Cellular Respiration Vocabulary
advertisement
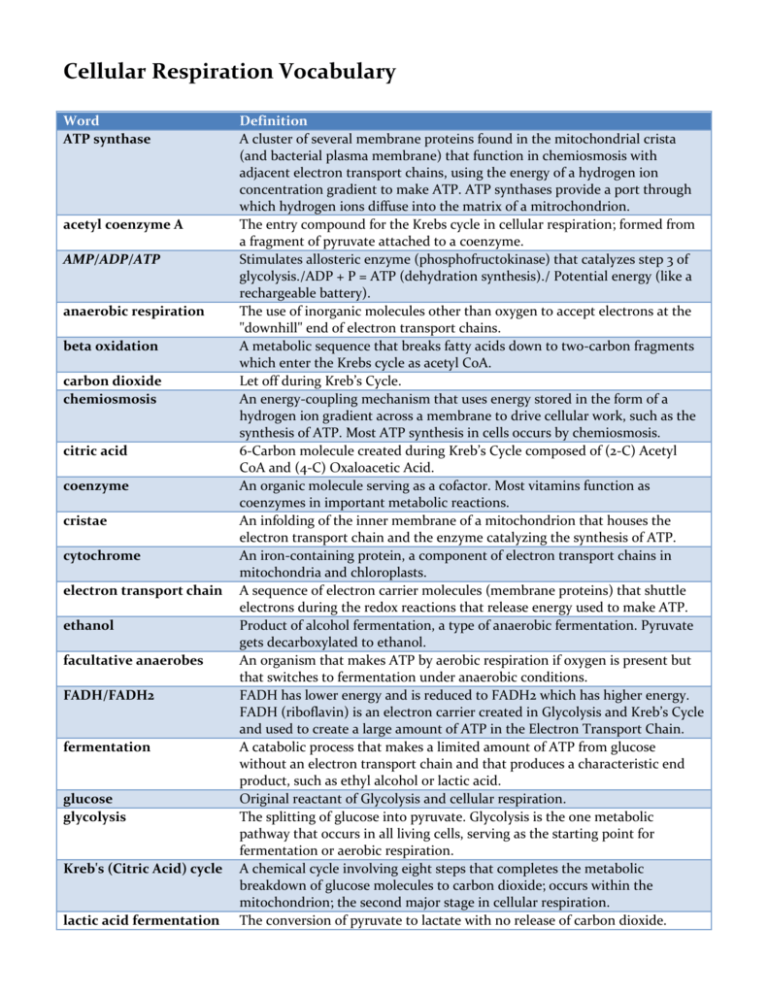
Cellular Respiration Vocabulary Word ATP synthase acetyl coenzyme A AMP/ADP/ATP anaerobic respiration beta oxidation carbon dioxide chemiosmosis citric acid coenzyme cristae cytochrome electron transport chain ethanol facultative anaerobes FADH/FADH2 fermentation glucose glycolysis Kreb's (Citric Acid) cycle lactic acid fermentation Definition A cluster of several membrane proteins found in the mitochondrial crista (and bacterial plasma membrane) that function in chemiosmosis with adjacent electron transport chains, using the energy of a hydrogen ion concentration gradient to make ATP. ATP synthases provide a port through which hydrogen ions diffuse into the matrix of a mitrochondrion. The entry compound for the Krebs cycle in cellular respiration; formed from a fragment of pyruvate attached to a coenzyme. Stimulates allosteric enzyme (phosphofructokinase) that catalyzes step 3 of glycolysis./ADP + P = ATP (dehydration synthesis)./ Potential energy (like a rechargeable battery). The use of inorganic molecules other than oxygen to accept electrons at the "downhill" end of electron transport chains. A metabolic sequence that breaks fatty acids down to two-carbon fragments which enter the Krebs cycle as acetyl CoA. Let off during Kreb’s Cycle. An energy-coupling mechanism that uses energy stored in the form of a hydrogen ion gradient across a membrane to drive cellular work, such as the synthesis of ATP. Most ATP synthesis in cells occurs by chemiosmosis. 6-Carbon molecule created during Kreb’s Cycle composed of (2-C) Acetyl CoA and (4-C) Oxaloacetic Acid. An organic molecule serving as a cofactor. Most vitamins function as coenzymes in important metabolic reactions. An infolding of the inner membrane of a mitochondrion that houses the electron transport chain and the enzyme catalyzing the synthesis of ATP. An iron-containing protein, a component of electron transport chains in mitochondria and chloroplasts. A sequence of electron carrier molecules (membrane proteins) that shuttle electrons during the redox reactions that release energy used to make ATP. Product of alcohol fermentation, a type of anaerobic fermentation. Pyruvate gets decarboxylated to ethanol. An organism that makes ATP by aerobic respiration if oxygen is present but that switches to fermentation under anaerobic conditions. FADH has lower energy and is reduced to FADH2 which has higher energy. FADH (riboflavin) is an electron carrier created in Glycolysis and Kreb’s Cycle and used to create a large amount of ATP in the Electron Transport Chain. A catabolic process that makes a limited amount of ATP from glucose without an electron transport chain and that produces a characteristic end product, such as ethyl alcohol or lactic acid. Original reactant of Glycolysis and cellular respiration. The splitting of glucose into pyruvate. Glycolysis is the one metabolic pathway that occurs in all living cells, serving as the starting point for fermentation or aerobic respiration. A chemical cycle involving eight steps that completes the metabolic breakdown of glucose molecules to carbon dioxide; occurs within the mitochondrion; the second major stage in cellular respiration. The conversion of pyruvate to lactate with no release of carbon dioxide. matrix mitochondrion NAD+/NADH oxaloacetic acid oxidation/reduction oxidative phosphorylation oxidizing agent phosphofructokinase phosphorylation pyruvic acid reducing agent respirometer substrate-level water The nonliving component of connective tissue, consisting of a web of fibers embedded in homogeneous ground substance that may be liquid, jellylike, or solid. An organelle in eukaryotic cells that serves as the site of cellular respiration. NAD+ has lower energy and is reduced to NADH which has higher energy. NAD+ (niacin) is an electron carrier created in Glycolysis and Kreb’s Cycle and used to create a large amount of ATP in the Electron Transport Chain. A 4-Carbon molecule that attaches to Acetyl CoA (2-C) on its way to the top of Kreb’s Cycle to create a 6-C citrate. The loss of electrons from a substance involved in a redox reaction. / The addition of electrons to a substance involved in a redox reaction. The production of ATP using energy derived from the redox reactions of an electron transport chain. The electron acceptor in a redox reaction. Enzyme that catalyzes step 3 in glycolysis. It is inhibited by ATP and citrate and stimulated by AMP. A molecule that has been the recipient of a phosphate group. Pyruvate – Product of glycolysis. Necessary for the start of Kreb’s Cycle but does not enter Kreb’s Cycle. The electron donor in a redox reaction. The formation of ATP by directly transferring a phosphate group to ADP from an intermediate substrate in catabolism. In the Electron Transport Chain, water is created by the H+ in the membrane and the oxygen at the terminal point for the electrons. Good luck on this phosphofructokinase-ing test!!!





