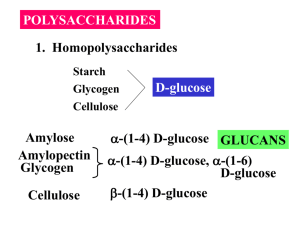
Carbohydrates Solutions
advertisement

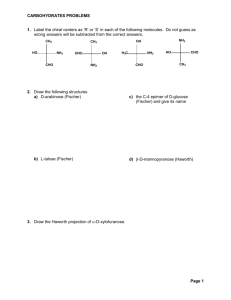
CARBOHYDRATES SOLUTIONS 1. Label the chiral centers as ‘R’ or ‘S’ in each of the following molecules. Do not guess as wrong answers will be subtracted from the correct answers. 4 CH3 HO 1 1 OH 4 CH3 NH2 2 OHC 3 3 CHO H3C 4 OH 1 2. Draw the following structures a) D-arabinose (Fischer) 4 CH3 (R) c) the C-4 epimer of D-glucose (Fischer) and give its name O HO CHO 3 (S) (R) NH2 HO 1 NH2 2 3 CHO 2 NH2 (R) 2 O H H O OH H OH HO H OH H OH H OH H H 4 OH HO H HO H H OH OH OH OH D-glucose D-galactose d) -D-mannopyranose (Haworth) b) L-talose (Fischer) O O OH O HO HO HO H H H H HO H H H OH OH OH OH H HO HO H H H H OH OH OH OH OH L-talose D-talose D-mannose O OH H OH OH HO H H H H -D-mannopyranose 3. Draw the Haworth projection of -D-xylofuranose. O HO H HO H OH H OH OH D-xylose H O OH H H OH OH H -D-xylofuranose Page 1 CARBOHYDRATES SOLUTIONS 4. Draw the structures of the products you would expect to obtain from the following reactions. Name the products where required. a) -D-ribofuranose + CH3I, Ag2O ..................................................... (no name required) O permethylation OH H H H OH OH OH H O OH CH 3I H H OH OH OH H H O H H Ag2O D-ribofuranose D-ribose OCH 3 H OCH 3 OCH 3OCH 3 D-ribofuranose tetramethyl ether b) D-threose + Tollens reagent (Ag+ in NH3) .............................................. (name) O O - O Na + + HO H H OH Ag in NH 3 HO H OH H OH OH D-threonic acid sodium salt D-threose i.e., sodium D-threonate c) -D-altrofuranose + isopropyl alcohol, HCl ....................................................... (name) O HO H H H H HO H H H H OH OH OH OH D-altrose OH H O OH (CH 3)2CHOH, HCl OH OH H O H HO H O OH H OH CH 2OH CH3 CH3 isopropyl D-altrofuranoside D-altrofuranose d) -D-arabinofuranose + acetic anhydride (CH3CO)2O in pyridine solvent (no name) (H 3 C)OCO O HO H H H OH OH OH D-arabinose H HO H H OH H O OH CH2OH D-arabinofuranose HO OCO(CH 3 ) H O C5 H5 N H O H H HO H OCO(CH 3 ) H OH (CH 3CO) 2O H OH H OCO(CH 3 ) D-arabinofuranose tetraester Page 2 CARBOHYDRATES SOLUTIONS e) D-idose + NaBH4, then H2O .............................................................. (name required) O HO H HO H OH H OH H OH 1. NaBH 4 2. H2O HO H HO H H OH H OH OH OH D-iditol D-idose f) D-lyxose in Kiliani Fischer Synthesis ...........................................(name both products) O O HO HO H 1. NaCN, HCN H H OH 2. H3O + H HO HO H O OH H H OH OH HO HO HO H + OH D-lyxose H H H OH OH D-talose D-galactose g) D-glucose in Wohl Degradation ............................................................ (name product) O H HO H H O 1. NH 2OH OH H OH OH HO H H 2. (CH 3CO) 2O NaAc 3. NaOCH 3 OH OH D-arabinose D-glucose 5. Draw the following structures ... a) cellobiose CH2OH 4' CH2OH .. O .. b) any deoxyribose c) any amino sugar O O .. O .. OH C OH H OH C H H OH H OH H OH H NH2 H H H OH 1 OH OH O H OH OH CH2OH OH D-deoxyribose CH2OH an amino sugar of D-ribose Page 3 CARBOHYDRATES SOLUTIONS 6. Write the correct name of each of the following ... a) polysaccharide in potatoes and digestible by humans ..........starch..... b) polysaccharide stored in the liver and muscles of humans ........... glycogen................... c) polysaccharides in grass …………………………………… cellulose……………… d) the disaccharide produced when starch is metabolized ……… maltose…………….. e) water soluble form of starch ......................................... amylose.................................. f) pulverized with hot water ............................................. tritutated................................ g) the 2 monosaccharides which make up sucrose ........ glucose + fructose..... h) the polysaccharide imparting strength and rigidity to plants ..... cellulose........ i) textile fiber made from wood pulp, CS2, and NaOH ....... viscose rayon............ j) milk sugar .................................................... lactose......................... k) carbohydrate which yields 3 to 10 monosaccharides on hydrolysis .. oligosaccharides... l) general name for a 5 carbon aldehydic monosaccharide ........ aldopentose...... m) general name for a 7 carbon ketonic monosaccharide ........ ketoheptose............. n) general name for the 2 diastereomers produced when an open chain monosaccharide cyclicizes to its hemiacetal form ....................... anomers....................... o) Name the 2 reagents, which are combined to produce ‘acetate rayon’. ………………………… cellulose + acetic anhydride………………………… p) Explain the difference between an epimer and an anomer. …………………………….. … anomers have cis- or trans-stereochemistry at the #1 Carbon in the cyclic sugar…….. … epimers (also diastereomers) have opposite configuration at any one of their chiral carbons…… 7. Identify all chiral centers as (R) or (S) in the following and give their IUPAC and common names D-xylose (3S,4R,5R)-1,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxy-2-hexanone a) OH (S) HO H (R) H (R) O H OH OH OH D-fructose O b) H HO H OH (R) H (S) OH (R) OH (2R,3S,4R)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxypentanal Page 4 CARBOHYDRATES SOLUTIONS 8. Explain in words or by a drawing, the structural difference between cellobiose and maltose. Be sure to identify which is which Maltose is a 1,4’---D-glycoside of D-glucose , whereas Cellobiose is a 1,4’---D-glycoside of D-glucose. Page 5