Honors Biology
advertisement

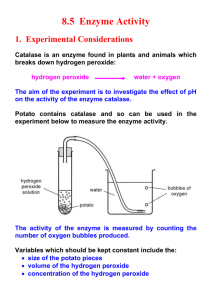
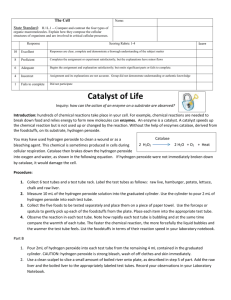
Honors Biology Lab: Testing Enzyme Activity Instructions Background Information Many living tissues contain the enzyme catalase. This enzyme breaks down hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), which is a harmful by-product of the process of cellular respiration if it builds up in concentration in the cells. If we use tissue containing catalase, we can measure the relative influence of varying several different factors on the activity of enzymes in living tissue. In order to obtain energy and building blocks from food, the digestive system must break down proteins, fats and carbohydrates. In this process, specific enzymes catalyze hydrolysis reactions in which foods are broken down into monomers. In this lab, you will perform reactions involved in digestion of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins and observe the results of these reactions. Introduction: What would happen to your cells if they made a poisonous chemical? You might think that they would die. In fact, your cells are always making poisonous chemicals. They do not die because your cells use enzymes to break down these poisonous chemicals into harmless substances. Enzymes are proteins that speed up the rate of reactions that would otherwise happen more slowly. The enzyme is not altered by the reaction. You have hundreds of different enzymes in each of your cells. Each of these enzymes is responsible for one particular reaction that occurs in the cell. In this lab, you will study an enzyme that is found in the cells of many living tissues. The name of the enzyme is catalase (KATuh-LAYSS); it speeds up a reaction that breaks down hydrogen peroxide, a toxic chemical, into 2 harmless substances--water and oxygen. The reaction is as follows: 2H2O2 ----> 2H2O + O2 This reaction is important to cells because hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is produced as a byproduct of many normal cellular reactions. If the cells did not break down the hydrogen peroxide, they would be poisoned and die. In this lab, you will study the catalase found in liver cells. You will be using chicken or beef liver. It might seem strange to use dead cells to study the function of enzymes. This is possible because when a cell dies, the enzymes remain intact and active for several weeks, as long as the tissue is kept refrigerated Problem How does pH and temperature influence the activity of the enzyme catalase? Materials (per group) 5 x 75 ml test tubes 10 ml graduated cylinder Petri dish 1 medicine dropper Glass marking pencil Safety goggles Heating element 1 M sodium hydroxide 1 M hydrochloric acid 3% hydrogen peroxide Small piece of raw beef liver Liver puree (catalase) Heat bath Ice bath Procedure Part A 1. Record your observations in the data table in the lab report. 2. Put on safety goggles. 3. Put a small piece of raw liver in an open petri dish. Using a medicine dropper, put a drop of hydrogen peroxide on the liver. CAUTION: Hydrogen peroxide can be irritating to skin and eyes. If you spill any on yourself or your clothes, wash it off immediately. Observe what happens. Liver contains the enzyme catalase, which breaks down hydrogen peroxide formed in cells. When hydrogen peroxide is broken down by catalase, bubbles of oxygen gas are released. 4. Using the glass marking pencil, number the test tubes from 1-5. 5. Add the following amounts of solutions to the test tubes: Test tube 1: 2.5 mls HCl/ 5 drops water Test tube 2: 5 drops HCl/ 2.5 mls water Test tube 3: 2.5 mls water Test tube 4: 5 drops NaOH/ 2.5 mls water Test tube 5: 2.5 mls NaOH/ 5 drops water 6. Using a clean graduated cylinder, add 2 mls of hydrogen peroxide to each test tube. Look for bubbles. Identify the amount of activity in each tube by assigning it a number from 0 to 3. 0 no bubbles 1 few bubbles 2 moderate bubbles 3 many bubbles 7. Rinse out the test tubes and repeat the same procedure, but replace the water with liver puree. 8. Record you results in the table in the lab report. 4. Answer the questions pertaining to this part of the lab. Name ______________________________ Honors Biology Testing Enzyme Activity Lab Report Identify the following: Independent variable Dependent variable Control group Experimental group Controlled variables Observations Part A Data Table Tube Number 1 2 3 4 5 Graph your results. Without Liver Puree pH Activity 2 4 6 12 14 With Liver Puree pH Activity 2 4 6 12 14 Observations Part A Observations Part B Data Table Temperature Condition Test tube at 20 Test tube in ice bath Test tube in heat bath Reactivity Critical Thinking Part B 1. Explain how temperature affects enzyme activity. Be specific what happens at either temperature extreme.__________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Which condition would be worse for an organism. Exposure to cold or excessively hot temperatures. Explain your answer. ___________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________