View Presentation Slides
advertisement

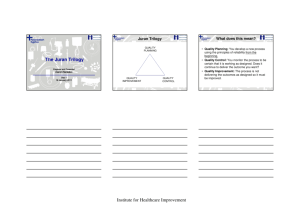
Improving Quality: Theories of Change Pierre Barker MD Senior Vice President IHI What are we trying to solve? The “How” The “What” Basic science Proof of concept Large scale efficacy Study Guidelines, Training & Resources, Reliable “real-life” implementation Scale-up to populations Adaptive Designs that are context sensitive Designs that can be scaledup with the resources at hand Quality Improvement: Bringing Together Two Types of Knowledge – (Deming) Evidence Based Subject Matter Knowledge Protocols/Guidelines, Physical resources, Clinical Training the “what” the “how” Implementation Knowledge Common view of the System Motivation/Leadership Accurate Reflective Data “Learning by Doing” Improvement: Bringing Together Two Types of Knowledge Evidence-based Subject Matter Knowledge Improvement Implementation Knowledge 5 Dr. Joseph M. Juran’s “Quality Trilogy” QUALITY PLANNING QUALITY IMPROVEMENT QUALITY CONTROL Juran Trilogy: All three elements are needed Sporadic spike Chronic waste (opportunity for improvement) PERFORMANCE SHIFT Source: Juran J, Godfrey AB, eds. Juran’s Quality Handbook: Fifth Edition. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1999. 6 Juran Trilogy: All three elements are needed Sporadic spike Chronic waste (opportunity for improvement) PERFORMANCE SHIFT Source: Juran J, Godfrey AB, eds. Juran’s Quality Handbook: Fifth Edition. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1999. 7 Juran Trilogy: All three elements are needed Sporadic spike Chronic waste (opportunity for improvement) PERFORMANCE SHIFT Source: Juran J, Godfrey AB, eds. Juran’s Quality Handbook: Fifth Edition. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1999. 8 Juran Trilogy: All three elements are needed Sporadic spike Chronic waste (opportunity for improvement) PERFORMANCE SHIFT Source: Juran J, Godfrey AB, eds. Juran’s Quality Handbook: Fifth Edition. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1999. 9 Components of quality: structure, quality control and quality improvement Quality Planning Quality Control (Assurance) Standards/ Guidelines/ protocols Professional oversight Policy, resources, coordination, accountability, mandates, etc. IMPROVED OUTCOMES Quality Improvement Rapid cycle improvement Motivation Accreditation Building knowledge Checklists Continuous data 10 QA and “QI” confusion: both can/should use Model for Improvement 11 Quality Planning Quality Control Quality Improvement Aims Measures Changes Aims IMPROVED OUTCOMES Measures Changes QA Approach PROBLEM Context & Local Knowledge SOLUTION (DEVELOP STANDARDS) IMPLEMENT STANDARDS SYSTEM BARRIERS Review (Succeed/Fail) QI Approach PROBLEM SYSTEM ANALYSIS GREAT IDEAS IMPLEMENT SUCCEED/ FAIL Context & Local Knowledge Rapid Test System Where do approaches fit on the QA/QI Spectrum COPE QA QI Accreditation Standards based approaches SBM-R IHI Breakthrough Series Preterm mortality ~60/1000 births Theory of Change: Drivers of Maternal and Newborn Survival Decrease Maternal and newborn mortality by 50% Drills, mentoring Knowledgeable health workers ready to use their skills Decision support, checklists Immediate access to essential commodities Key suppliers part of QI team Supportive Supervision Multi-level leaders promote change Motivation for change Progress celebrated, challenges supported Informed/activated patients & communities Data systems in real time Data for improvement vs data for reporting Data “owned” at every level A Learning System Cross-professional teams meet regularly, review data, test changes, report progress % mothers receiving ACS Essential QI methods SCREEN The Gap Data-driven process improvement TREAT AVAILABLE DRUGS & SUPPLIES RELIABLE MEASURES Systems approach Rapid cycle testing of local ideas % eligible women received at least one dose of corticosteroids 1 2 Sustainability June 2014 December 2014 February 2014 % eligible women received at least one dose of corticosteroids QI Zone of control/assurance Essential QI methods Local leadership Context-sensitive learning systems Phased Scale up methods Summary 1. What is the problem we are trying to solve? Context-sensitive implementation and scale up, using adaptive designs 2. How do you change system performance? Deming – the “what” and the “how” (common systems, psychology/motivation, reflective data, learning while doing) 3. A balanced view of quality Juran Trilogy (planning, assurance/control, improvement)