Chemistry 160 Final Exam key Pg. Chemistry 160 Final Exam key
advertisement

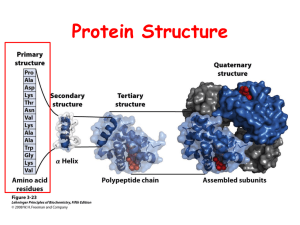
Chemistry 160 Final Exam key Please put your name on this exam. There is some useful information on the last page. I hope you have gotten from this class what you needed. Keep in touch. 100 points (5) 1. Draw a peptide of the sequence S—K—I at pH 2. O H3N+ H N O H N O OH OH NH3+ (5) 2. Describe the 5 levels of protein structure. Primary = amino acid sequence Secondary = simple folding like alpha helix, beta sheet Supersecondary = patterns of secondary…beta barrels, etc Tertiary = 3D structure Quaternary = subunits (5) 3. Describe the “induced fit” for protein ligand binding. In the induced fit model, the ligand and protein are near fits. Both change shape a bit during the binding process. (5) 4. Describe an alpha helix. Right handed helix 3.6 aa/turn with backbone H-bonding between the carboxyl oxygen and amino hydrogen 4 aa away. R- groups are perpendicular to the helix and on the outside. Chemistry 160 Final Exam key Pg. 2 (5) 5. When an enzyme catalyzes a reaction, it somehow supplies the activation energy for the reaction. Where does this energy come from? Several places: expulsion of highly ordered water of hydration from the binding site, induced fit shape changes that force the substrate into an unstable transition state (5) 6. Draw a phosphoacylglycerol where the fatty acids are both stearate and choline is attached. O H2C CH3 + H3C N CH3 HC O O O P O O O (CH2)16 (CH2)16 CH3 CH3 C H2 O (5) 7. Describe the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane. Tired of drawing diagrams: Phospholipid bilayer with proteins and cholesterol interspersed. The cholesterol regulates fluidity. There is 2-dimensional diffusion in the membrane. A good analogy is proteins in a lipid ocean. (5) 8. Give three ways particles can get across a membrane. Diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport, endocytosis (with and without receptors) (5) 9. Give three roles of cholesterol. Regulate membrane fluidity, part of bile salts, basis of steroid hormones, part of vitamin D, Gives Pfizer a market for Lipitor (5) 10. What is a second messenger? Give two examples of second messengers. A molecule released on the inside of a membrane as a response to a binding event in a receptor on the outside of the membrane. Examples include cAMP, inositol, Ca2+ Chemistry 160 Final Exam key Pg. 3 (5) 11. Draw the following: a. glucose-glucose in an α 1,4 linkage CH2OH CH2OH O O OH OH O OH OH OH OH b. glucose-glucose in an α 1,6 linkage CH2OH O OH HO O OH CH2 O OH HO OH OH (10) 12. How much energy do we get from 2.50g of glucose in a prokaryote (180g/mol glucose, 7.3 kcal/mol ATP). Assume aerobic respiration. 2.50 g X 1 mole glucose X 32 mole ATP X 7.3 kcal = 3.2 kcal 180 g glucose mole glucose mole ATP (5) 13. Where do each of the following take place: a. glycolysis cytosol b. beta oxidation mitochondrial matrix c. pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction mitochondrial matrix d. electron transport inner membrane of mitochondrion e. Kreb’s cycle mitochondrial matrix Chemistry 160 Final Exam key Pg. 4 (5) 14. For each cofactor below, give its role a. GTP energy production b. ATP energy production c. NAD+ electron carrier (redox) d. FAD electron carrier (redox) e. coenzyme A acyl group transfer (acetyl) (5) 15. Draw a GC base pair H N O -- -- -- H N NH -- -- -- N N N N O N H -- -- -H Guanine cytosine (5) 16. Draw a short segment of RNA with the sequence G-C-C-G. Chemistry 160 Final Exam key Pg. 5 O 5' end N N O O P O G CH2 N O NH2 N O NH2 OH O O O N P O C CH2 N O O O OH NH2 O N O P O CH2 N O C O O O O OH N N O P O CH2 N O N NH2 G OH OH 3 ' end Chemistry 160 Final Exam key Pg. 6 (5) 17. When we say the vectorial nature of nucleic acids is preserved through translation, what do we mean? The 5’ end of the RNA corresponds to the amino terminus of the protein (10) 18. Given the DNA sequence below, determine the RNA sequence and the amino acid sequence. 3’ DNA T C G G T A C A T G T A A T T T C T T A G T A T T C T G C 5’ 5’ RNA AGCC AUG UAC AUU AAA GAA UCA UAA GACG 3’ Amino acid start Y - I - K --- E -- S stop Chemistry 160 Final Exam key Pg. 7 Useful Information O H3N+ O pK = 8.95 pK = 2.18 O pK = 9.15 pK = 10.53 H3N+ O NH3+ pK = 2.21 OH Lysine (K) serine (S) O pK = 9.68 H3N+ O pK = 2.21 O O (CH2)16 Isoleucine (I) CH3 stearate O O CH3 + H3C N CH3 Choline OH N N OH NH2 NH N Guanine NH2 N N Cytosine O H OH H OH CH2OH ribose Chemistry 160 Final Exam key Pg. 8 U F F L L S S S S Y Y Stop Stop C C Stop W U C A G L P H R U L P H R L P Q R L P Q R A G A I I I M, start T T T T N N K K S S R R U C A G G V V V V A A A A D D E E G G G G U C A G U First letter Genetic Code second letter C A G C C Third letter