Mitochondrial cristae Kreb’s cycle Acetyl co-A Electron transport Chemiosmosis Proton motive force Electrochemical gradient Oxidative phosphorylation Cytochromes ATP synthase FMN Co-enzyme Q Co-enzyme a/a3 Hydrogen cyanide Dinitrophenol (DNP) Chloroplast Thylakoids Grana Stroma Photon Wavelength Chlorophyll a Chlorophyll b P680 (PS II) P700 (PS I) Carotenoids Antennae pigments Cyclic photophosphorylation Non-cyclic Photophosphorylation Photolysis Carbon fixation PGAL PGA Ribulose phosphate Ribulose biphosphate (RuBP) Light Dependent reactions Light Independent reactions RUBISCO NADPH * terms and concepts in italics are involved in photosynthesis (On a separate test!) In addition to knowing the above terms, students should be able to know and do the following: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. Why is ATP important in coupled reactions? Describe the role of NAD+ and FAD. Where do these molecules come from? Explain what is meant by substrate-level phosphorylation and give two examples. Trace the path of glycolysis from glucose through to pyruvate, listing all major intermediates in the correct order. Be sure to keep track of any phosphorylations and oxidation/reduction reactions that occur along the way. What happens to pyruvate if little or no oxygen is present in the cell? What is the purpose of this process? Label a diagram of a mitochondrion, indicating the following: outer mitochondrial membrane, cristae, mitochondrial matrix. Name the location where each of the following cell processes occur: Glycolysis, Kreb’s cycle, Electron Transport (oxidative phosphorylation) Name three(3) ways that pyruvate is modified as it moves into to mitochondrion and prepares to enter Kreb’s cycle. Describe the formation of citric acid in Kreb’s cycle. How many carbons does citric acid have? For glycolysis, Kreb’s cycle and electron transport, list the following: location, aerobic/anaerobic, reactants, products, ATP produced (per glucose), NADH produced, FADH2 produced. What is the source of electrons for the electron transport chain? Describe how ATP is made in the electron transport chain. What is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain? Provide the summary chemical equation for cellular respiration and explain the origin of each of the reactants and products. Name two chemical poisons that may interfere with cellular respiration and describe their mode of action. How can the demand for oxygen be reduced in living animal cells? Give one real-life application of this. Explain how other nutrients such as proteins and lipids enter into the metabolic pathways. Do energy drinks really give you more energy? Explain. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. Label a diagram of the chloroplast and list the function of each part. Label a diagram of the parts of a leaf and give the function of each part. What is the function of photosynthetic pigments? Suppose you were trying to maximize photosynthesis. Explain what wavelength(s) of light you would expose your plants to and why. Refer to Question #24. What wavelength of light would be the least effective at supporting photosynthesis? Why? Compare cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation. Where does photophosphorylation occur? What is the function of water in photosynthesis? How much ATP and NADPH does it take to produce one glucose molecule? Where are these molecules produced? Describe the three (3) stages of the light independent reactions (Calvin cycle). How many PGAL molecules does it take to form one glucose molecule? Plants in warmer climates need to conserve water as much as possible and therefore must keep their stomata closed. This leads to a build up of oxygen. Explain why a build up of oxygen could be a problem for the plant and describe how these plants solve the problem. Textbook Review Questions to check out: p. 58 #1-3, 7 p. 68 # 1-9, 13 p. 82 # 2-5, 9, 10 p. 96-97 # 29, 39 p. 100-103 # 9-12, 15-18, 41,42