Chapter 41 Animal Nutrition

AP Biology/ Presentation Outline
Ashley Kelch, Melanie Diaz, Joy Chao
Chapter 41 Animal Nutrition
Overview: The Need to Feed
Herbivore, Carnivore, omnivore
Three nutritional needs
41.1 Homeostatic mechanisms manage an animal’s energy budget
Different types of feeders
1.
Suspension feeders (def + example)
2.
Substrate feeders (def + example)
3.
Fluid Feeders (def + example)
4.
Bulk feeders (def + example)
ATP generation by oxidation of energy-rich organic molecules
Glucose regulation, example of Homeostasis
1.
Excess calories
2.
Glycogen depots
Caloric Imbalance
1.
Undernourishment
2.
Overnourishment
3.
Fats and Carbohydrates
Obesity as a Human Health Problem
1.
Inheritence
2.
Weight regulation treatment
3.
Example of leptin
Obesity and Evolution
1.
Natural selection favors individuals able to obtain fatty foods
42.2 An animal’s diet must supply carbon skeleton and essential nutrients
Carbon skeleton
Essential nutrients
1.
Malnourishment (mineral) vs. undernourishment (caloric)
2.
Four essential nutrients
Essential Amino Acid
1.
Protein deficiency
2.
Reliable source
3.
Animal products vs. plant products
Essential Fatty Acid
1.
Types needed for animals
2.
Usage
Vitamins
1.
Amount needed
2.
Water soluble
3.
Fat soluble
4.
Usage
Minerals
1.
Amount needed
2.
Different minerals, usage
AP Biology/ Presentation Outline
Ashley Kelch, Melanie Diaz, Joy Chao
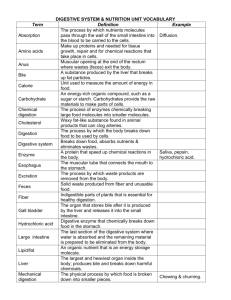
41.3 The main stages of food processing are ingestion, digestion, absorption, and elimination
Food Processing
1.
First stage- ingestion
2.
Second stage- digestion
3.
Third stage- absorption
4.
Fourth stage- elimination
Digestive compartments
1.
Intracellular digestion
2.
Extracellular digestion
3.
Gastrovascular cavity
4.
Complete digestive tract (alimentary canal)
Digestion is different animals
1.
Hydra
2.
Earthworm
3.
Grasshopper
4.
Bird
41.4 Each organ of the mammalian digestive system specialized food-processing functions
Digestion Process
1.
Begins in the mouth . . .
Gastric juices
1.
In stomach
2.
Break the peptide bonds of proteins
Villi and microvilli
1.
In the small intestine
2.
Increase surface area for the absorption of nutrients
3.
(Figure 41.21 Flowchart of enzymatic digestion in the human digestive system)
Hormones
1. Regulation of digestive organs
Large intestine
1.
Absorbs most of the water from the digested food back into the body before the remains are excreted
Bacterias
1.
Those living in the large intestine produce vitamins
2.
Minerals absorbed by mammals
41.5 Evolutionary adaptations of vertebrate digestive systems are often associated with diet
Mammalian bodies
1.
Development of adaptations
2.
Specialized diet
Herbivores
1.
Benefit of bacteria in alimentary canal