Catalase Enzyme Activity: pH & Temperature Lab Report
advertisement

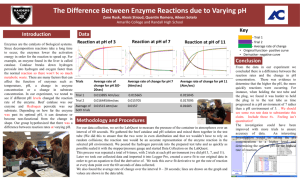
8.5 Enzyme Activity 1. Experimental Considerations Catalase is an enzyme found in plants and animals which breaks down hydrogen peroxide: hydrogen peroxide water + oxygen The aim of the experiment is to investigate the effect of pH on the activity of the enzyme catalase. Potato contains catalase and so can be used in the experiment below to measure the enzyme activity. The activity of the enzyme is measured by counting the number of oxygen bubbles produced. Variables which should be kept constant include the: size of the potato pieces volume of the hydrogen peroxide concentration of the hydrogen peroxide 2. Effect of pH Method: the apparatus was set up as shown. 5cm3 of pH 7 solution was added to the test tube. 4 potato disks were also added to the test tube. the mixture was left to stand for 2 minutes. after this time 5 cm3 of hydrogen peroxide was added to the test tube the stopper with delivery tube was inserted and the timer started. the number of bubbles produced was counted over a 3 minute period. the experiment was repeated using fresh potato and solutions of different pH. Results: pH of solution Number of oxygen bubbles In 3 minutes 1 4 7 10 13 0 6 28 63 45 Graph of Results: 70 Number of oxygen bubbles 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 pH of Solution Conclusion: The activity of catalase increases with pH to an optimum pH of 10. Thereafter, the activity decreases with increasing pH. 3. Effect of Temperature This activity examines the effect of temperature on the activity of the enzyme catalase. Method: The previous experiment was repeated at pH 7. Instead of altering the pH, the temperature was changed. Graph of results: 25 Number of bubbles 20 15 10 5 0 0 20 40 60 80 Temperature (˚C) Conclusion: The activity of the enzyme increases with temperature up to the optimum temperature of 40˚C. Thereafter, the activity drops off very quickly to zero with increasing temperature.