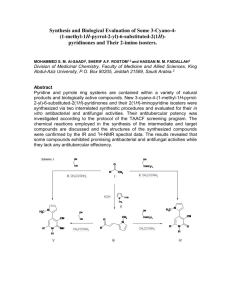
Назва наукового напрямку (модуля): Семестр: 4 Module 2
advertisement

Назва наукового напрямку (модуля): Семестр: 4 Module 2. Carboxylic acids, heterocyclic and natural compounds. O H2C CH C 1. What are the products of reaction A. 2-bromopropanoic acid B. 2-bromopropanoic acid and HBr C. 2-bromopropanoic acid and water D. *3-bromopropanoic acid E. 3-bromopropanoic acid and HBr + HBr ? OH O C OH CH2 CH2 OH C 2. Choose the right name of carboxylic acid A. oxalic acid B. mallonic acid C. adipic acid D. formic acid E. *succinic acid O O CH2 CH C + Br2 3. What are the products of reaction A. 2,3-dibromopropanoic acid and H2O B. *2,3-dibromopropanoic acid C. bromoanhydride of propanoic acid + H2O + HBr D. 3-bromopropanoic acid and HBr E. 2-bromopropanoic acid and HBr ? OH O CH CH C OH 4. Choose the right name of carboxylic acid A. *cinnamic acid B. succinic acid C. formic acid D. isovaleric acid E. valeric acid 5. Which of the following reagent can be used to form anhydrides? A. B. C. D. .* E. 6. What are the products of the reaction between phthalic anhydride and primary amines? A. .* B. C. D. E. 7. What is the identity of the intermediate (A) and the end-product (B) in the following scheme? A. B. C. * D. E. 8. Choose the correct range of acidity increase for the following compounds. A. a, c, b B. c, a, b C. c, b, a D. b, a, c E. *a, b, c 9. Choose the correct range of acidity increase for the following compounds. A. a, c, b B. c, a, b C. *c, b, a D. b, a, c E. a, b, c 10. Choose the correct range of acidity increase for the following compounds. A. *b;c;a B. c;a;b C. c, b, a D. b;a;c E. a;b;c 11. Which of the following compounds will interact with carboxylic acids to get anhydrides? A. B. C. D. * E. 12. Which intermediate and the end-product are formed in the reaction of ammonia with acetic acid? A. B. C. D. * E. 13. Choose the correct range of acidity increase for the following compounds. A. a, c, b B. c, a, b C. *c, b, a D. b, a, c E. a, b, c 14. Choose the correct range of acidity increase for the following compounds. A. a, c, b B. c, a, b C. c, b, a D. *b, a, c E. a, b, c 15. Choose the correct range of acidity increase for the following compounds. A. a, c, b B. c, a, b C. c, b, a D. b, a, c E. *a, b, c 16. Choose the correct range of acidity increase for the following compounds. A. *a, c, b B. c, a, b C. c, b, a D. b, a, c E. a, b, c 17. Which of the following compound will interact with benzoic acid? A. B. C. D. * E. 18. Which of the following reactions leads to the formation of acetophenone? A. B. C. D. * E. 19. Compound with characteristic smell, which changes coloration of litmus paper, forms gas after the adding of zinc and gives „silver mirror” reaction, is: A. НС(О)Н B. С6Н5ОН C. *НСООН D. СН3С(О)Н E. СН3СООН 20. At the interaction of carboxylic acids with alcohols at the heating in the presence of H2SO4 form: A. Aldehydes B. Ethers C. Phenols D. Ketones E. *Esters 21. Potassium stearate – liquid soap, its formula: A. C17H33COOK B. *C17H35COOK C. C17H31COOK D. C17H29COOK E. C3H7COOК 22. Choose formula of unsaturated carboxylic acid: A. *C17H33COOH B. C17H35COOH C. C3H7COOH D. C10H21COOH E. C12H23COOH 23. Which of the following carboxylic acids has properties of aldehyde and acid? A. CH2Cl – COOH B. CH3COOH C. *HCOOH D. CCl3 – COOH E. C3H7COOH 24. Which of the following compounds is a product of propanoic acid chlorination? A. CH3 – CH2 – COCl B. *CH3 – CHCl – COOH C. CH2Cl – CH2 – COOH D. CH3 – CH2 – COOCl E. C3H7COOH 25. Choose the strongest carboxylic acid: A. CH3COOH. B. CH3CH2COOH. C. CH2Cl – COOH. D. *CCl3 – COOH. E. CH3CH2CH2COOH 26. In the reaction CH3CH2COOH + NaHCO3 the following gaseous product forms: A. CH4 B. CO C. *CO2 D. C2H6 E. C2H4 27. Among of the following compounds specify formula of chloroacetic acid: A. CH3COOH B. *CH2(Сl)COOH C. CH2(NH2)COOH D. CH2(CH3)COOH E. CСl3COOH 28. Determine reaction that cases propanoic acid formation: A. CH3-C(O)H + [O] - CH3-COOH B. H-C(O)H + [O] - H-COOH C. CH3-CH2-CH2-C(O)H + [O] - CH3-CH2-CH2-COOH D. *CH3-CH2-C(O)H + [O] - CH3-CH2-COOH E. CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-C(O)H + [O] - CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-COOH 29. Soap belongs to the following class of compounds: A. Alcohols B. Carboxylic acids C. Esters D. *Salts E. Phenols 30. Ethyl ester of acetic acid can be obtained by the following reaction: A. CH3-CH2-OH + CH3-CH2-OH B. CH3-COOH + CH3-COOH C. *CH3-COOH + CH3-CH2-OH D. CH3 COOH + CH3-OH E. CH3-COOH + Na2CO3 31. Specify compound, which with acetic acid will not form salts: A. *CH3-COOH + C2H5OHO B. CH3-COOH + Na2CO3 C. CH3-COOH + Na D. CH3-COOH + Mg E. CH3-COOH + CH3-COOH 32. Lead (ІІ) acetate has the following formula: A. Pb(OH)CH3COO B. Pb(CH3COO)4 C. *Pb(CH3COO)2 D. Pb(CH3COO)3 E. Pb(CH3COO)5 33. In the reaction CH3-COOH + NaOH = the following compounds form: A. *CH3-COONa + H2O B. CH3-COONa + H2 C. CH3-COONa + O2 D. 2CH3-COONa + H2O2 E. 3CH3-COONa + H2O2 34. At the interaction of acetic acid and magnesium (CH3?COOH + Mg) gas … evaporates: A. CO2 B. CO C. *H2 D. H2O(water steam) E. С2Н2 35. Ion CH3-COO- has the following name: A. Formiate B. Carbonate C. Hydrocarbonate D. *Acetate E. Dihydrocarbonate 36. 125. Specify compound, which will not interact with acetic acid: A. Nа B. NaOH C. Na2O D. *CO2 E. Mg 37. Specify compound, which will interact with carboxylic acids: A. *NaOH B. CO2 C. H2O D. NaCl E. KBr 38. Litmus paints solution of acetic acid in ... color: A. Green B. *Red C. Blue D. Colorless E. Purple 39. For the detection of acetic acid can be used: A. *Indicator and sodium hydrogen carbonate B. Bromine water C. Freshly precipitated Cu(OH)2 D. Ammonium solution of Ag2O E. Lime water 40. In the esterification reaction ОН-group eliminates (for the water formation) from the molecule of: A. Alcohol B. Ketone C. Aldehyde D. *Acid E. Phenol 41. Method of formic acid obtaining: A. Ethane oxidation B. *Methane oxidation C. Phenol oxidation D. Reaction of СН3ОН with СО E. Ethylene oxidation 42. For the acetic acid obtaining, as primer compound is used: A. HCOON B. CH3OH C. C4H10 D. C3H7OH E. *С2Н2 43. Glycerin and stearic acid can be obtained by the reaction of: A. Etherification B. Hydrolysis of carbohydrates C. Esterification D. *Hydrolysis of fat E. Hydratation of carbohydrates 44. Glycerin and palmitic acid can be obtained by the reaction of: A. Cracking of petroleum B. Esterification C. *Hydrolysis of fat D. Hydrolysis of carbohydrates E. Hydratation of carbohydrates 45. At the hydrolysis of solid fats the following acid forms: A. Glycerin B. Formic acid C. Ethylene glycol D. Acetic acid E. *Stearic acid 46. Which of the following reaction conducts with hydrogen evaporation? A. *СН3 – СООН + Са B. СН3 – СООН + NaOH C. СН3 – СООН + СаО D. СН3 – СООН + СН3OH O E. СН3 – СООН + Са(ОН)2 47. Choose the reaction of Carbon (ІV) oxide formation: A. СН3 – СООН + NaOH B. СН3 – СООН + Zn C. *СН3 – СООН + Na2СO3 D. СН3 – СООН + СаО E. СН3 – СООН + Са(ОН)2 48. Which of the following properties are common for methanoic and hydrochloric acid? A. Interaction with alkalis and ammonium solution of Ag2O B. *Interaction with metals and alkalis C. Action of conc. Н2SO4. D. Decomposition at the heating E. Interaction with fuxin sulfite acid 49. In which of the following rows all compounds will react with formic acid? A. СН3С(О)Н; СН3 – ОН; СН3СООН B. *С2Н5ОН; Ag2O(ammonium solution); Мg(met.) C. Сu(OH)2; Na2CO3; C3H8 D. CH4; NaOH; CH3Cl E. Сu(OH)2; CH4; NaOH; CH3Cl 50. Functional group -COOH has the name: A. Aldehyde-group B. Hydroxyl group C. *Carboxyl group D. Keto-group E. Phenol hydroxyl 51. Saturated monobasic carboxylic acids have the following general formula: A. R-OH B. R-C(O)H C. R-CH2-OH D. *R-COOH E. R-C(O)OR 52. Among of the following compounds specify formula of carboxylic acid: A. *CH3-COOH B. CH3-OH C. CH3-CH2-OH D. CH3-COH E. CH3-C(O)OCH3 53. Methanoic acid has the following formula: A. CH3-COOH B. CH3-OH C. CH3-CH2-OH D. *H-COOH E. CH3-COH 54. Choose chemical formula of valeric acid: A. CH3COOH B. CH3CH2COOH C. CH3CH2CH2COOH D. *CH3CH2CH2CH2COOH E. CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2COOH 55. Choose chemical formula of butyric acid: A. CH3COOH B. CH3CH2COOH C. *C3CH2CH2COOH D. CH3CH2CH2CH2COOH E. CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2COOH 56. The strongest monobasic saturated carboxylic acid is the following one: A. *HCOOH B. CH3COOH C. CH3CH2COOH D. CH3CH2CH2COOH E. CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2COOH 57. To distinguish formic acid from acetic acid the following reagent can be used: A. NH3 B. NaOH C. *[Ag(NH3)2]OH D. NaHCO3 E. Ca(OH)2 58. Salts of methanoic acid are called: A. Acetates B. Carbonates C. Lactates D. Propionates E. *Formiates 59. Formic acid, except acidic properties, also has properties of: A. Alcohols B. Ketones C. *Aldehydes D. Amines E. Phenols 60. Product of the formic acid dehydration is: A. СО2 B. *СО C. СН4 D. С2Н2 E. С2Н4 61. Organic product of the interaction of carboxylic acid with alcohol is: A. *Ester B. Ether C. Ketone D. Aldehyde E. Anhydride 62. At the total reduction of carboxylic acids are formed: A. *Alcohols B. Aldehydes C. Ketones D. Esters E. Ethers 63. Choose the formula of ammonium acetate: A. NH4Cl B. *CH3COONH4 C. HCOONH4 D. CH3COON E. СН3СН2СООNH4 64. What compound has the biggest acidic properties? A. Ethanol B. Glycerin C. Acetic acid D. *Formic acid E. Phenol 65. Gaseous product of the “silver mirror” reaction by the participant of methanoic acid is: A. CH4 B. H2 C. CO D. *CO2 E. С2Н2 66. Gaseous product of the methanoic acid dehydration is: A. CH4 B. H2 C. *CO D. CO2 E. С2Н2 67. Compound НСООН gives reactions, which are characteristic for: A. Organic acids and alcohols B. *Organic acids and aldehydes C. Alcohols and aldehydes D. Aldehydes and esters E. Phenols and aldehydes 68. How many asymmetric carbon atoms and possible stereoisomers does tartaric acid have? A. no asymmetric carbon atoms and it is optically inactive B. two asymmetric carbon atoms and two stereoisomers C. *two asymmetric carbon atoms and three stereoisomers D. two asymmetric carbon atoms and four stereoisomers E. one asymmetric carbon atom and two stereoisomers 69. How many asymmetric carbon atoms and possible stereoisomers does malic acid have? A. no asymmetric carbon atoms and it is optically inactive B. two asymmetric carbon atoms and four stereoisomers C. *one asymmetric carbon atom and two stereoisomers D. one asymmetric carbon atom and one stereoisomer E. two asymmetric carbon atoms and two stereoisomers 70. Which of the following reagent interact with carboxylic-group of α-bromopropanoic acid? A. B. C. D. * E. 71. How many asymmetric carbon atoms and possible stereoisomers does lactic acid have? A. no asymmetric carbon atoms and it is optically inactive B. two asymmetric carbon atoms and four stereoisomers C. two asymmetric carbon atoms and two stereoisomers D. *one asymmetric carbon atom and two stereoisomers E. one asymmetric carbon atom and one stereoisomer 72. Which hydroxyacid does decompose at treatment with conc. H2SO4 according to the following scheme? A. B. C. D. E. * 73. Which hydroxyacid decomposes at treatment with conc. H2SO4 according to the following scheme? A. B. C. D. E. * 74. Which hydroxyacid decomposes at treatment with conc. H2SO4 according to the following scheme? A. B. C. D. E. * 75. What is the product of reaction between pyruvic acid and hydroxylamine? A. B. C. D. E. * 76. What products are formed when diethylacetoacetic ester is treated with diluted mineral acid? A. B. C. D. E. * 77. What products are formed when methylpropylacetoacetic ester is treated with concentrated solution of alkali? A. B. C. D. * E. 78. What product is formed when γ -hydroxyvaleric acid is heated? A. B. C. * D. E. F. 79. What product is formed when β -hydroxybutyric acid is heated? A. B. C. * D. E. 80. Choose the correct range of acidity increase for the following compounds. A. d > b > a > c B. d < b < a < c C. c < b < a < d D. b < a < c < d E. *c < d < b < a 81. Which is the product of salicylic acid nitration? A. B. C. D. E. * 82. How many asymmetric carbon atoms and possible stereoisomers does α-hydroxybutyric acid have? A. no asymmetric carbon atoms and it is optically inactive B. two asymmetric carbon atoms and one stereoisomer C. one asymmetric carbon atom and one stereoisomer D. two asymmetric carbon atoms and two stereoisomers E. *one asymmetric carbon atom and two stereoisomers 83. Malic acid is: A. monobasic biatomic acid B. tribasic biatomic acid C. *dibasic triatomic acid D. dibasic monoatomic acid E. tribasic triatomic acid 84. What product is formed when tartaric acid is heated in the presence of KHSO4? A. B. C. D. * E. 85. What product is formed when γ-hydroxybutyric acid is heated? A. B. * C. D. E. 86. What is the identity of the reagent ¬¡ and intermediate B in the following scheme? A. B. * C. D. E. 87. Choose the pair of reagents which can be used to obtain β-hydroxybutyric acid by Reformatsky reaction. A. B. * C. D. E. 88. Choose the correct name of the following compound. A. oxoketoglutaric acid B. α-ketopentanedioic acid C. *β- ketoglutaric acid D. 2- ketoglutaric acid E. oxopentanedioic acid 89. Choose the correct name of the following compound. A. chlorosuccinic acid B. 3- chlorobutyric acid C. *3- chlorobutanoic acid D. α - chloropentanoic acid E. 3-chloropentanoic acid 90. Which of the following reagent shall react with both functional groups of βchloropropanoic acid? A. B. C. D. E. * 91. Citric acid is: A. monobasic triatomic acid B. tribasic monoatomic acid C. *tribasic tetraatomic acid D. tetrabasic triatomic acid E. tribasic triatomic acid 92. Trataric acid is: A. tribasic tetraatomic acid B. tetrabasic tetraatomic acid C. tetrabasic biatomic acid D. *dibasic tetraatomic acid E. dibasic biatomic acid 93. Which hydroxycarboxylic acid decomposes at treatment with conc. H2SO4 according to the following scheme? A. B. C. D. E. * 94. Which way does citric acid decomposes? A. B. C. D. E. * 95. What product is formed when α-hydroxypropanoic acid is heated? A. B. * C. D. E. 96. What products are formed when acetoacetic ester is treated with concentrated solution of alkali? A. B. C. D. * E. 97. What product is formed when urea is slowly heated? A. B. C. * D. E. 98. What products are formed when ethylacetoacetic ester is treated with diluted mineral acid? A. B. C. D. E. * 99. Which is the product of the following reaction? A. * B. C. D. E. 100. What products are formed when methylacetoacetic ester is treated with diluted mineral acid? A. B. C. D. * E. 101. Which wayα-chlorosuccinic acid could be obtained? A. B. C. D. * E. 102. Which of the following is α - ketoglutaric acid? A. * B. C. D. E. 103. Which of the following compounds is glyoxylic acid? A. B. C. D. * E. 104. Which way α-chloropropanoic acid could be obtained? A. B. C. D. * E. 105. Which of the following is tartaric acid? A. * B. C. D. E. 106. Which of the following reaction lead to formation of pyruvic acid? A. B. C. D. 107. E. * Which of the following is acetylsalicylic acid? A. B. C. D. * E. 108. Which of the following is salicylic acid? A. B. C. * D. E. 109. Which of the following is citric acid? A. B. C. D. * E. 110. Which of the following is oxalacetic acid? A. B. * C. D. E. 111. Which of the following is acetoacetic acid? A. B. * C. D. E. 112. Which of the following compounds is o-hydroxycinnamic acid? A. * B. C. D. E. 113. Which of the following compounds is malic acid? A. B. C. * D. E. 114. Choose the correct name of the following compound. A. B. C. D. E. propylbromoacetic acid α - bromovaleric acid 2-bromo-3-methylpropanoic acid *2-bromo-3-methylbutanoic acid α - bromobutyric acid 115. Salicylic acid has two acidic centers and therefore forms two rows of salts. What reagent can be used to form disodium salt of salicylic acid? A. *NaOH B. NaНCO3 C. NaCl D. Na2SO4 E. CH3COONa 116. α–Hydroxyacids at the heating will form: A. lactides B. *lactones C. saturated α-acids D. esters with open carbon chain E. acetoacetic ester 117. Salicylic acid has two acidic centers and therefore forms two rows of salts. What reagent can be used to form disodium salt of salicylic acid? A. *NaOH B. NaНCO3 C. NaCl D. Na2SO4 E. CH3COONa 118. Choose acid, which forms -lactone after the heating? A. pyruvic B. glycolic C. lactic D. *4-hydroxybutanoic E. malic 119. At the adding to the organic compound FeCl3, dark violet color will form. Name this compound? A. benzoic acid B. benzene C. toluene D. acetylsalicylic acid E. *salicylic acid 120. Galic acid is a part of thiamine. To which class of compounds does this acid belong? A. alcohol acids B. *phenoloacids C. aminoacids D. aldehyde acids E. ketoacids 121. What compound will form at the interaction of lactic acid with excess of SOCl2? A. 2-chloropropanoic acid B. chloroanhydride of lactic acid C. *chloroanhydride of 2-chloropropanoic acid D. 2-chlorolactic acid E. 3-chlorolactic acid 122. What reagent is used for the acetoacetic ester determination? A. *FeCl3 B. CuSO4 C. Formaldehyde D. Ethyl alcohol E. KMO4 123. Which of the following reagents will react with glyoxylic acid by aldehyde group? A. Nа B. NaOH C. SОCl2 D. *NH2OH E. NaHCO3 124. A. B. C. D. E. 125. A. B. C. D. E. 126. A. B. C. D. E. 127. A. B. C. D. E. 128. A. B. C. D. E. 129. A. B. C. D. E. 130. A. B. C. D. E. 131. A. B. C. D. E. 132. A. B. C. D. E. 133. A. B. Which of the following reagents will react with glyoxylic acid by aldehyde group? Nа NaHCO3 NaOH SОCl2 *Ag(NH3)2OH Which of the following reagents will react with glyoxylic acid by aldehyde group? NaOH NaHCO3 *HCN SОCl2 Nа Which of the following reagents will react with glyoxylic acid by aldehyde group? NaHCO3 *NH2NH2 NaOH SОCl2 Nа Which of the following reagents will react with glyoxylic acid by aldehyde group? *NH2NHC6H5 NaHCO3 NaOH SОCl2 Nа Which of the following reagents will react with glyoxylic acid by aldehyde group? Nа NaHCO3 NaOH SОCl2 *NH2NHC(O)NH2 Which of the following reagents will react with glyoxylic acid by aldehyde group? NaOH NaHCO3 *NH2NHC(S)NH2 SОCl2 Nа Which of the following reagents will react with glyoxylic acid by carboxylic group? Ag(NH3)2OH C6H5NHNH2 NH2OH *NaHCO3 NH2NH2 Which of the following reagents will react with glyoxylic acid by carboxylic group? Ag(NH3)2OH *NaOH NH2OH C6H5NHNH2 NH2NH2 Which of the following reagents will react with glyoxylic acid by carboxylic group? *Na2CO3 Ag(NH3)2OH NH2OH C6H5NHNH2 NH2NH2 Which of the following reagents will react with glyoxylic acid by carboxylic group? Ag(NH3)2OH NH2NH2 134. 135. 136. 137. 138. 139. 140. 141. 142. C. NH2OH D. C6H5NHNH2 E. *Na Which of the following reagents will react with glyoxylic acid by carboxylic group? A. Ag(NH3)2OH B. C6H5NHNH2 C. NH2OH D. *C2H5OH E. NH2NH2 Which of the following reagents will react with glyoxylic acid by carboxylic group? A. Ag(NH3)2OH B. *CH3OH C. NH2OH D. C6H5NHNH2 E. NH2NH2 Which of the following reagents will react with acetoacetic acid by keto-group? A. Nа B. NaOH C. *NaHSO3 D. SОCl2 E. NaHCO3 Which of the following reagents will react with acetoacetic acid by keto-group? A. NaOH B. *NH2OH C. SОCl2 D. Nа E. NaHCO3 Which of the following reagents will react with acetoacetic acid by keto-group? A. Nа B. NaHCO3 C. NaOH D. SОCl2 E. *NH3 Which of the following reagents will react with acetoacetic acid by keto-group? A. SОCl2 B. NaHCO3 C. NaOH D. *HCN E. Nа Which of the following reagents will react with acetoacetic acid by keto-group? A. *NH2NH2 B. NaHCO3 C. NaOH D. SОCl2 E. Nа Which of the following reagents will react with acetoacetic acid by keto-group? A. NaHCO3 B. *NH2NHC6H5 C. NaOH D. SОCl2 E. Nа Which of the following reagents will react with acetoacetic acid by keto-group? A. NaOH B. NaHCO3 C. *NH2NHC(O)NH2 D. SОCl2 E. Nа 143. Which of the following reagents will react with acetoacetic acid by keto-group? A. SОCl2 B. NaHCO3 C. NaOH D. *NH2NHC(S)NH2 E. Nа 144. Which of the following reagents will react with acetoacetic acid by carboxylic group? A. Ag(NH3)2OH B. NH2NH2 C. NH2OH D. C6H5NHNH2 E. *NaHCO3 145. Which of the following reagents will react with acetoacetic acid by carboxylic group? A. *NaOH B. Ag(NH3)2OH C. NH2OH D. C6H5NHNH2 E. NH2NH2 146. Which of the following reagents will react with acetoacetic acid by carboxylic group? A. Ag(NH3)2OH B. NH2OH C. *Na2CO3 D. C6H5NHNH2 E. NH2NH2 147. Which of the following reagents will react with acetoacetic acid by carboxylic group? A. Ag(NH3)2OH B. *Na C. NH2OH D. C6H5NHNH2 E. NH2NH2 148. Which of the following reagents will react with acetoacetic acid by carboxylic group? A. Ag(NH3)2OH B. NH2NH2 C. NH2OH D. C6H5NHNH2 E. *C2H5OH 149. Which of the following reagents will react with acetoacetic acid by carboxylic group? A. Ag(NH3)2OH B. C6H5NHNH2 C. NH2OH D. *CH3OH E. NH2NH2 150. γ-Aminobutyric acid takes part in the brain metabolism, is a neuromediator. What substances important for the medicine will γ-aminoacids form at the heating? A. *lactames B. unsaturated acids C. diketopiperazine D. lactides E. lactones 151. At the heating of α–aminoacids will form: A. lactones B. lactides C. *diketopiperazine D. esters E. unsaturated aminoacids 152. What compound after the heating does form lactame? A. 3-aminobutanoic acid B. C. D. E. *4-aminobutanoic acid 3-hydroxypentanoic acid 4-amonobenzoic acid 3-aminopropanoic acid 153. Tyrosine belongs to the aromatic aminoacids. Choose the most correct systematic name foe tyrosine: A. *2- amino – 3-(p-hydroxyphenyl) propanoic acid B. α- amino-2-hydroxyphenyl propanoic acid C. α-amino-4-hydroxyphenyl propanoic acid D. 2-amino-3-hydroxyphenyl propanoic acid E. 2-amino-3-(m-hydroxyphenyl) propanoic acid 154. Which of the following acids includes asymmetric carbon atom and has optical activity? A. (СН3)2-С(ОН)-СООН (α-hydroxyisobutyric acid) B. С6Н5СН2СООН (phenylacetic acid) C. СН3-С(О)-СООН (pyruvic acid) D. *СН3-СН(NН2)-СООН (α-aminopropionic acid) E. СН2=СН-СООН (acrylic acid) 155. Choose acid, which forms γ-lactone after the heating? A. malic B. glycolic C. lactic D. pyruvic E. *4-hydroxybutyric 156. Alanine – aminoacid enters to the protein structure. Choose reagent, which can help to confirm presence of amino-group: A. *NaNO2 (HCl) B. H2SO4 C. NaNO3 (HCl) D. Ba(OH)2 E. NaHCO3 157. Choose reagent that is used to protect amino-group of alanine: A. CH3–CH2–Cl B. CH3OH C. *CH3COCl D. CH3–NH2 E. CH3–CHO 158. What reaction is used for deamination of α-aminopropionic acid? A. etherification B. with formaldehyde C. salts formation D. *with nitrite acid E. acylation 159. Aromatic aminoacids can be detected by the usage of the specific reaction: A. biuret reaction B. *xantoprotein sample C. at the boiling with alkalis with following adding of lead acetate D. with Felling reagent E. interaction with ninhydrin 160. Point, which of the following w-aminoacids contains imidazole cycle: A. alanine B. tryptophan C. tyrosine D. glycine E. *histidine 161. What reagent can be used to confirm presence of the primary amino-group in the serotonin molecule? A. AgNO3 and NH4OH B. C. D. E. *NaNO2 (H+) Br2 NaHCO3 H2N-NH2 162. Chose reaction of phosgene obtaining: A. СО2 + Н2О > B. С + Н2 + Cl2 > C. *СО + Cl2 > D. СО2 + Cl2 > E. Cl2 + СН4 > 163. Process 2NH3 + CO2 > cases formation of: A. Ether of carbaminic acid B. Carbaminic acid C. Uretane D. Methyl urea E. *Urea 164. Which of the following reactions will case formation of methane sulfoacid? A. СН4 + SO2 > B. *СН4 + SO3 > (at the presence of H2SO4 conc.) C. С + Н2 + SO2 > D. СO2 + Н2O + SO2 > E. СН4 + SO2 > (at the higher pressure) 165. What reaction will case formation of benzene sulfoacid? A. *C6H6 + H2SO4 > (oleum) B. C6H6 + SO3 > C. C6H6 + SO2 > D. C6H6 + S + O2 > E. C6H6 + SO2 + H2O > 166. 1,3,5-benzene trisulfonic acid forms as a result of double sulfonation of benzene sulfoacid. Choose the mechanism of this reaction. A. AN B. SN1 C. SN2 D. *SE E. AE 167. As a result of melting of sulfoacids with alkalis the following compounds form: A. Sulfites B. Sulfates C. Hydrosulfates D. *Sulfonates E. Carbonates 168. What compound can be obtained by the following reaction? СО + Cl2 > A. Urethane B. Chlorocarbonic acid C. *Phosgene D. Carbamide E. Carbaminic acid 169. Benzolsulfoacid reduces to: A. Sulfur and toluene B. Sulfur oxide (VІ) C. Benzene and sulfur D. Sulfur oxide (ІV) E. *Thiophenol 170. For arenesulfoacids the following reactions are characteristic: A. AE,AN B. *SE,SN C. SE,AN D. [O] E. [H],AE 171. One of the products of arenesulfoacid hydrolysis is: A. SO2 B. S C. H2S D. *H2SO4 E. H2SO3 172. Carbonate acid Н2СО3 is unstable. What products will form after its decomposition? A. 2СО2 +Н2 B. НСОН + Н2О C. *СО2 + Н2О D. СО + Н2О E. НСООН + Н2О 173. Carbamide hydrolyses with formation of: A. CO2 + 2N2 B. *CO2 + 2NH3 C. CO2 + H2O + N2 D. CO2 + NO + H2 E. CO + NO2 + H2 174. Few soluble in water urea nitrate forms at the action on carbamide: A. *Nitrate acid B. Nitrogen oxide (V) C. Nitrogen oxide (ІІІ) D. Nitrite acid E. Potassium nitrate 175. N–acyl derivatives of urea are called: A. Carbamides B. Urethanes C. Anhydrades D. *Ureides E. Halogenanhydrides 176. As a result of biuret reaction that is used for the detection of urea and proteins will form: A. Red color complex B. Green color complex C. *Red-purple complex D. Yellow precipitate E. Blue precipitate 177. Barbituric acid is in the base of medical drugs – barbiturates. It belongs to: A. Aliphatic ureides B. *Cyclic ureides C. Uretanes D. Anhydrides E. Carbamides 178. During the biuret reaction the following side product forms: A. *Cyanuric acid B. Cyanide acid C. Potassium hexacyanoferrate (ІІ) D. Potassium hexacyanoferrate (ІІІ) E. Potassium cyanide 179. What reaction does case formation of sulfoacid? A. Sulfochlorination B. Oxidation of thiols C. *Oxidation of alcohols D. Alkanes sulfonation by oleum E. Accession of hydrosulfites to alkenes 180. What reagents will interact with sulfoacids to confirm its acidic properties? A. Cu B. *NaOH C. NO2 D. HCl E. NH3 181. Mixture of o- and p-toluene sulfonic acids will form as a result of sulfonation. Choose the mechanism of this reaction. A. AN B. SN1 C. SN2 D. *SE E. AE 182. Sodium benzolsulfonate will form as a result of interaction of: A. C6H5SO2OH + Na + O2 > B. C6H5SO2OH + Na2O2 > C. C6H5SO2OH + Na2O > D. C6H5SO2OH + Na > E. *C6H5SO2OH + NaOH > 183. Chloroanhydrides of carbonate acids will form as a result of interaction of sulfoacids with: A. CHCl3 B. HClO3 C. Cl2 D. *PCl5 E. HCl 184. Sodium benzolsulfonate is a primary compound for the obtaining: A. *Phenols, nitrites B. Amides, nitrocompounds C. Alcohols, nitrocompounds D. Phenols, halogenderivatives E. Amides, halogenderivatives 185. Choose the mechanism of benzene sulfonation (formation of benzolsulfoacid): A. AN B. SN1 C. SN2 D. *SE E. AE 186. Which reagent can be used in the following reaction? A. B. C. 187. D. E. * Which is the end-product of the reaction of hydrazine with maleic dialdehyde? A. * B. C. D. E. 188. Which is the product of pyridazine reaction with hydrochloric acid excess? A. B. C. * D. E. 189. Select the mechanism of the following reaction and the position of quinoline it will principally occur? A. B. * C. D. E. 190. What is the product of the following reaction? A. B. C. * D. E. 191. What is the product of indigo Blue reduction with glucose solution? A. B. C. D. E. indoxyl pyrrole indole *white indigo isatin 192. Choose the correct range of aromaticity decrease for furan, benzene, pyrrole, and thiophene. A. B. C. D. 193. E. * What is the product of the following reaction? A. * B. C. D. E. 194. Which of the following compounds are used for pyrrole acetylation? A. B. C. D. E. * 195. The derivatives of which heterocycle are formed as the result of the following reaction (Paale-Knorr synthesis)? A. B. C. D. E. 2-aminothiazole indole thiazole *thiophene furane 196. What heterocyclic compound is formed when diammoniac salt tetrahydroxyadipic acid is heated? A. B. C. D. E. thiazole aziridne *pyrrole pyrazole azetidine 197. Which of the following heterocycle is the structural fragment of the substance presented below (make the accordance of the substance name with the name of proper heterocyclic moiety)? Haloperidol - neuroleptic: A. B. C. D. E. acridine isoquinoline quinoline *piperidine pyridine 198. Which of the following heterocycle is the structural fragment of the substance presented below (make the accordance of the substance name with the name of proper heterocyclic moiety)? Ftivazide (phthivazide) - antimycobacterial drug: A. B. C. D. E. acridine isoquinoline quinoline piperidine *pyridine 199. Which of the following heterocycle is the structural fragment of the substance presented below (make the accordance of the substance name with the name of proper heterocyclic moiety)? Cordiamin - CNS stimulant: A. B. C. D. E. acridine benzo[n]pyridine piperidine *pyridine benzo[n]pyrone-2 200. Which of the following heterocycle is the structural fragment of the substance presented below (make the accordance of the substance name with the name of proper heterocyclic moiety)? Neocoumarin - anticoagulant: A. B. C. D. E. acridine benzo[с]pyridine piperidine pyridine *benzo[в]pyrone-2 201. Which of the following heterocycle is the structural fragment of the substance presented below (make the accordance of the substance name with the name of proper heterocyclic moiety)? Lobelin - alkaloid, analeptic: A. B. C. D. E. 202. A. B. acridine isoquinoline quinoline *piperidine α-pyrone What is the product of the following reaction? C. * D. E. 203. Choose the correct range of acidity decrease for the following compounds. A. B. C. D. E. 4, 3, 2, 1 1, 3, 2, 4 3, 1, 2, 4 *4, 2, 3, 1 1, 2, 3, 4 Which type of tautomerism is possible for indoxyl? A. B. C. D. E. amino-imine nito-aci-nitro azole *keto-enol lactam-lactim What is the product of pyrrole nitration? 204. 205. A. B. C. * D. E. 206. Choose the product of the following reaction. A. B. C. * D. E. 207. Select the mechanism of the following reaction and the position of coumarin it will principally occur? A. B. C. D. * E. 208. Select the mechanism of the following reaction and the position of acridine it will principally occur? A. B. C. * D. E. 209. Which is the product of the following reaction? A. B. C. D. 210. E. * Which is the product of the following reaction? A. B. * C. D. E. 211. Which is the product (4) of N-phenylanthranilic acid cyclization? A. B. * C. D. E. 212. Which is the product (2) of the following cyclization? A. B. C. * D. E. 213. Which is the identity of the end-product (№3) in the following scheme? A. B. * C. D. E. 214. Which reaction is Yuriev’s cycle reaction? A. B. C. D. * E. 215. Which of the following conpounds can be starting compounds for pyrrole synthesis? A. B. C. D. E. 216. acetoacetic ester acetylene diazomethane glyoxal, ammonia, formaldehyde *diammoniac salt tetrahydroxyadipic acid Which of the following reagents can be used for nitration of acidophobic heterocycles? A. * B. C. D. E. 217. The derivatives of which heterocycle are formed as the result of the following reaction (Paale-Knorr synthesis)? A. indole B. imidazole C. pyrazole D. *pyrrole E. furane 218. The derivatives of which heterocycle are formed as the result of the following reaction (Paale-Knorr synthesis)? A. B. C. D. E. pyrrole isooxazole oxazole thiophene *furane At what position of indole will electrophilic substitution reactions principally A. B. C. D. E. position 5 position 4 *position 3 position 2 position 1 Which is the product of the following reaction? 219. occur? 220. A. * B. C. D. E. 221. Choose the product of the following reaction. A. B. * C. D. E. 222. Choose the product of the following condensation. A. B. * C. D. E. 223. Which of the following compound can be classified as azoles? antipyrine pyrrole azetidine *thiazole aziridine 224. Select the mechanism of the following reaction and the position of quinoline it will principally occur? A. B. C. D. E. A. * B. C. D. E. 225. Which is the identity of the intermediates (A and B) in the following scheme? A. B. C. * D. E. 226. Which of the following reactions does lead to the barbituric acid formation? A. B. C. * D. E. 227. At what position of pyrimidine will electrophilic substitution reactions (SE) principally occur? A. B. C. D. E. *the fifth the fourth the third the second the first 228. Which of the following heterocycle is the structural fragment of the substance presented below (make the accordance of the substance name with the name of proper heterocyclic moiety)? Rivanol - antiseptic : A. B. C. D. E. 229. A. B. C. *acridine isoquinoline quinoline piperidine α-pyrone Which reaction characterize the basic properties of purine? D. 230. E. * Choose the product of pyrazine oxidation? A. B. * C. D. E. 231. What is the product of pyrazine reduction with sodium in ethanol? A. B. * C. D. E. 232. What is the identity of the intermediate (A) and the end-product (B) in the reaction of ethylenediamine with glyoxal? A. B. * C. D. E. 233. What is the end-product of diethylmalonate condensation with urea? A. B. * C. D. E. 234. Select the mechanism of the following reaction and the position of isoquinolin it will principally occur? A. B. C. D. * E. 235. At what positions of quinoline will the following reaction principally occur? A. B. C. * D. E. 236. What is the product of indigo Blue oxidation with conc. HNO3? A. B. C. D. E. indoxyl pyrrole indole *isatin white indigo 237. The condensation of which compounds leads to formation of polyvinylpirrolidone? A. B. C. D. E. 238. cycle? furane with ethene pyrrole with ethylene pyrrole with acetylene pyrrolidone with ethylene *pyrrolidone with acetylene Which of the following compound can be used as catalyst in the reactions of Yuriev’s A. B. C. D. E. * 239. Which of the following compounds will form oxiran when treated with concentrated solution of alkali? A. B. C. D. 240. E. * Which group of alkaloids does theophylline belongs to? A. B. C. D. E. 241. isoquinoline and phenanthroisoquinoline alkaloids *purine alkaloids tropane alkaloids pyridine and piperidine alkaloids quinoline alkaloids Choose the correct name for theophylline. A. B. C. D. E. 242. A. B. C. D. E. 243. alkaloids? 5,7- dimethylxanthine 3,5- dimethylxanthine 2,4- dimethylxanthine 4,6- dimethylxanthine *1,3-dimethylxanthine Choose the most complete definition of alkaloids. Alkaloids – naturally occurring (plants) oxygencontaining organic compounds. Alkaloids – naturally occurring (plants and animals) compounds, which display basic properties. Alkaloids – heterocyclic compounds with one or more hydroxyl-groups. Alkaloids – nitrogencontaining organic compounds with glycosidic bonds *Alkaloids – naturally occurring (plants) nitrogencontaining organic compounds, which display basic properties and high level of biological activity. Which of the following reagent can be used to confirm the basic properties of A. B. C. * D. E. 244. Which of the following reactions result purine? A. B. C. D. E. * 245. Which is the identity of the intermediate (A) and the end-product (B) in the following scheme? A. B. C. D. * E. 246. Choose the product of purine reaction with hydrochloric acid? A. B. C. * D. E. 247. For which purine derivative lactam-lactim tautomerism is possible? A. B. C. * D. E. 248. Which salt is formed when uric acid react with alkali? A. B. C. D. * E. 249. What reaction can be used to identify uric acid? A. B. C. D. E. 250. A. xanthoprotein test *murexide test indophenine test xanthogenic test isonitrile test Choose the product of the following reaction. B. C. * D. E. 251. Which of the following reaction result piperidine? A. B. C. D. * E. 252. Which end-product is formed when β -picoline (1) first treated with PCl5, and then with NH3? A. B. C. D. E. picolinic acid amide *nicotinamide (vitamin PP) isonicotinamide ammonium salt of nicotinic acid ammonium salt of isonicotinic acid 253. Select the mechanism of the following reaction and the position of quinoline it will principally occur? A. B. C. D. * E. 254. Which is the end-product of acridine oxidation? A. B. * C. D. E. 255. Which is the end-product of isoquinoline oxidation? A. * B. C. D. E. 256. What is the end-product of the following reaction? A. B. C. D. * E. 257. Choose the proper pair of products of the following reaction. A. B. C. D. * E. 258. Choose the product of the following reaction. A. B. C. D. * E. 259. Which is the end-product of acrolein condensation? A. B. * C. D. E. 260. Which of the following compounds can be used for furan sulfonation? A. B. * C. D. E. 261. Which is the product of pyrazole reduction with hydrogen according to the following scheme? A. B. C. D. * E. 262. Which is the identity of the end-product (4) in the following scheme? A. B. C. D. E. 263. A. B. C. D. 4-nitrofurfural semicarbazone 3-nitrofurfural 5-nitrofurfural diacetate 5-nitrofurfural *5-nitrofurfural semicarbazone Which of the following compounds is indole? E. * 264. Which reagent can be used to proof the presence of keto-group in isatin molecule? A. B. C. acid fuchsine sulfite D. 265. E. * What is the product of the following reaction? A. B. C. D. E. N- methylpyrrole N- acetylpyrrolium chloride b-acetylpyrrole a-acetylpyrrole *N-acetylpyrrole 266. Which is the identity of the intermediate (X) and the end-product (Y) in the following scheme? A. B. C. * D. E. 267. Choose the correct range of SE reactivity decrease for thiophene, furan, benzene, and pyrrole. A. B. C. * D. E. 268. Which of the following heterocycle is acidophobic? A. B. C. D. * E. 269. What is the identity of the end-product 2 in the following scheme? A. B. C. * D. E. 270. Which of the following heterocycle is acidophobic? A. B. * C. D. E. 271. Which reaction is Yuriev’s cycle reaction? A. B. C. D. * E. 272. Which of the following heterocycle is aromatic? A. B. * C. D. E. 273. Which type of isomerism is possible for pyrazole and imidazole? A. B. C. D. E. nitro-aci-nitro *azole keto-enol amino-imino lactam-lactim 274. Which is the identity of the intermediate (A) and the end-product (B) in the following scheme? A. B. C. * D. E. 275. Choose the correct systematic name of purine. A. B. C. D. E. 276. A. B. C. *imidazo[4,5-d] pyrimidine pyrazolo[4,5-d] pyrimidine pyridino[4,5-d]pyrimidine pyrimidino[4,5-d]imidazole pyridazo[4,5-d]pyrimidine What starting compound is required for barbituric acid synthesis? D. * E. 277. Which of the following reactions lead to pyrimidine formation? A. B. C. * D. E. 278. Which of the following reaction is impossible? A. B. C. D. * E. 279. Which of the following reactions lead to pyrazine? A. B. C. * D. E. 280. Which of the following reaction lead to coumarin formation? A. B. C. D. * E. 281. Which of the following pyrimindine derivative shall undergo the electrophilic substitution reactions? A. B. C. D. * E. 282. Choose the correct way for purine atoms numbering. A. B. C. D. * E. 283. At what positions of pyridine N-oxide will electrophilic substitution reactions (SE) principally occur? A. B. C. D. E. 284. occur? 1, 4 3, 5 *2, 4, 6 1, 4, 6 1, 3, 5 At what position of pyridine shall electrophilic substitution reactions (SE) principally A. B. C. D. E. 6 4 *3 2 1 285. At what positions of pyridine will nucleophilic substitution reactions (SN) principally occur? A. B. C. D. E. 286. A. B. 3, 5 2, 5 1, 3, 5 *2, 4, 6 2, 4, 5 Choose the product of the following reaction. C. * D. E. 287. occur? At what position of pyrazole will reaction with nitric acid (heat) principally A. B. C. D. E. 288. position 5 *position 4 position 3 position 2 position 1 Choose the structure of analgin. A. B. * C. D. E. 289. Which is the identity of the end-product (3) in the following scheme? A. B. * C. D. E. 290. Which reagent shall react with cyclic nitrogen atom of 2-aminothiazole? A. B. C. D. 291. E. * Which is the identity of the end-product (№3) in the following scheme? A. B. C. D. * E. 292. Which is the starting reagent in the synthesis of 5-methyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-5? A. B. C. D. E. 293. ethyl acetate diethyl malonate acetic acid *acetoacetic ester ethyl propionate At what position of pyrazole will reaction with CH3I principally occur? A. B. C. D. E. 294. position 5 position 4 position 3 *position 2 position 1 What is the product of imidazole sulfonation? A. B. C. * D. E. 295. Which of the following compound can be used for furane chlorination? A. B. C. D. 296. E. * Which of the following heterocycle is acidophobic? A. B. C. * D. E. 297. What is the end-product of reaction of potassium-pyrrolide with iodomethane? A. B. C. D. E. α,α’-dimethylpyrrole α,β-dimethylpyrrole β- methylpyrrole *α-methylpyrrole N-methylpyrrole Which statement about furfural is not true? A. B. C. D. E. *it forms a-furamide with NH3 it forms hydrofuramide with NH3 it undergoes Cannizzaro reaction can be obtained from aldopentose it undergoes SE reactions at position 5 Which of the following heterocycle is acidophobic? 298. 299. A. B. C. D. * E. 300. Which of the following reactions lead to formation of thiophene? A. B. C. D. * E. 301. Three- and four-membered heterocycles, such as oxetane, aziridine, and azitidine are: A. heterocycles with three heteroatoms B. heterocycles with two heteroatoms 302. C. aromatic heterocycles D. unsaturated heterocycles E. *saturated heterocycles Which of the following compounds can be cyclized to aziridine? A. * B. C. D. E. 303. Which reaction characterize aziridine as secondary cyclic amine? A. B. C. D. 304. E. * Which reaction does oxiran undergo? A. B. C. D. E. 305. electrophilic addition electrophilic substitution nucleophilic substitution free-radical substitution *nucleophilic addition Choose the products of the following reaction. A. B. C. * D. E. 306. Which of the following reaction of oxiran are possible? A. B. C. * D. E. 307. Choose the mechanism of the following reaction: A. B. C. D. * E. 308. Heterocyclic compound pyrrole belongs to: *fivemember heterocycles with one heteroatom fivemember heterocycles with two heteroatoms sixmember heterocycles with one heteroatom fivemember heterocycles with two heteroatoms condensed heterocycles 309. Heterocyclic compound pyrrole is a part of: A. anesthetic means B. nucleic acids C. preparations for the tuberculosis treatment D. bactericide means E. *hem of hemoglobin 310. According to the level of saturation heterocyclic compounds are divided on: A. condensed and non-condensed B. *saturated, unsaturated, aromatic C. azoth containing, oxygen containing, sulfur containing D. fivemember, sixmember, sevenmember E. cycles with one and two heteroatoms 311. According to the nature of heteroatom heterocyclic compounds are divided on: A. saturated, unsaturated, aromatic B. *nitrogen containing, oxygen containing, sulfur containing C. fivemember, sixmember, sevenmember D. cycles with one and two heteroatoms E. condensed and non-condensed heterocycles 312. 3- and 4-member heterocycles oxethane, azeridine, azetidine are: A. *saturated heterocycles B. unsaturated heterocycles C. aromatic heterocycles D. heterocycles with tree heteroatoms E. heterocycles with trwo heteroatoms 313. How does pyrrole basic properties change in the comparison with the products of its partial and complete reduction? A. does not change B. *increases from pyrrole to pyrolidine C. increases in the row of pyrolidine, pyroline, pyrrole D. decreases in the row of pyroline, pyrolidine, pyrrole E. increases in the row of pyrolidine, pyrrole, pyrroline 314. Nitrogen atom in the pyrrole molecule can react with: A. *potassium amide B. potassium chloride C. potassium sulfate D. sulfate acid E. chloride acid 315. For three- and fourmember heterocycles the following types of reactions are characteristic: A. radical substitution B. electrophilic and nucleophilic substitution C. *electrophilic and nucleophilic accession D. radical accession E. polymerization 316. According to the size of cycle (total number of atoms in the cycle) heterocyclic A. B. C. D. E. compounds can be classified on: A. saturated, unsaturated, aromatic B. azoth containing, oxygen containing, sulfur containing C. *fivemember, sixmember, sevenmember D. cycles with one or two heteroatoms E. condensed and non-condensed heterocycles 317. To fourmember heterocyclic compounds with one atom of oxygen belongs the following one: A. *oxethane B. pyrazole C. oxyrane D. pyrimidine E. pyridine 318. To threemember heterocyclic compounds with one atom of oxygen belongs the following one: A. pyrimidine B. oxethane C. *oxyrane D. pyrrole E. pyridine 319. To fourmember heterocyclic compounds with one atom of sulfur belongs the following one: A. thiophene B. pyrazole C. pyrrole D. pyridine E. *thiethane 320. To threemember heterocyclic compounds with one atom of sulfur belongs the following one: A. thiophene B. thiethane C. pyrrole D. *thiirane E. pyridine 321. What compound with concentrated alkali solution will form oxyrane? A. *HOCH2—CH2—Cl B. HOCH2—CH2—CH2—Cl C. H2C=CH2 D. HOCH2—CH2—OH E. H3C—CH3 322. Among of the following compounds choose nitration reagent for the acidophobic compounds: A. HNO3 conc B. CH3COOH C. H3BO3 D. NaNO2 + HCl E. *(CH3CO)2O + HNO3 323. To fivemember heterocyclic compounds with one atom of sulfur belongs the following one: A. pyrimidine B. pyrazole C. pyrrole D. *thiophene E. pyridine 324. To fivemember heterocyclic compounds with one atom of nitrogen belongs the following one: A. pyridine B. C. D. E. pyrazole *indole furane pyrimidine 325. Furacilline – medical drug that is used for the treatment of pyoinflammatory processes cased by microorganisms. What heterocycle is a primer compound for furacilline synthesis? A. pyrrole B. *furan C. thiophene D. imidazole E. pyridine 326. Furfural (2-furylcarbaldehyde) – primer compounf for the synthesis of furacilline, furazolidone and furadonine. Choose reagent that can be used to obtain semicarbazone. A. H2N–C6H5 B. H2N–OH C. *H2N–NH–C(O)–NH2 D. H2N–NH–C(S)–NH2 E. H2N–NH2 327. 5 – nitrofurfural is a primer compound for the synthesis of furacilline, furazolidone and furadonine. Choose the type of reaction of furfural nitration by conc. nitrate acid in the medium of acetic anhydride? A. AN B. SR C. E D. SN E. *SE 328. 5 – nitrofurfural is a primer compound for the synthesis of furacilline, furazolidone and furadonine. Choose the mechanism of furfural nitration by conc. nitrate acid in the medium of acetic anhydride? A. *radical B. ionic C. nucleophilic D. substitutin by m-position E. substitutin by o- and p-position 329. Choose compound, which with 5-nitrofurfural forms furacilline. A. *semicarbazide B. phenylhydrazide C. hydrazine D. hydraxylamine E. sodium hydrosulfite 330. Nitrogen atom in the pyrrole molecule can react with: A. *potassium amide B. potassium chloride C. potassium sulfate D. sulfate acid E. chloride acid 331. Choose the more correct name for complete thiophene hydration: A. 1,2,3,4,5-pentahydrothiophene B. 2,3-dihydrothiphene C. 1,2-dihydrothiophene D. 3,4-dihydrothiophene E. *2,3,4,5-tetrahydrothiophene 332. Which of the following substances can not be sulfonated with concentrated sulfate acid? A. thiophene B. pyridine C. toluene D. *pyrrole E. naphthalene 333. Which of the following substances has acidophobic properties? A. pyridine B. pyrazole C. *pyrrole D. pyrimidine E. imidazole 334. Name product of the pyrrole sulfonation: A. 3-pyrrole sulfoacid B. *2-pyrrole sulfoacid C. 4-pyrrole sulfoacid D. 5-pyrrole sulfoacid E. 1-pyrrole sulfoacid 335. Choose the reagent for furan nitration: A. HNO3; H2SO4 B. HNO3 (dil.) C. HNO3 (conc.) D. *CH3COONO2 E. HNO2 336. Pyrrole and furan are sulfonated by: A. concentrated sulfate acid B. *pyridinesulfotrioxide C. diluted sulfate acid D. mixture of sulfate and nitrate acids E. oleum 337. To fivemember heterocyclic compounds with one atom of nitrogen belongs the following one: A. pyrimidine B. pyrazole C. *pyrrole D. furan E. pyridine 338. Which of the following reagents will react with pyrrole by heteroatom? A. *NaNH2 B. СН3СОOH C. (CH3CO)2O D. SnCl4 E. SO2Cl2 339. Weak acidic properties the following heterocyclic compound has: A. pyridine B. thiophene C. quinoline D. furane E. *pyrrole 340. To fivemember heterocyclic compounds with one atom of oxygen belongs the following one: A. pyrimidine B. pyrazole C. pyrrole D. *furane E. pyridine 341. To fivemember heterocyclic compounds with one atom of sulfur belongs the following one: A. pyrimidine B. *thiphene C. pyrrole D. pyrazole E. pyridine 342. Heterocyclic compound pyrrole belongs to: A. *fivemember heterocycles with one heteroatom B. fivemember heterocycles with two heteroatoms C. sixmember heterocycles with one heteroatom D. fivemember heterocycles with two heteroatoms E. condensed heterocycles 343. Heterocyclic compound pyrrole is a part of: A. anesthetic means B. nucleic acids C. preparations for the tuberculosis treatment D. bactericide means E. *hem of hemoglobin 344. What substance will form as a result of interaction of acetoacetic ester with phenylhydrazine? A. Amidopyrine B. Analgin C. Antipyrine D. *3-methyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-5 E. 2,3-dimethyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-5 345. What substance will form as a result of interaction of 4-methylaminoantipyrine with formalin and sodium hydrosulfite? A. Amizon B. Antipyrine C. Aspirin D. *Analgin E. Amidopyrine 346. 1,3-diazol is isomer of: A. Indole B. Benzimidazole C. *Pyrazole D. Pyrole E. Pyridine 347. 1,2-diazole is isomer of: A. Indole B. Benzimidazole C. *Imidazole D. Pyrole E. Pyridine 348. Oxazole is isomer of: A. Azole B. Thiazole C. Furan D. *Isooxazole E. Pyrrole 349. Which of the following heterocycles does belong to azoles? A. Indole B. *Thiazole C. Thiophene D. Pyrrole E. Furan 350. Which of the following heterocycles has basic properties? A. *Pyrazole B. tetrahydrofurane C. Thiophene D. Pyrolidine E. Pyrroel What heterocycle is in the content of vitamin В1 (thiamin)? A. Thiophene B. Pyridine C. *Thiazole D. Oxazole E. Purine 352. Which of the following medical compounds does contain imidazole heterocycle? A. analgin B. *histidine C. antipyrine D. amidopyrine E. furacilline 353. If oxazole cycle is activated by electronodonor subtitution the reactions of SE takes place. Specify the position, by which this reaction will go: A. 3 and 2 B. 2 and 5 C. *4 and 5 D. 3 and 4 E. 2 and 1 354. What reaction does case pyrazole formation? A. Intramolecular dehydration of ethanol B. Melting with alkali solution of benzolsulfoacid C. Cyclotrimerization of acetylene D. Pentose dehydratation E. *Accession of diazoalkanes to acetylenes 355. What reaction does case pyrazole formation? A. Intramolecular dehydration of ethanol B. Melting with alkali solution of benzolsulfoacid C. Cyclotrimerization of acetylene D. Pentose dehydratation E. *Interaction of hydrazine with pentadione-2,4 356. Pyrazole according to its physical properties is: A. Crystalline orange compound B. Liquid, good soluble in water C. Gaseous substance D. *Colorless crystalline compound, good soluble in water E. Liquid, insoluble in water 357. Alkylation and acylation of pyrazole conduct with formation of the following products: A. *N–substitution B. m–substitution C. p–substitution D. o- and p-substitution E. Mixture of N- and m-substituution 358. Choose the product of pyrazole reduction: A. Pyridine B. Hydropyrazole C. *Pyrazoline–2 D. Pyrazolidine E. Pyrrole 359. Choose the product of pyrazole partial reduction: A. Pyridine B. *3,4-dihydropyrazole C. Hydropyrazole D. 1-,2-dihydropyrazole E. Trihydropyrazole 360. Choose the product of pyrazole complete reduction: A. Pyridine 351. B. C. D. E. Dihydropyrrole Trihydropyrazole Pyrrole *Pyrazolidine 361. Choose the product of pyrazole complete reduction: A. Pyridine B. *Tetrahydropyrazole C. 3,4-dihydropyrazole D. Trihydropyrazole E. Pyrrole 362. Choose reagent for pyrazole partial reduction: A. CH3COOH B. C2H5OH C. 2H2(Pt) D. *2H(C2H5OH+Na) E. KMnO4 363. Choose reagent for pyrazole complete reduction: A. CH3COOH B. 2H(C2H5OH+N C. *2H2(Pt) D. C2H5OH E. KMnO4 364. Choose chemical name for antipyrine: A. 4-nitrozoantipyrine B. *2,3-dimethyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-5 C. 3-methyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-5 D. 2,3-dimethyl-4-dimethylamino-1-phenylpyrazolone-5 E. sodium 2,3-dimethyl-4-dimethylamino-1-phenylpyrazolone-5-N-methanesulfonate 365. Choose chemical name for amidopyrine: A. 4-nitrozoantipyrine B. 2,3-dimethyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-5 C. 3-methyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-5 D. *2,3-dimethyl-4-dimethylamino-1-phenylpyrazolone-5 E. sodium 2,3-dimethyl-4-dimethylamino-1-phenylpyrazolone-5-N-methanesulfonate 366. Choose chemical name for analgin: A. 4-nitrozoantipyrine B. 2,3-dimethyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-5 C. 3-methyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-5 D. 2,3-dimethyl-4-dimethylamino-1-phenylpyrazolone-5 E. *sodium 2,3-dimethyl-4-dimethylamino-1-phenylpyrazolone-5-N-methanesulfonate 367. Choose chemical name for sodium methamizole: A. 4-nitrozoantipyrine B. 2,3-dimethyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-5 C. 3-methyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-5 D. 2,3-dimethyl-4-dimethylamino-1-phenylpyrazolone-5 E. *sodium 2,3-dimethyl-4-dimethylamino-1-phenylpyrazolone-5-N-methanesulfonate 368. Choose correct name of the preparation with the chemical name 2,3-dimethyl-1phenylpyrazolone-5: A. *Antipyrine B. Aspartic acid C. Aspirin D. Amidopyrine E. Analgin 369. Choose correct name of the preparation with the chemical name 2,3-dimethyl-4dimethylamino-1-phenylpyrazolone-5: A. Antipyrine B. Aspartic acid C. Aspirin D. *Amidopyrine E. Analgin 370. Choose correct name of the preparation with the chemical name sodium 2,3-dimethyl-4dimethylamino-1-phenylpyrazolone-5-N-methanesulfonate: A. Antipyrine B. Aspartic acid C. *Analgin D. Amidopyrine E. Aspirin 371. Choose correct name of the preparation with the chemical name sodium 2,3-dimethyl-4dimethylamino-1-phenylpyrazolone-5-N-methanesulfonate: A. *Sodium methamizole B. Aspartic acid C. Aspirin D. Amidopyrine E. Antipyrine 372. Analgin is used in the medical practice as: A. Form of vitamin PP B. Antibacterial mean C. *Analgesic mean D. Vasodilator E. Drug against tuberculosis 373. For imidazole obtaining use interaction of the following compounds: A. Acetoacetic ester and phenylhydrazine B. *Glyoxal, ammonia, formaldehyde C. Ethanol and alkali D. Ethanoic acid and ethyl alcohol E. Acetylene and ammonium 374. Imidazole is: A. Crystalline yellow compound B. Liquid, insoluble in water C. *Colorless crystalline compound, good soluble in water D. Gaseous compound E. Liquid with sharp smell 375. To the imidazole derivatives the following compound belongs: A. *Histidine B. Vitamin PP C. Furfural D. Norsulfazole E. Cordiamine 376. To the imidazole derivatives the following compound belongs: A. Vitamine PP B. Norsulfazole C. Furfural D. *Histamine E. Cordiamine 377. To the imidazole derivatives the following compound belongs: A. Vitamine PP B. *Pilocarpine C. Furfural D. Norsulfazole E. Cordiamine 378. Benzimidazole can be obtained by the interaction of: A. *О-phenylenediamine with formic acid; B. Acetylene with ammonia C. Ethanoic acid and ethanol D. Glyoxal, ammonia, formaldehyde E. Acetoacetic ester and phenylhydrazine 379. Benzimidazole has: A. Oxidative properties B. Reductive properties C. Acidic properties D. *Amphoteric properties E. Basic properties 380. Benzimidazole cycle is a part of vitamin: A. *В12; B. С; C. А; D. Н; E. РР. 381. Benzimidazole cycle is a part of the following drug: A. Analgin B. *Dibazole C. Norsulfazole D. Phthalazol E. Furacilline 382. Thiazole is a part of the following natural compound: A. *Vitamin В1 B. Vitamin С C. Vitamin А D. Vitamin РР E. Vitamin Н 383. Thiazole is a part of the following natural compound: A. Vitamin РР B. Vitamin Н C. *Penicillin D. D–carotene E. itamin С 384. Thiazole is a part of the following medical drug: A. Isoniazide B. Phenobarbital C. Cordiamine D. *Norsulfazole E. Furacilline 385. Thiazole is a part of the following medical drug: A. Isoniazide B. Phenobarbital C. Cordiamine D. *Phthalazol E. Furacilline 386. A thizole nucleus is a part of natural penicillins. The drug has: A. Analgesic properties B. *Antimicrobial properties C. Vasodilatation activity D. Bronchodilatation activity E. Antituberculosis properties 387. By the presence of free pare of electrons of pyridine type nitrogen atom oxazole has the following properties: A. *Weak basic properties B. Strong basic properties C. Weak acidic properties D. Strong acidic properties E. Amphoteric properties 388. Isooxazole has the following properties: A. Amphoteric B. Strong acidic C. Weak acidic D. Strong basic E. *Weak basic 389. Qualitative reaction on antipyrine is reaction with: A. H2 B. HCl C. NH3 D. CH3OH E. *FeCl3 390. Qualitative reaction on antipyrine is intereaction with: A. H2 B. *NaNO2(H+) C. NH3 D. CH3OH E. HCl 391. Qualitative reaction on antipyrine is reaction with FeCl3. As a result complex salt (ferropyrine) will form. What is the color of this complex? A. Red B. Yellow C. Brown D. *Orange E. Blue 392. Qualitative reaction on antipyrine is reaction with FeCl3. As a result orange color complex salt will form. This is: A. *Ferropyrine B. Furazolidone C. Furadonine D. Furfural E. Furacilline 393. Qualitative reaction on antipyrine is reaction with NaNO2(H+). As a result 4– nitrozoantipyrine will form. This compound has the following color: A. Colorless B. Orange C. Blue D. Yellow E. *Emerald-green color 394. Qualitative reaction on antipyrine is reaction with NaNO2(H+). As a result emeraldgreen compound will form. This is: A. 3–aminoantipyrine B. Amidoantipyrine C. 4–aminoantipyrine D. 2–nitrozoantipyrine E. *4–nitrozoantipyrine 395. Qualitative reaction on amidopyrine is intereaction with: A. H2 B. *FeCl3 (Н+) C. CH3OH D. H2SO4 E. HCl 396. Qualitative reaction on anmidopyrine is intereaction with: A. H2 B. *К3[Fe(СN)6] and Fe3+ C. CH3OH D. H2SO4 E. HCl 397. Choose the reaction that can be used to distinguish analgin from amidopyrine: A. H2 B. H2SO4 C. NaNO2 D. *FeCl3 (Н+) E. HCl,t 398. Choose the reaction that can be used to distinguish analgin from amidopyrine: A. H2 B. H2SO4 C. NaNO2 D. *К3[Fe(СN)6] Fe3+ E. HCl,t 399. As a result of interaction of amidopyrine with К3[Fe(СN)6], in the presence of FeCl3 blue color complex will form with the following content: A. Fe[Fe(СN)6] B. *Fe4[Fe(СN)6]3 C. К4[Fe(СN)6] D. КFe[Fe(СN)6] E. К2Fe[Fe(СN)6] 400. To the preparation, which is a derivative of pyrazolone-5, solution of FeCl3 is added. Observe the appearance of the intense orange coloration. Choose this preparation: A. Penicilline B. Anesthesin C. Amidopyrine D. *Antipyrine E. Analgine 401. As a result of antipyrine nitrozation with the following reduction the next compound will form: A. *4-nitrozoantipyrine B. 2-aminoantipyrine C. Amidopyrine D. 3-aminoantipyrine E. 4-aminoantipyrine 402. As a result of 4-aminoantupyrine methylation the following compound will form: A. *Amidopyrine B. 3-methyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-5 C. 2,3-dimethyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-5 D. 4-nitrozoantipyrine E. Analgin 403. Why quinoline and isoquinoline give reactions of eletrophilic substitution previously by the positions 5 and 8? A. nitrogen atom has bigger electronegativity than carbon atom B. *positions 5 and 8 have bigger electronic density C. nitrogen atom has sp2 –hybridization of the electronic D. benzene cycle has three double bounds E. nucleophilic substitution reactions are not possible 404. For pyridine reactions of electrophilic (SE) nucleophilic (SN) substitution are characteristic. Lower reaction ability of pyridine in the reactions of SE is caused by: A. size of the cycle B. aromatic character of the pyridine cycle C. basic properties D. carbon atom hybridization атомів вуглецю E. *electron acceptor properties of nitrogen atom 405. How many π-electrons do form aromatic system of pyridine? A. 14 B. 10 C. *6 D. 8 E. 12 406. Choose the mechanism of pyridine hydroxylation in position 2: A. *SN B. SE C. AE D. SR E. AN 407. Point the mechanism of the 2-aminopyridine formation by Chichibabin: A. AR B. SE C. AE D. SN E. *SR 408. Choose the way of piperidine from pyridine obtaining in one stage: A. pyridine amination B. pyridine nitration C. pyridine methylation D. *pyridine hydration E. pyridine interaction with hydrochloric acid 409. For pyridine the following reactions are characteristic: A. electrophilic accession andта electrophilic substitution B. *electrophilic and nucleophilic substitution C. nucleophilic accession and nucleophilic substitution D. nucleophilic substitution and elimination E. radical substitution and electrophilic accession 410. Pyridine – aromatic heterocycle, which is a part of many medical drugs. Determine how many monomethyl substituted pyridines exist. A. 1 B. 2 C. *3 D. 4 E. 5 411. According to the Hukel rule quantity of π-electrons in the aromatic system can be determined by the following formula 4n+2. What number of π-electrones does acridine molecule contain? A. 10 B. *14 C. 8 D. 6 E. 12 412. Nitrogen atom in the pyridine molecule can react with: A. *hydrochloric acid B. potassium hydroxyde C. calcium oxide D. potassium carbonate E. potassium amide 413. Nicotinic acid amide (vitamin РР) is the derivative of: A. pyrazole B. thiphene C. pyrrole D. furan E. *pyridine 414. Acridine gives reactions of electrophilic substitution previously by the position: A. 2 and 3 B. *2 C. 5 D. 5 and 8 E. 2 and 7 415. Reactions of electrophilic and nucleophilic substitution in the quinoline nuclei go in the following positions: A. SE in position 5, SN – in position 4 B. SE in position 2, SN – in position 4 C. SE in position 3, SN – in positions 2 and 4 D. *SE in positions 5 and 8, SN – in position 2 E. SE in position 6, SN – in positions 3 and 4 416. After the nicotine oxidation in the hard conditions the following compound will form: A. pyridine-3,4-dicarboxylic acid B. pyridine-2-carboxylic acid C. pyridine-4-carboxylic acid D. pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid E. *pyridine-3-carboxylic acid 417. Derivatives of cyclic and heterocyclic compounds are the structural fragment of the many medical drugs. Which of the following compounds does not have carbon atom in sp2 – hybridized state? A. *piperidine B. pyridine C. pyrrole D. pyroline E. pyridazine 418. Which of the following acids is pro-vitamin РР? A. pycolinic B. isonicotinic C. *nicotinic D. salicylic E. anthranilic 419. Which of the following compounds after the oxidation will form nicotinic acid? A. pyrazine B. *β-pycoline C. γ-pycoline D. propylene glycol E. α-pyrone 420. Which of the following cycles is a structural fragment of alkaloid lobeline, anabazine, is a part of analgesic mean promedol? A. *piperidine B. piperazine C. pyrimidine D. pyridazine E. pyridine 421. Pyrimidine is an aromatic heterocyclic compound; its derivatives are in the content of nucleic acids, vitamins, antibiotics, medical drugs. Enter the number of electrons involved in the formation of the closed conjugated system and corresponded to the Huckel’s rule. A. *6 B. 14 C. 10 D. 26 E. 18 422. Pyrimidine is an aromatic heterocyclic compound. Determine the number of electrons that take part in the formation of aromatic system of the pyrimidine molecule: A. 2 B. 4 C. *6 D. 8 E. 10 423. Barbituric acid is one of the most important pyrimidine derivatives. What type of tautomery is characteristic for barbituric acid? A. Azol and nitro-acy-nitro tautomery B. Keto-enol and nitro-acy-nitro tautomery C. Lactam-lactim and nitro-acy-nitro tautomery D. *Keto-enol and lactam-lactim E. Cyclic-chain and nitro-acy-nitro tautomery 424. Pyrazole – aromatic heterocycle. Determine the product of pyrazole interaction with conc. НNO3 at the heating: A. 3-Nitropyrazole B. *4-Nitropyrazole C. Pyrazolyl nitrate D. 5-Nitropyrazole E. 3,5-Dinitropyrazole 425. Barbituric acid is in the base of some medical preparations. What heterocycle is in the base of barbituric acid? A. *Pyrimidine B. Pyrazine C. Pyridazine D. Pyridine E. Insole 426. Point the type of tautomery of pyramiding foundations – thymine, uracil, and cytosine: A. azol B. nitro-acy-nitro C. keto-enol D. thion-thiol E. *Lactam-lactim 427. Derivatives of which heterocycle has azol tautomery? A. pyridazine B. pyrazine C. *pyrazole D. thiazole E. oxazole 428. What reaction can be used to obtain pyridazine? A. Condensation of malondialdehyde with hydrazine B. *Condensation of maleinedialdehyde with hydrazine C. Condensation of acetaldehyde with ammonia D. Condensation of ethylenediamine with glyoxal E. Diethylmalonate interaction with urea 429. Choose heterocycle that is in the base of barbituric acid, which derivatives are used in the medicine as medical drugs and have hypnotic and anticonvulsion action. A. pyridine B. pyridazine C. pyrazine D. piperidine E. *pyrimidine 430. Sixmember azotcontaining heterocyclic compounds have basic properties. Specify the compound, which has the biggest basic properties. A. Pyrazine B. Pyridine C. Pyrimidine D. *Piperazine E. Pyridazine 431. To the sixmember heterocycles with two nitrogen heteroatoms the following compound belongs: A. Pyrrolidine B. C. D. E. 432. A. B. C. D. E. 433. A. B. C. D. E. 434. A. B. C. D. E. 435. A. B. C. D. E. 436. A. B. C. D. E. 437. A. B. C. D. E. 438. A. B. C. D. E. 439. A. B. C. D. E. Purine *Pyrimidine Pyrrole Pyridine Choose the compound, which derivatives are used in the medicine as hypnotic means: Pyridine Nicotinic acid Xanthine Uric acid *Barbituric acid Derivatives of barbituric acid are used in the medical practice as: Antipyretic means Antiseptic means Antibiotics *Hypnotic means Preparations with anti-mycosis action For diazines is cheracteristic: The high reactivity in the reactions of Е Low reactivity in the reactions of SN The high reactivity in the reactions of SR The high reactivity in the reactions of SЕ and SN *The high reactivity in the reactions of SN and low reactivity in the reactions of SЕ What compound can be obtained by the interaction of maleinealdehyde with hydrazine? Pyrrole *Pyridazine Pyrimidine Pyrazine Pyridine Pyridazine is: *A weak base An inert compound A strong base A weak acid a strong oxidant What compound will form after the pyridazine interaction with HCl? 5-chloropyridazine 3-chloropyridazine *pyridazinium chloride pyrimidinium chloride pyrazinium chloride What compound will form after the pyridazine interaction with CH3I? 6-methylpyridazine iodide *N-methylpyridazine iodide 3-methylpyridazine iodide 4-methylpyridazine iodide 5-methylpyridazine iodide Under the action of peroxyacid (CH3COOOH) pyridazine oxidizes with formation of: *pyridazine N-oxide pyrimidine N-oxide pyrazine N-oxide pyridazinone-4 pyridazinone-5 At the pyridazine reduction by sodium in alcohol solution the following compound will 440. form: A. Butylamine B. Diethylamine C. Piperidine D. *Tetramethylenediamine E. Pyrimidine 441. Choose the chemical name of pyrimidine: A. 1,5-diazine B. diazepine C. 1,4-diazine D. 1, 2-diazine E. *1,3 -diazine 442. Choose the mechanism of the reaction of the pyrazine interaction with sodium amide: A. SE B. SR C. *SN D. E E. AN 443. The reaction of the pyrazine interaction with sodium amide will go in the following position: A. 5 B. *2 C. 1 D. 3 E. 4 444. Under the action of peroxyacids pyrazine oxidizes with formation of: A. *Pyrazine mono-N-oxide B. Pyrazone-2 C. Pyrazine di-N,N-oxide D. Pyrazone-3 E. Pyrazone-5 445. Choose the product of pyrazine reduction by sodium in ethanol: A. Pyrrole B. *Piperazine C. Pyrimidine D. Pyridazine E. Pyridine 446. Choose systematic name of phenothiazine: A. Dibenzo-1,4-thiophene B. Benzo-2-thiazole C. Benzo-1-thiazole D. *Dibenzo-1,4-thiazine E. Dibenzo-1,5-thiazine 447. What products will form after the phenothiazine interaction with iodomethane? A. 7-methyl derivatives B. *N-methyl derivatives C. S-methyl derivatives D. 2-methyl derivatives E. 5-methyl derivatives 448. What products will form after the phenothiazine interaction with chloroanhydride of acetic acid? A. S-acetyl derivatives B. S-methyl derivatives C. N-methyl derivatives D. *N-acetyl derivatives E. N-chloroderivatives 449. Oxidation of phenothiazine goes by: A. *S atom B. N atom C. С2 atom D. С4 atom 450. 451. 452. 453. 454. 455. 456. 457. 458. 459. E. С6 atom Which of the following preparations does include phenothiazine nuclei? A. Phthivazide B. Furacylline C. Cordiamine D. *Aminazine E. Vitamin РР What gas will evaporates after the melting of barbituric acids with NaOH: A. SO3 B. CO C. SO2 D. NO2 E. *NH3 After the barbiturates interaction with NaOH solution forms: A. Black precipitate B. White precipitate C. *Mono- and disodium salts D. NH3 E. Gas CO2 After the adding of an excess of AgNO3 to the barbital sodium salt will form: A. Gas NH3 B. White precipitate of disilver salt C. *Yellow precipitate of disilver salt D. Gas СО E. Black precipitate of Ag Barbituric acid can exist in these two forms: A. Acy- and nitroB. *Oxo- and hydroxyC. Lactim and lactam D. Cyclo- and oxoE. Keto- and enol For its physical properties pyrimidine is: A. Gaseous substance B. Liquid, insoluble in water C. A black crystalline substance D. Yellow liquid E. *Colorless crystalline substance, easily soluble in water Pyrimidine molecule in the reactions with mineral acids forming salts of: A. Complex compounds B. *With the participation of one nitrogen atom C. Involving two nitrogen atoms D. Acidic salts E. Basic salts Electronodonor substituents in the pyrimidine nuclei: A. Promote the passage of the АN reactions B. Promote the passage of the АЕ reactions C. *Promote the passage of the SЕ reactions D. Promote the passage of the SN reactions E. Promote the passage of the Е reactions Nitration of the pyrimidine derivative (SЕ) is conducted with the following reagent: A. *HNO3(conc.), H2SO4(conc.) B. CH3COONO2 C. HNO3(dil.) D. NO2, H2SO4(conc.) E. N2, H2SO4(conc.) Sulfonation of the pyrimidine derivative (SЕ) is conducted with the following reagent: A. SO3 B. C. D. E. *H2SO4 (conc.) SO2 C6H5SO3H S 460. Halogenation of the pyrimidine derivative (SЕ) is conducted with the following reagent: A. HClO3 B. HBrO C. *Br2(AlCl3) D. HBr E. HCl 461. Choose the positions in the pyrimidine molecule for SN reactions: A. 2,5,6 B. 1,4,6 C. *2,4,6 D. 2,3,5 E. 1,2,3 462. Choose the mechanism of the pyrimidine interaction with NaNH2: A. АЕ B. АN C. Е D. SE E. *SN 463. Reaction of pyrimidine interaction with HNО3 (conc.) in the presence of H2SO4 (conc.) will go by the following mechanism: A. АЕ B. SR C. SN D. *SE E. E 464. Interaction of pyrimidine derivative with Br2 in the presence of H2SO4 (conc.) will go by the following mechanism: A. АЕ B. SR C. SN D. *SE E. E 465. Barbiturates - 5,5-disubstituted barbituric acid derivatives show: A. *Hypnotic and antispasmodic action B. Analgesic effect C. Antituberculosis action D. Expectorant action E. Hemostatic effect 466. Barbital - 5,5-disubstituted barbituric acid derivative. R and R’ are: A. *C2H5, C2H5 B. CH3, CH3 C. C2H5, iso-C5H11 D. CH3, C6H5 E. C6H5, C2H5 467. Phenobarbital - 5,5-disubstituted barbituric acid derivative. R and R’ are: A. C2H5, C2H5 B. CH3, CH3 C. C2H5, iso-C5H11 D. CH3, C6H5 E. *C6H5, C2H5 468. Barbamil - 5,5-disubstituted barbituric acid derivative. R and R’ are: A. C2H5, C2H5 B. CH3, CH3 469. 470. 471. 472. 473. 474. 475. 476. 477. C. *C2H5, iso-C5H11 D. CH3, C6H5 E. C6H5, C2H5 To the pyrimidine bases the following compound belongs: A. Pteridine B. Guanine C. Purine D. *Thymine E. Adenine The pyrimidine bases the following compound belongs: A. Pteridine B. Guanine C. Purine D. *Uracil E. Adenine To the pyrimidine bases the following compound belongs: A. Pteridine B. Guanine C. Purine D. *Cytosine E. Adenine Uracil is a part of: A. Phthalazol B. *Nucleic acid C. Aminoacid D. Barbiturates E. Norsulfazolum Thymine is a part of: A. Phthalazol B. *Nucleic acid C. Aminoacid D. Barbiturates E. Norsulfazolum Cytosine is a part of: A. Phthalazol B. *Nucleic acid C. Aminoacid D. Barbiturates E. Norsulfazolum For uracil is characteristic the following type of tautomery: A. *Lactim-lactam tautomery B. Acy-nitro tautomery C. Cyclo-oxo tautomery D. Keto-enol tautomery E. Oxo-hydroxy tautomery For cytosine is characteristic the following type of tautomery: A. *Lactim-lactam tautomery B. Acy-nitro tautomery C. Cyclo-oxo tautomery D. Keto-enol tautomery E. Oxo-hydroxy tautomery For thymine is characteristic the following type of tautomery: A. *Lactim-lactam tautomery B. Acy-nitro tautomery C. Cyclo-oxo tautomery D. Keto-enol tautomery E. Oxo-hydroxy tautomery 478. A. B. C. D. E. 479. A. B. C. D. E. 480. A. B. C. D. E. 481. A. B. C. D. E. 482. A. B. C. D. E. 483. A. B. C. D. E. 484. A. B. C. D. E. 485. A. B. C. D. E. 486. A. B. C. D. E. 487. A. B. What compound does include pyrimidine cycle? Vitamin РР Vitamin Н Vitamin С Vitamin А *Vitamin В1 Which of the following alkaloids does not have optical activity? Nicotine *Caffeine Anabasine Lobeline Quinine Which of the following alkaloids does not have optical activity? *Theophylline Nicotine Lobeline Anabasine Quinine Which of the following alkaloids does not have optical activity? Nicotine Lobeline Anabasine Quinine *Theobromine Which of the following alkaloids does not have optical activity? Anabasine Nicotine *Papaverine Quinine Lobeline Which of the following alkaloids does not have optical activity? Lobeline Nicotine Anabasine *Codeine Quinine Which of the following alkaloids does not have optical activity? Nicotine *Scopolamine Anabasine Lobeline Quinine Which of the following alkaloids does not have optical activity? *Cocaine Anabasine Nicotine Quinine Lobeline Which of the following alkaloids does not have optical activity? Quinine Nicotine Lobeline Anabasine *Reserpine Which of the following alkaloids does not have optical activity? Nicotine Anabasine C. Quinine D. *Strychnine E. Lobeline 488. Which of the following reagents can be used to show basic properties of alkaloids? A. NH4OH B. HNO2 C. *HCl D. NaOH E. NaCl 489. Uric acid belongs to: A. *Dibasis, triatomic acids B. Onebasic diatomic acids C. Tribasic, oneatomic acids D. Dibasic, diatomic acids E. Tribasic, triatomic acids 490. Atropine - belladonna alkaloid. Determine reagent that can be used to identify primary alcoholic group in the atropine molecule: A. *K2Cr2O7 (H+) B. HNO3 C. H2SO4 D. FeCl3 E. Ag(NH3) 2OH 491. Which of the following heterocycles is the base of uric acid? A. *Purine B. Indole C. Pyrimidine D. Imidazole E. Pyridine 492. Adenine, guanine, xanthine and hypoxantine are purine derivatives. How many and what heteroatoms are in the primer structure of these compounds? A. *four nitrogen atoms B. one nitrogen atom and three oxygen atoms C. two nitrogen atoms and two oxygen atoms D. three nitrogen atoms and one oxygen atom E. nothing 493. Morphine – alkaloid of isoquinoline and phenanthrene isoquinoline group. At the interaction with FeCl3 solution gives blue color. This reaction is qualitative on: A. Primary amino-group B. *Phenol hydroxyl C. Aldehyde group D. Secondary nitrogroup E. α-diol fragment 494. A purine nucleus is the main structural fragment of caffeine, theophylline, theobromine, adenine, guanine and uric acid, which have higher physiological activity. Purine is an aromatic heterocycle. Determine the number of ?-electrons that take part in the formation of aromatic system. A. *10 B. 6 C. 14 D. 18 E. 26 495. The most used method for alkaloids extraction is the following one: A. Filtration B. *Extraction C. Sublimation D. Recrystallization E. Distillation 496. Extraction in the form of salts is one of the methods of alkaloids elimination. In this case raw materials are processed by: A. Hexane B. Formalin C. Carbon tetrachloride D. Chloroform E. *Water or ethyl alcohol acidified by tartaric acid 497. Extraction in the form of bases is one of the methods of alkaloids elimination. In this case raw materials are processed by: A. Hexane B. Formalin C. Carbon tetrachloride D. Chloroform E. *Water or ethyl alcohol acidified by tartaric acid 498. From the following list choose general alkaloid reagent: A. Frede B. Lughole C. Felling D. *Mayer E. Selivanov 499. From the following list choose general alkaloid reagent: A. Frede B. Lughole C. *Zonnenstein D. Felling E. Selivanov 500. From the following list choose general alkaloid reagent: A. Frede B. *Berthran C. Lughole D. Felling E. Selivanov 501. From the following list choose general alkaloid reagent: A. *Sheibler B. Lughole C. Frede D. Felling E. Selivanov 502. From the following list choose general alkaloid reagent: A. Frede B. Lughole C. *Dragendorff D. Felling E. Selivanov 503. From the following list choose general alkaloid reagent: A. Frede B. Lughole C. Selivanov D. Felling E. *Wagner-Bushard 504. From the following list choose specific alkaloid reagent: A. Felling B. *Erdman C. Lughole D. Selivanov E. Mayer 505. From the following list choose specific alkaloid reagent: A. B. C. D. E. Felling Selivanov Lughole *Frede Mayer 506. From the following list choose specific alkaloid reagent: A. *Marky B. Felling C. Lughole D. Selivanov E. Mayer 507. From the following list choose specific alkaloid reagent: A. Felling B. Mayer C. Lughole D. Selivanov E. *Mandelin 508. From the following list choose specific alkaloid reagent: A. Felling B. Lughole C. *Sodium nitroprusside D. Selivanov E. Mayer 509. Which of the following alkaloids does belong to pyridine and piperidine group? A. Quinine B. *Nicotine C. Morphine D. Codeine E. Atropine 510. Which of the following alkaloids does belong to pyridine and piperidine group? A. Isoquinoline B. Scopolamine C. Morphine D. Codeine E. *Anabasine 511. Which of the following alkaloids does belong to pyridine and piperidine group? A. Quinoline B. Codeine C. Papaverine D. *Lobeline E. Atropine 512. Which of the following alkaloids does belong to quinoline group? A. *Quinine B. Nicotine C. Morphine D. Codeine E. Atropine 513. Which of the following alkaloids does belong to isoquinoline and phenenthrene isoquinoline group? A. Nicotine B. Scopolamine C. Quinine D. *Papaverine E. Anabasine 514. Which of the following alkaloids does belong to isoquinoline and phenenthrene isoquinoline group? A. Nicotine B. C. D. E. *Morphine Quinine Lobeline Anabasine 515. Which of the following alkaloids does belong to isoquinoline and phenenthrene isoquinoline group? A. Atropine B. Papavarine C. *Codeine D. Quinine E. Anabasine 516. Which of the following alkaloids does belong to tropane group? A. *Atropine B. Nicotine C. Papaverine D. Quinine E. Morphine 517. Which of the following alkaloids does belong to tropane group? A. Nicotine B. *Scopolamine C. Codeine D. Quinine E. Morphine 518. Which of the following alkaloids does belong to tropane group? A. Papaverine B. Lobeline C. *Cocaine D. Quinine E. Morphine 519. Which of the following alkaloids does belong to indole group? A. Quinine B. *Reserpine C. Nicotine D. Morphine E. Cocaine 520. Which of the following alkaloids does belong to indole group? A. Codeine B. Cocaine C. Nicotine D. Morphine E. *Strychnine 521. To which group of alkaloids does theophylline belong? A. Indole B. Tropane C. *Purine D. Quinoline E. Pyridine and piperidine 522. To which group of alkaloids does theobromine belong? A. Indole B. Phenanthrene isoquinoline C. Quinoline D. *Purine E. Pyridine and piperidine 523. To which group of alkaloids does caffeine belong? A. Pyridine and piperidine B. Indole C. Isoquinoline 524. 525. 526. 527. 528. 529. 530. 531. 532. 533. D. Quinoline E. *Purine To which group of alkaloids does nicotine belong? A. *Pyridine and piperidine B. Tropane C. Purine D. Quinoline E. Indole To which group of alkaloids does anabasine belong? A. Phenanthrene B. Tropane C. Purine D. *Pyridine and piperidine E. Quinoline To which group of alkaloids does lobeline belong? A. Indole B. *Pyridine and piperidine C. Piperidine D. Isoquinoline E. Pyridine To which group of alkaloids does quinine belong? A. Isoquinoline B. Tropane C. Purine D. *Quinoline E. Pyridine and piperidine To which group of alkaloids does papaverine belong? A. *Isoquinoline and phenanthrene isoquinoline B. Quinoline C. Tropane D. Indole E. Purine To which group of alkaloids does morphine belong? A. Isoquinoline B. Quinoline C. *Isoquinoline and phenanthrene isoquinoline D. Indole E. Phenanthrene To which group of alkaloids does codeine belong? A. Purine B. Pyridine and piperidine C. Indole D. Tropane E. *Isoquinoline and phenanthrene isoquinoline To which group of alkaloids does atropine belong? A. Isoquinoline and phenanthrene isoquinoline B. Quinoline C. *Tropane D. Indole E. Purine To which group of alkaloids does scopolamine belong? A. Phenanthrene isoquinoline B. Quinoline C. Isoquinoline D. *Tropane E. Indole To which group of alkaloids does cocaine belong? A. B. C. D. E. Purine *Tropane Isoquinoline Indole Quinoline 534. To which group of alkaloids does reserpine belong? A. Isoquinoline and phenanthrene isoquinoline B. Quinoline C. Tropane D. *Indole E. Purine 535. To which group of alkaloids does strychnine belong? A. Tropane B. Quinoline C. *Indole; D. Isoquinoline E. Putine 536. Nicotine – alkaloid of pyridine and piperidine group in the little amount nicotine has: A. Spasmolytic action B. *Arousing effect on the autonomic system C. Antituberculosis action D. Antipyretic action E. Analgesic action 537. Nicotine, being a poisonous substance is used as: A. Flavor B. Stain C. Bleach D. Solvent E. *Insecticide 538. Anabasine – alkaloid of pyridine and piperidine group. Anabasine is used in the medicine as: A. *Mean against smoking B. Antituberculosis mean C. Expectorant mean D. Spasmolytic mean E. Sedative mean 539. Quinine – alkaloid of quinoline group. Quinine is used in the medicine as: A. *Antimalarial remedy B. Antituberculosis mean C. Expectorant mean D. Spasmolytic mean E. Sedative mean 540. Papaverine – alkaloid of quinoline and phenanthrene isoquinoline group. Papaverine is used in the medicine: A. Antimalarial remedy B. Antituberculosis mean C. Expectorant mean D. *Spasmolytic mean E. Sedative mean 541. What is the name of the following terpene? A. B. C. D. E. α-pinene squalene limonene *ocimene myrcene What is the name of the following terpene compound? A. B. C. D. E. camfora squalene *limonene ocimene myrcene Choose the product of β-lactose interaction with excess of acetic anhydride 542. 543. A. B. C. D. 544. E. * What is the name of the following terpenoid? A. B. C. D. E. menthol *α-terpineol farnesol nerol geraniol Which group of compounds does menthol belong? A. B. C. D. E. *diene aldehyde diene alcohol alicyclic aldehyde bicyclic alcohol monocyclic aldehyde Which group of compounds does menthol belong? A. B. C. D. E. bicyclic ketone aliphatic alcohol cycloalkane *monocyclic alcohol bicyclic alcohol Which group of compounds does squalene belong? 545. 546. 547. A. B. C. D. E. monocyclic alkane monocyclic alcohol bicyclic alkane *polyene bicylic aldehyde Which group of compounds does farnesol belong? A. B. C. D. E. saturated alcohol bicyclic ketone *polyene alcohol monocyclic alcohol bicyclic alcohol Choose the product of the following reaction? A. B. C. D. E. camphene terpin hydrate terpin α-pinene *borneol What is the name of the following terpene? 548. 549. 550. A. B. C. D. E. 551. α-pinene squalene limonene ocimene *myrcene What is the product of primary oxidation of camphor with nitric acid? A. B. C. D. * E. 552. What is the product of nerol cyclization in acidic media? A. B. C. * D. E. 553. Choose the number of chiral atom in the molecule of ¥á-terpineol. A. B. C. D. E. 554. 5 *4 3 2 1 Choose the number of chiral atom in the molecule of limonene. A. 5 B. *4 555. C. 3 D. 2 E. 1 Which group of compounds does geraniol belong? A. B. C. D. E. bicyclic diene aliphatic alcohol diene alcohol *diene alcohol diene aldehyde Which group of compounds does myrcene belong? A. B. C. D. E. cycloalkane bicyclic aldehyde monocyclic aldehyde *aliphatic polyene aliphatic alcohol Which of the following reagents can be used to distinguish phenylalanine from tyrosine? 556. 557. A. B. C. D. * E. 558. A. B. C. D. E. 559. Choose the correct definition of nucleotide. *nucleotide is the phosphoric acid ester of nucleoside nucleotide is N-glycoside, which consist of nucleobase and D-ribose nucleotide is the phosphoric acid ester of pyrimidine nucleobase nucleotide is the phosphoric acid ester of purine nucleobase nucleotide is the compound which consist of carbohydrate and heterocyclic nucleobase What is the product of α-amino acids reaction with nitrous acid ? A. B. C. * D. E. 560. Choose the systematic name of α-cellobiose. A. B. C. D. * E. 561. Choose the name of the following disaccharide. A. * B. C. D. E. 562. A. B. C. D. E. 563. How many chiral carbon atomes does β-D-fructofuranose have? three three five *four one Choose the product of D-glucose reduction. A. B. C. * D. E. 564. How many asymmetric carbon atoms does β-D-glucopyranose have? A. B. C. D. E. six *four five one three 565. Among the peptides listed below choose the one with peptide sequence: alanine, glutamine and glycine (Ala-Glu-Gly). A. B. C. D. * E. 566. Among the peptides listed below choose the one with peptide sequence: glutamic acid, glycine and alanine (Glu-Gly-Ala). A. * B. C. D. E. 567. What is the name of the following terpenoid? A. B. C. D. E. *α-pinene squalene limonene ocimene myrcene What is the name of the following terpenoid? A. B. C. D. E. menthol α-terpineol farnesol *nerol geraniol What is the name of the following terpenoid? A. B. C. D. E. *menthol α-terpineol farnesol nerol Geraniol What is the name of the following terpenoid? 568. 569. 570. A. B. C. D. E. menthol α-terpineol farnesol nerol *geraniol What is the name of the following terpenoid? A. B. C. D. E. menthol α-terpineol *farnesol nerol geraniol Which of the following reagents can be applied to obtain acyl halide from alanine? 571. 572. A. B. C. D. 573. E. * Choose the name of the following disaccharide. A. B. C. D. * E. 574. Choose the systematic name of β-maltose. A. * B. C. D. E. 575. Choose the name of the following disaccharide. A. B. C. D. E. 576. A. B. C. D. E. 577. β- maltose *β-cellobiose β- lactose sucrose α- maltose Which of the following disaccharides gives galactose and glucose after hydrolysis? mannose cellobiose *lactose maltose sucrose Choose the systematic name of beta-cellobiose. A. B. C. D. * E. 578. Choose the systematic name of α-maltose. A. B. C. * D. E. 579. A. B. C. D. E. 580. A. B. C. D. E. deoxymonosaccharide aldohexose ketohexose *ketopentose aldopentose What is the name of the following monosaccharide? A. B. C. D. E. D–xylose D–galactose *D–glucose D–mannose D–fructose What is the name of the following monosaccharide? 581. 582. The change of the specific rotation of sucrose solution caused by its hydrolysis is called: in all possible tautomeric forms *inversion mutorotation isomerization epimerization The following monosaccharide belongs to: A. B. C. D. E. 583. A. B. C. D. E. 584. A. B. C. D. E. 585. *L– mannose L– galactose D–galactose L– glucose D–glucose Choose the correct definition for protein denaturation. *destruction of the protein form, with retention of primary structure of protein destruction of quaternary structure, with retention of primary secondary and tertiary structures of protein destruction of tertiary structure, with retention of primary and secondary structures of protein destruction of secondary structure, with retention of primary structure of protein destruction of primary structure of protein What are the products of nucleic acids complete hydrolysis? *nucleobases, monosaccharides and phosphoric acid nucleobases, monosaccharides and water glycosides and phosphoric acid nucleosides and phosphoric acid nucleotides What is the product of glycine reaction with ethanol? A. B. * C. D. E. 586. Choose the cationic form of amino acids. A. B. C. * D. E. 587. Choose the product of borneol oxidation. A. B. * C. D. E. 588. Choose the systematic name of β-lactose. A. B. C. D. 589. 590. 591. E. * What are the products of glucose oxidation with Fehling’s reagent? A. *mixture of oxidation products + Cu2O B. glucaric acid + CuO C. gluconic acid + Cu D. glucuronic acid + Cu2O E. sorbitol + CO2 Which is the correct definition of epimeric monosaccharides? A. monoses, which have the different configuration of all chiral carbon atoms B. monoses, which have the different configuration of four chiral carbon atoms C. monoses, which have the different configuration of three chiral carbon atoms D. *monoses, which have the different configuration of one chiral carbon atom E. monoses, which have the different configuration of two chiral carbon atoms What is the name of the following monosaccharide? A. B. C. D. E. 592. *D–mannose L– galactose D–galactose L– glucose D–glucose What is the name of the following monosaccharide? A. B. C. D. E. 593. L–galactose D–xylose *D–ribose L–arabinose D–arabinose Choose the correct systematic name of α -lactose. A. B. C. D. 594. E. * Amylose (water-soluble fraction of starch) is planar polymer which consists of: A. B. C. * D. E. 595. A. B. C. D. E. 596. A. B. C. D. E. 597. Choose the correct complementary pair of nucleobases among the listed below. hypoxanthine - cytosine thymine - uracil uracil - hypoxanthine *adenine - thymine guanine - uracil Which group of compounds does camphor belong? cycloalkanol aliphatic alcohol bicyclic alkene *bicyclic ketone aliphatic ketone Which group of compounds does limonene belong? A. B. C. D. E. cyclopolyene bicyclic aldehyde cycloalkane aliphatic ketone *monocyclic diene 598. Terpenes are unsaturated compounds with the formula (C5H8)n, where n - number of isoprene fragments. What is the name of terpenes type with п = 8? A. *tetraterpenes B. triterpenes C. diterpenes D. sesquiterpenes E. monoterpenes 599. Terpenes are unsaturated compounds with the formula (C5H8)n, where n - number of isoprene fragments. What is the name of terpenes type with п = 6? A. tetraterpenes B. *triterpenes C. diterpenes D. sesquiterpenes E. monoterpenes 600. To which group of lipids do terpenes belong? A. phospholipids B. waxes C. fats D. *isoprenoids E. prostaglandins 601. Which group of compounds does borneol belong? A. B. C. D. E. 602. cycloalkane *bicyclic alcohol polycyclic polyene bicyclic ketone aliphatic alcohol Which group of compounds does α-pinene belong? A. *bicyclic alkene B. bicycles polyene C. bicyclic alkyne D. aromatic hydrocarbon E. monocyclic alkene 603. Terpenes are unsaturated compounds with the formula (C5H8)n, where n - number of isoprene fragments. What is the name of terpenes type with п = 4? A. tetraterpenes B. triterpenes C. *diterpenes D. sesquiterpenes E. monoterpenes 604. Terpenes are unsaturated compounds with the formula (C5H8)n, where n - number of isoprene fragments. What is the name of terpenes type with п = 3? A. tetraterpenes B. triterpenes C. diterpenes D. *sesquiterpenes E. monoterpenes 605. Terpenes are unsaturated compounds with the formula (C5H8)n, where n - number of isoprene fragments. What is the name of terpenes type with n = 2? A. tetraterpenes B. triterpenes C. diterpenes D. sesquiterpenes E. *monoterpenes 606. Choose the correct reaction scheme of oxyproline with hydrochloric acid. A. B. * C. D. E. 607. Choose the correct reaction scheme of histidine with iodo methane. A. B. C. * D. E. 608. A. B. C. D. E. 609. Which monosaccharide is the part of RNA? arabinose fructose glucose deoxyribose *ribose What are the products of adenosinemonophosphoric acid complete hydrolysis? A. B. C. D. E. 610. three molecules of phosphoric acid and adenine two molecules of phosphoric acid, deoxyribose and adenine *one molecule of phosphoric acid, ribose and adenine one molecule of phosphoric acid and adenine two molecules of phosphoric acid and adenine Choose peptide-group among the listed below. A. B. * C. D. E. 611. A. B. C. D. E. 612. A. Which bond is used for construction of primary structure of protein? coordinative semi polar *peptide ionic hydrogen Which of the following reaction occurs on the aryl moiety of phenylalanine molecule? B. * C. D. E. 613. A. B. C. D. E. 614. Which of the following monosaccharides is the part of DNA? mannose ribose glucose *deoxyribose fructose Choose the acidic amino acids among the listed below. A. B. * C. D. E. 615. A. B. C. D. E. 616. The bond of which type plays the essential role in the nucleobase pairing? semi polar bond ionic bond hydrophobic interactions *hydrogen bond non-polar covalent bond Which of the following acids forms γ-lactame of the structure listed below? A. B. C. D. E. 617. 5– aminohexanoic acid 3–aminopropanoic acid 5– aminohexanoic acid *4-aminobutanoic acid 4–aminohexanoic acid Which of the following amino acids will form crotonic acid when heated? A. B. C. *beta-aminobutyric acid D. γ-glutamic acid amide (glutamine) E. 618. Choose the amino acid which forms the 3,6-dimethyl-2,5-dioxopiperazine when heated. A. B. C. D. 619. E. * Which of the following reactions can be used for quantitative analyses of α-amino acids? A. B. C. D. E. * 620. With which of the following reagents 3-aminobutanoic acid will undergo dezamination reaction? A. B. C. * D. E. 621. Choose the reaction of oxidative dezamination which proceeds in the human body. A. B. C. * D. E. 622. Choose the correct scheme of α-aminoisovaleric acid (valine) transformation: A. * B. C. D. E. 623. Which bond plays the essential role in formation of spiral secondary structure of proteins? A. hydrophobic interactions B. semipolar C. peptide D. ionic E. *hydrogen 624. Among the listed below choose α-amino acids. A. B. C. * D. E. 625. Choose the structure of ascorbic acid (vitamin C): A. B. C. D. * E. 626. The interaction of cellulose with excess of acetanhydride in the presence of H2SO4 (catalyst) leads to formation of: A. cellulose sulfate B. *cellulose triacetate C. cellulose xanthogenate D. cellulose diacetate E. cellulose acetate 627. What is the product of reaction of cellulose with excess mixture of nitric and sulfuric acids? A. cellulose disulfate B. *cellulose trinitrate (pyroxiline) C. cellulose sulfate D. cellulose dinitrate E. cellulose mononitrate 628. Choose the name of the following disaccharide. A. B. C. * D. E. 629. Choose the product of interaction of β-cellobiose with excess of ¬³¬¯3І. A. B. C. * D. E. 630. A. B. C. D. E. Which is the end-product of acidic hydrolysis of cellulose? α-lactose β-maltose D-fructofuranose *D-glucopyranose D- galactopyranose 631. Starch consists of amylose and amylopectine which can be hydrolyzed by enzymes to Dglucose. Choose the correct scheme of starch hydrolysis. A. B. * C. D. E. 632. What is the systematic name of sucrose? A. B. * C. D. E. 633. What does symbol «D» in the name of D-(+)glucose means? A. B. C. D. E. 634. *the relative configuration of C5 atom the relative configuration of C4 atom the relative configuration of C2 atom levorotatory isomer dextrorotatory isomer D-Glucose in the sodium hydroxide solution in the course of time forms the mixture of D-glucose, D-mannose and D-fructose. What is the name of these transformations? A. Walden inversion B. anomerization C. cyclization D. *epimerization E. mutarotation 635. Amylopectine (the insoluble in water fraction of starch) is the branched polymer, which consists of: A. B. C. * D. E. 636. Choose the structure of alfa -D-galactopyranose? A. B. C. * D. E. 637. Which of the following reagents will form osazones with monosaccharides? A. semicarbazide B. hydrazine C. *phenylhydrazine 638. D. hydroxylamine E. ammonia What does the symbol “-“ in the name L-(-)-glucose means? the relative configuration of С2 atom the relative configuration of С5 atom dextrorotatory isomer *levorotatory isomer the relative configuration of С4 atom 639. When D-glucose is treated with sodium hydroxide solution for a few days it forms the mixture of: A. D– glucose, D– galactose and D– fructose B. D– glucose, D–galactose and D– mannose C. *D– glucose, D– mannose and D– fructose D. D–glucose and D–mannose E. D–glucose and D–fructose 640. What is the product of D-fructose oxidation with nitric acid? A. D–galacturonic acid B. *D–arabinaric acid C. D–mannitol D. D–glucaric acid E. D–gluconic acid 641. In the crystals the molecules of monosaccharides are in the: A. enolic hydroxyl B. endiol form C. in all possible tautomeric forms D. acyclic form E. *cyclic form 642. Choose the structure of β-D-galactopyranose? A. B. C. D. E. A. B. C. * D. E. 643. Choose the structure of β-D-ribofuranose? A. B. C. D. 644. E. * D-glucose and D-mannose are epimers because: A. B. C. D. E. 645. have? have the different configuration of the fifth carbon atom are the members of the same stereochemical range have the different number of chiral carbon atoms *have the different configuration of the second carbon atom have the equal number of chiral carbon atoms How many asymmetric carbon atoms (chiral C atoms) does the following monosacharide A. B. C. D. E. five four *two three one How many stereoisomers does the following aldohexose have? A. B. C. D. E. eight thirty two *sixteen four eight The mutarotation is caused by: have the equal number of chiral carbon atoms inversion of configuration of the cyclic forms of monosacharides *equilibrium of tautomeric forms conversion in the solution epimeric transformations of monosaccharides inversion of configuration of the last carbon atom Which of the following monosccharides are hexoses? galactose ribose arabinose *mannose xylose The change of specific rotation of monosaccharides solution in the course of time is 646. 647. A. B. C. D. E. 648. A. B. C. D. E. 649. called: A. enolic hydroxyl B. epimerization C. *mutarotation D. isomerization 650. E. inversion How many stereoisomers does the following aldopentose have? A. ten B. * C. D. E. 651. Glucose can react in the open and cyclic form. Glucose interacts with: 1)Br2 (H2O); 2) HNO3; 3) (CH3CO)2O; 4) [Ag(NH3)2]OH; 5)CH3OH (HCl). Which of the following reactions does glucose give in the cyclic form? A. *3, 5 B. 1, 3 C. 3, 4 D. 2, 5 E. 1, 2 652. Which isomers of monosaccharides are called anomers? Choose the correct definition. A. the cyclic forms of mannoses that differ only in their configuration at the С3 B. the cyclic forms of mannoses that differ only in their configuration at the С2 and С3 C. *the cyclic forms of mannoses that differ only by the position of hemiacetal hydroxyl D. the cyclic forms of mannoses that differ only in their configuration at the С2 E. the cyclic forms of mannoses that differ only in their configuration at the С5 653. The change of the specific rotation of the freshly prepared monosaccharides solution is called: A. inversion B. isomerization C. tautomery D. epimeryzation E. *mutarotation 654. Which of the following monosaccharides does belong to hexoses? A. xylose B. *mannose C. arabinose D. ribose E. lyxose 655. Which of the following monosaccharides does belong to hexoses? A. xylose B. ribose C. arabinose D. *glucose E. lyxose 656. Which of the following monosaccharides does belong to hexoses? A. *galactose B. xylose 657. 658. 659. 660. 661. 662. 663. 664. 665. C. arabinose D. ribose E. lyxose Which of the following monosaccharides does belong to hexoses? A. xylose B. lyxose C. arabinose D. ribose E. *fructose Which of the following monosaccharides does belong to pentoses? A. *xylose B. mannose C. glucose D. fructose E. galactose Which of the following monosaccharides does belong to pentoses? A. glucose B. mannose C. *arabinose D. fructose E. galactose Which of the following monosaccharides does belong to pentoses? A. glucose B. mannose C. galactose D. *ribose E. fructose Which of the following monosaccharides does belong to pentoses? A. fructose B. mannose C. galactose D. glucose E. *lyxose Which of the following monosaccharides does belong to ketoses? A. xylose B. mannose C. *fructose D. ribose E. arabinose Which of the following monosaccharides does belong to ketohexoses? A. xylose B. mannose C. *fructose D. ribose E. lyxose Which of the following monosaccharides does belong to aldohexoses? A. xylose B. ribose C. fructose D. *mannose E. arabinose Which of the following monosaccharides does belong to aldohexoses? A. xylose B. *glucose C. fructose D. ribose E. arabinose 666. Which of the following monosaccharides does belong to aldohexoses? A. xylose B. arabinose C. fructose D. ribose E. *galactose 667. Which of the following monosaccharides does belong to aldopentoses? A. *xylose B. mannose C. fructose D. galactose E. glucose 668. Which of the following monosaccharides does belong to aldopentoses? A. fructose B. mannose C. *ribose D. galactose E. glucose 669. Which of the following monosaccharides does belong to aldopentoses? A. galactose B. mannose C. fructose D. *arabinose E. glucose 670. Cyclic forms of monosaccharides in the chemical condition are: A. cyclic ethers B. *cyclic hemiacetals C. cyclic esters D. anhydrides E. cyclic hemiketals 671. The mutarotation is cased by: A. the change of the configuration at the last asymmetric carbon atom B. epimeric transformations of the monosaccharides C. *mutual transformations of the monosaccharides formf in the solution and achievement of the equilibrium between them D. the change of the monosaccharides cyclic forms configuration E. the change of the configuration at the С4 672. The hydroxyl-group, which is formed by monosaccharides cyclization is called: A. *hemiacetal hydroxyl B. epimeric hydroxyl C. anomeric hydroxyl D. hemiketal hydroxyl E. enolic hydroxyl 673. The hydroxygroup, which is formed by monosaccharides cyclization is called: A. epimeric hydroxyl B. *glycosidic hydroxyl C. anomeric hydroxyl D. hemiketal hydroxyl E. enolic hydroxyl 674. D-glucose and D-mannose are epimers, because: A. have an equal number of chiral carbon atoms B. have the different configuration of the fifth carbon atom C. have the different number of the chirality centers D. are the members of the same stereochemical range E. *have the different configuration of the second carbon atom 675. Phenomenon, which is cased by the change of the sucrose solution specific optical rotation during the hydrolysis, is called: A. B. C. D. E. epimerization isomerization *mutarotation inversion tautomery 676. Monosaccharides in the crystalline state have: A. cyclic struscture B. alicyclic structure C. epimeric forms D. endiol structure E. *structure that includes all tautomeric forms 677. Determine compound, which will form after the oxidation of D–fructose by concentrated nitrate acid: A. D–gluconic acid B. D–glucaric acid C. D–mannite D. *D–arabinaric acid E. D–galacturonic acid 678. Determine compound, which will form after the oxidation of D–glucose by concentrated nitrate acid: A. D–gluconic acid B. *D–glucaric acid C. D–mannite D. D–arabinaric acid E. D–galacturonic acid 679. Determine compound, which will form after the oxidation of D–mannose by concentrated nitrate acid: A. D–gluconic acid B. *D–mannaric acid C. D–mannite D. D–arabinaric acid E. D–galacturonic acid 680. Determine compound, which will form after the oxidation of D–galactose by concentrated nitrate acid: A. D–gluconic acid B. *D–glucaric acid C. D–mannite D. D–galactaric acid E. D–galacturonic acid 681. Determine compound, which will form after the D–galactose oxidation by bromine water: A. *D–galactonic acid B. D–glucaric C. D–mannite D. D–galactaric acid E. D–galacturonic 682. Determine compound, which will form after the D–glucose oxidation by bromine water: A. D–mannite B. D–glucaric acid C. *D–gluconic acid D. D–galactaric acid E. D–galacturonic acid 683. Determine compound, which will form after the D–mannose oxidation by bromine water: A. D–gluconic acid B. D–glucaric acid C. D–mannite D. *D–mannonic acid E. D–galacturonic acid 684. Determine compound, which will form after the oxidation of D–ribose by concentrated nitrate acid: A. D–gluconic acid B. D–glucaric acid C. D–ribonic acid D. *D–ribaric acid E. D–galacturonic acid 685. Determine compound, which will form after the oxidation of D–ribose by bromine water: A. D–gluconic acid B. D–glucaric acid C. *D–ribonic acid D. D–ribaric acid E. D–galacturonic acid 686. Which isomers of monosaccharides are called epimers? A. hexoses that are different by the configuration of two asymmetric carbon atoms B. *hexoses that are different by the configuration of one asymmetric carbon atoms C. hexoses that are different by the configuration of three asymmetric carbon atoms D. hexoses that are different by the configuration of all asymmetric carbon atoms E. hexoses that are different by the configuration of four asymmetric carbon atoms 687. What reaction do monosaccharides in the cyclic form? A. *alkylation B. epimeryzation C. reduction D. ozazones formation E. hydrazides formation 688. Determine what compound will form after the glucose oxidation by Felling reagent: A. sorbite + CO2 B. glucuronic acid + Cu2O C. gluconic acid + Cu D. glucaric acid + CuO E. *mixture of the oxidation products + Cu2O 689. D–glucose in the sodium hydroxide solution during few days forms the mixture of monosaccharides, which consists of: A. D–glucose and D–fructose B. D–glucose and D–mannose C. *D–glucose, D–mannose and D–fructose D. D–glucose, D–galactose and D–mannose E. D–glucose, D–galactose and D–fructose 690. Choose the reagent that can oxidize aldoses: A. hydrochloric acid B. acetic acid C. phenylhydrazine D. *bromine water E. sodium hydroxide alcoholic solution 691. Choose the reagent that can oxidize aldoses: A. hydrochloric acid B. *nitrate acid C. phenyl hydrazine D. acetic acid E. sodium hydroxide alcoholic solution 692. Which of the following reactions, characteristic for aldehydes, do monosaccharides give? A. formation of hydrosulfite derivatives B. formation of ethers C. formation of esters D. *formation of phenyl hydrazones E. interaction with fuchsine sulfite acid 693. What disaccharide will give reaction with Tollens reagent? A. sucrose B. maltose C. amylose D. amylopectin E. *cellulose 694. Choose the end product of the cellulose hydrolysis, which will form after its heating with mineral acids: A. D-galactopyranose B. *D-glucopyranose C. D-fructofuranose D. D-maltose E. E-lactose 695. What reagents can be used to distinguish maltose and sucrose? A. *Tollens reagent B. Reaction with α-naphthalene C. Felling liquid D. Fuchsine sulfite acid E. Trommer test 696. What product will form after the adding of an excess of nitric mixture to cellulose? A. cellulose mononitrate B. cellulose dinitrate C. cellulose sulfate D. *cellulose trinitrate (pyroxylin) E. cellulose disulfate 697. What product will form after the cellulose interaction with acetic anhydride at the presence of conc. H2SO4 (catalyst)? A. cellulose acetate B. cellulose diacetate C. cellulose xanthogenate D. *cellulose triacetate E. cellulose sulfate 698. What monosaccharide is a product of starch hydrolysis? A. *glucose B. fructose C. mannose D. ribose E. galactose 699. To the heteropolysaccharides the following compound belongs: A. starch B. cellulose C. methyl-D-galactopyranoside D. deoxyribose E. *chondroitin sulfate 700. Nonreducing disaccharide is the following one: A. cellobiose B. maltose C. *sucrose D. lactose E. xylose 701. Which of the following polysaccharides is used in the pharmacy in the production of “polyglucin’ and “rheopolyglucin”? A. *dextrans B. dextrins C. cellulose D. pectines E. inulin 702. Sucrose, maltose and lactose are disaccharides. They found wide application in the food industry and medicine. With which of the proposed reagents can be identified among of these disaccharides reducing and nonreducing? A. H2SO4 B. NaOH C. K2CO3 D. *[Ag(NH3)2]OH E. CH3COOH 703. Disaccharide form by hydrolysis of polysaccharides. What disaccharide will form after the hydrolysis of starch? A. pyrogalose B. lactose C. cellobiose D. sucrose E. *maltose 704. Cellulose belongs to the polysaccharides. Choose monosaccharide, which will form after the cellulose hydrolysis: A. β- D -fructopyranose B. α- D -glucopyranose C. *β- D -glucopyranose D. α- D -fructofuranose E. β- D -glucofuranose 705. Which of the following sugars does not form brick-red precipitate after the heating with Felling reagent? A. *sucrose B. glucose C. lactose D. cellulose E. mannose 706. Fraction of starch is: A. cellulose B. maltose C. fructose D. *amylose E. glycogen 707. Choose monosaccharides that are structural elements of sucrose: A. only glucose B. *glucose, fructose C. glucose, galactose D. only fructose E. fructose, mannose 708. Which of the following disaccharides will not react with Felling reagent? A. lactose and maltose B. lactose C. maltose D. cellobiose E. *sucrose 709. Disaccharides form by hydrolysis of polysaccharides. What disaccharide will form after the cellulose hydrolysis? A. lactose B. maltose C. *cellobiose D. sucrose E. pyrogalose 710. From the following compounds choose reducing disaccharide: A. B. C. D. E. 711. A. B. C. D. E. 712. A. B. C. D. E. 713. A. B. C. D. E. 714. A. B. C. D. E. 715. A. B. C. D. E. 716. A. B. C. D. E. 717. A. B. C. D. E. 718. A. B. C. D. E. 719. A. B. C. inulin *lactose stachyose sucrose fructose Choose chemical name of lactose: *β–D–galactosido–1,4–?–D–glucopyranose β–D–fructofuranose α–D–glucopyranosido–1,2–?–D–fructofuranose α–D–glucopyranosido–1,4–?– D–dlucopyranose β–D–glucopyranosido–1,4–?– D–glucopyranose Choose chemical name of maltose: β–D–galactose–1,4–?–D–glucopyranose β–D–galactosido–1,4–?–D–fructofuranose α–D–– glucopyranosido-1,2–?–D–fructofuranose *α–D– glucopyranosido –1,4–?–D–glucopyranose β–D-glucopyranosido –1,4–?–D–glucopyranosido Choose chemical name of sucrose: β–D–galactosido–1,4–?–D–glucopyranose 2-β–D–fructofuranose *α–D–glucopyranosido–1,2–?–D–fructofuranose α–D––glucopyranosido-1,4–?– D–glucopyranose β–D–glucopyranosido –1,4–?– D–glucopyranose Choose chemical name of cellobiose: β–D–galactosido–1,4–?–D–glucopyranose β–D–fructofuranose; α–D–glucopyranosido–?–D–fructofuranose α–D–glucopyranosido–1,4–?– D–glucopyranose *β–D– glucopyranosido–1,4–?– D–glucopyranose At the disaccharides hydrolysis the following compounds form: esters carboxylic acids and water polysaccharides 1 molecule of Carbon (IV) oxide and water *2 molecules of monosaccharides At the lactose hydrolysis the following compounds form: α-glucose and β-fructose *β-galactose and α-glucose 2 molecules of β-glucose 2 molecules of β-galactose 2 molecules of α-glucose At the maltose hydrolysis the following compounds will form: α-glucose and β-fructose β-galactose and α-glucose 2 molecules of β-glucose 2 molecules of β-galactose *2 molecules of α-glucose At the cellulose hydrolysis the following compounds will form: α-glucose and β-fructose β-galactose and α-glucose *2 molecules of β-glucose 2 molecules of β-galactose 2 molecules of α-glucose At the sucrose hydrolysis the following compounds will form: *α-glucose and β-fructose β-galactose and α-glucose 2 molecules of β-glucose D. 2 molecules of β-galactose E. 2 molecules of α-glucose 720. In nature, disaccharides may exist both independently and as a part of many glycosides of plant and bacterial origin. Which of the pointed compounds are nonreducing disaccharides? A. cellobiose B. lactose C. maltose D. *sucrose E. starch 721. Sucrose relates to the nonreducing disaccharides. Sucrose is decomposed into two monosaccharides after the hydrolysis. Indicate which monosaccharides are a part of sucrose molecule: A. *glucose and fructose B. glucose and glucose C. glucose and galactose D. mannose and fructose E. fructose and fructose 722. It is known, that soaps are a salts of higher carboxylic acids (HCA). Which soap has a liquid consistency and is named as “green soap”? A. calcium B. sodium C. *potassium D. lithium E. antimony 723. What reagent will characterize camphor as ketone? A. HCl B. Br2 C. NH3 D. CH3COOH E. *C6H5NHNH2 724. What reagent can be used to confirm unsaturated character of camphor? A. oxidation on the air B. *bromine water C. HNO3 D. HNO2 E. H2SO4 725. What reagent can be used to get “liquid soap” by the alkaline hydrolysis of fats (saponification)? A. *K2CO3 B. NаOH C. CаO D. PbO E. NaHCO3 726. Stearic acid belongs to the fats content. Chose formula of this acid: A. C17H33COOH B. *C17H35COOH C. C15H31COOH D. C17H31COOH E. C19H33COOH 727. By the chemical structure fats belong to: A. salts B. *esters C. carboxylic acids D. alcohols E. aldehydes 728. Alkaline hydrolysis of fats has name: A. *saponification B. C. D. E. 729. A. B. C. D. E. 730. A. B. C. D. E. hydration hydratation oxidation hydrolysis For the transformation of liquid fats into the solid fats the following reaction is used: sulfonation chlorination bromination *hydration oxidation Prostaglandins in their content have: 10 carbon atoms 30 carbon atoms 25 carbon atoms *20 carbon atoms 15 carbon atoms