Digestive system & nutrition unit vocabulary
advertisement
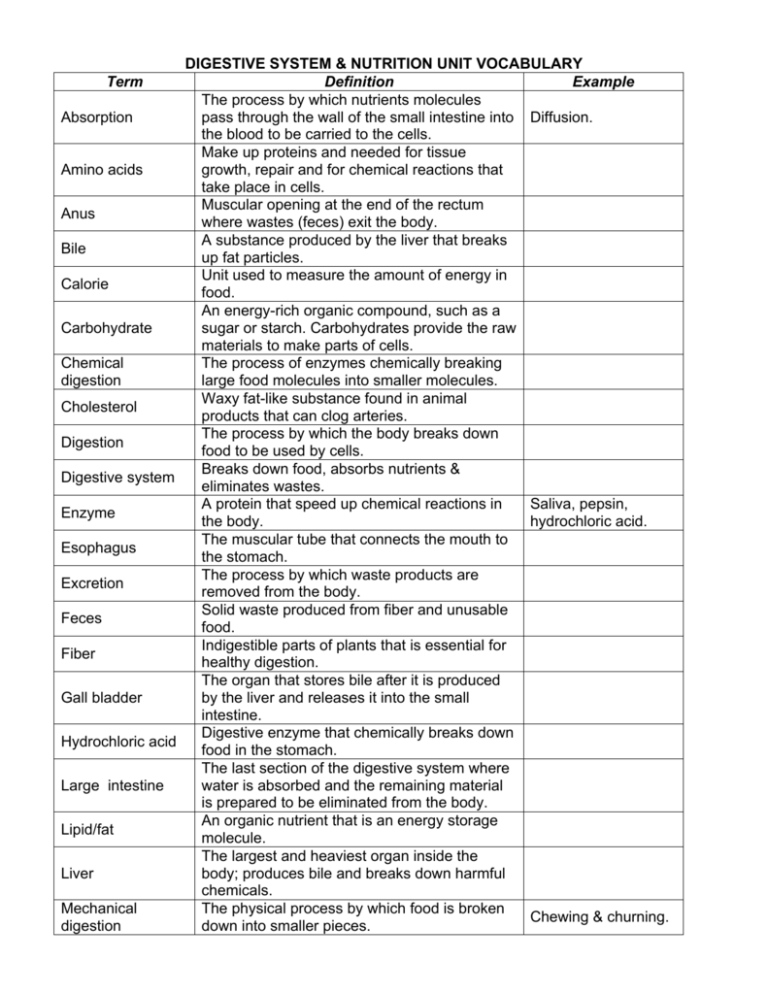
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM & NUTRITION UNIT VOCABULARY Term Definition Example The process by which nutrients molecules Absorption pass through the wall of the small intestine into Diffusion. the blood to be carried to the cells. Make up proteins and needed for tissue Amino acids growth, repair and for chemical reactions that take place in cells. Muscular opening at the end of the rectum Anus where wastes (feces) exit the body. A substance produced by the liver that breaks Bile up fat particles. Unit used to measure the amount of energy in Calorie food. An energy-rich organic compound, such as a Carbohydrate sugar or starch. Carbohydrates provide the raw materials to make parts of cells. Chemical The process of enzymes chemically breaking digestion large food molecules into smaller molecules. Waxy fat-like substance found in animal Cholesterol products that can clog arteries. The process by which the body breaks down Digestion food to be used by cells. Breaks down food, absorbs nutrients & Digestive system eliminates wastes. A protein that speed up chemical reactions in Saliva, pepsin, Enzyme the body. hydrochloric acid. The muscular tube that connects the mouth to Esophagus the stomach. The process by which waste products are Excretion removed from the body. Solid waste produced from fiber and unusable Feces food. Indigestible parts of plants that is essential for Fiber healthy digestion. The organ that stores bile after it is produced Gall bladder by the liver and releases it into the small intestine. Digestive enzyme that chemically breaks down Hydrochloric acid food in the stomach. The last section of the digestive system where Large intestine water is absorbed and the remaining material is prepared to be eliminated from the body. An organic nutrient that is an energy storage Lipid/fat molecule. The largest and heaviest organ inside the Liver body; produces bile and breaks down harmful chemicals. Mechanical The physical process by which food is broken Chewing & churning. digestion down into smaller pieces. Mouth Nutrition Nutrient Pancreas Pepsin Peristalsis Protein Rectum Saliva Small intestine Stomach Villi (plural) Villus (singular) Organ where chemical and mechanical digestion are started by teeth and saliva. The process by which organisms take n food to use as energy. A substance in food that provides energy or a raw material that the body needs in order to carry out its life processes. A triangular organ that produces enzymes that flow in to the small intestine. Digestive enzyme that chemically breaks down food in the stomach. Involuntary smooth muscle contractions that keep food moving along in one direction Swallowing. through the digestive system. A large organic molecule that is used for tissue growth and repair; plays an important role in the chemical reactions of cells. Short section at the end of the large intestine where waste is compressed into solid form. The enzyme released in the mouth that plays an important role in both mechanical and chemical digestion. The part of the digestive system where most chemical digestion & absorption of nutrients occurs. Muscular pouch located in the abdomen where mechanical & chemical digestion of proteins takes place. Tiny finger-shaped structures that line the inner surface of the small intestine to provide a large surface area for absorption of nutrients.