Photosynthesis vs. Cellular Respiration Worksheet
advertisement
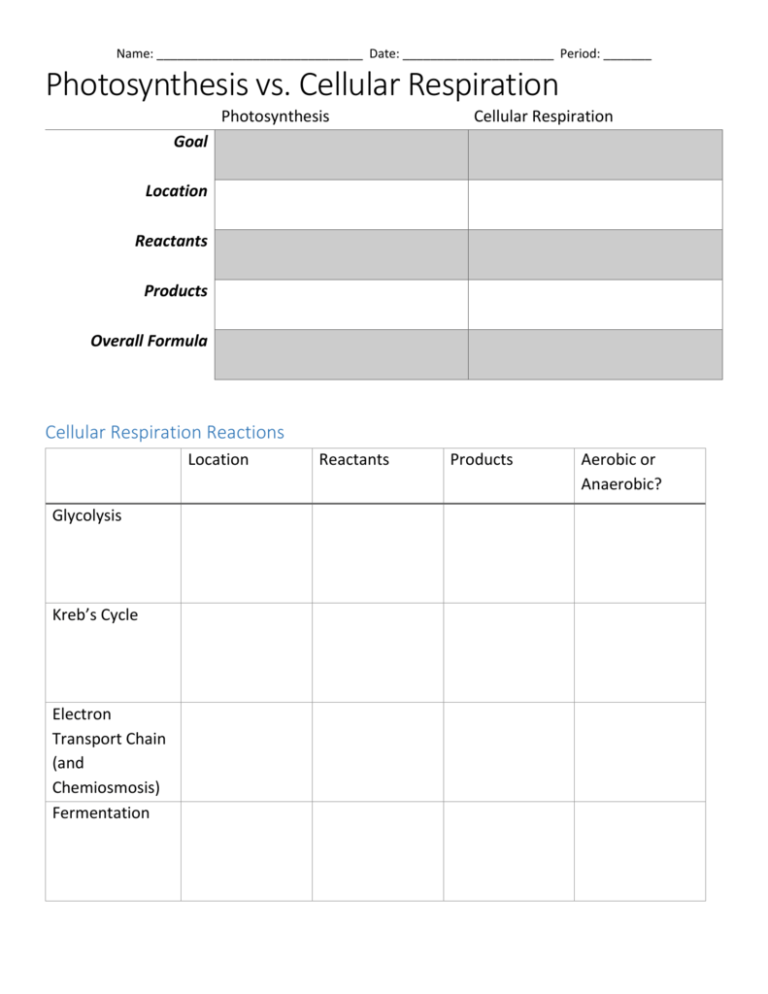
Name: ______________________________ Date: ______________________ Period: _______ Photosynthesis vs. Cellular Respiration Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Goal Location Reactants Products Overall Formula Cellular Respiration Reactions Location Glycolysis Kreb’s Cycle Electron Transport Chain (and Chemiosmosis) Fermentation Reactants Products Aerobic or Anaerobic? Name: ______________________________ Date: ______________________ Period: _______ Double Bubble: Photosynthesis Directions: Using the phrases below, organize them in to a double bubble comparing respiration and photosynthesis. Two ATP are produced during anaerobic glycolysis ATP is synthesized Light energy is changed to chemical energy Oxygen is released as a by-product Usable chemical energy is produced Light, chlorophyll, water, and carbon dioxide are raw materials and energy source Energy is released when the chemical bond to the third phosphate in ATP is broken Occurs in mitochondria of all eukaryotic cells Water is split during photolysis to harvest hydrogen for the light independent reactions Proteins in the electron transport chain pass energized electrons along during the formation of ATP Electron carrier molecules are used C6H12O6 + 6 O2 36 ATP + 6 CO2 + 6H2O Requires carbon dioxide Energy is used to bond phosphate to ADP Requires oxygen Light energy is trapped by a pigment called chlorophyll a In the Calvin cycle a series of reactions use CO2 to form carbohydrates Occurs in chloroplasts of some eukaryotic cells Glucose is split into two pyruvic acid molecules during glycolysis CO2 is released during the kreb’s cycle Glucose is split into two pyruvic acid molecules during glycolysis 6 CO2 + 12 H2O C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 6 H2O Glucose and oxygen are raw materials Water is released as a by-product ATP is the molecule that stores energy for biological work in cells The kreb’s cycle and the electron transport chain produce ATP in the mitochondria Potential energy is stored in the chemical bonds of the molecules of the reactants and products