A timeline for food, feasts, festivals
advertisement

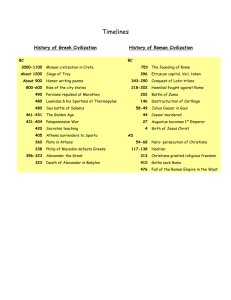
A timeline for food, feasts, festivals Greece 6500-­‐3000 3000-­‐2100 2100-­‐1600 1600-­‐1150 1600 1250-­‐1225 1150-­‐900 1050 1000 900-­‐750 900 800 750-­‐490 750-­‐700 750 750-­‐720 700 700-­‐650 650 600 582-­‐73 560-­‐514 507 499 5th Century 490-­‐323 490 480-­‐79 477 460-­‐445 454 431-­‐404 399 Neolithic Early Bronze Age (Early Halladic 2800-­‐1900) Middle Bronze Age (Middle Halladic 1900-­‐1580) Late Bronze Age (Late Helladic 1580-­‐1150) Mycenae/palace structures The Trojan War Early Dark Ages (Submycenaean 1125-­‐1050/Protogeometric 1050-­‐ 900) small chiefdoms established; migration of Greeks to Ionia (west coast of Turkey) Dorian Greeks settle on the islands Late Dark Age (Early Geometric 900-­‐850/Middle Geometric 850-­‐750) population increase; new settlements rapid population increase; Greeks develop an alphabet; earliest temples built Archaic Period (Late Geometric 750-­‐700) City-­‐states emerge overseas colonization in the West Iliad and Odyssey composed Hesiod; lyric poetry evolution of hoplite armor and tactics colonization of the Black Sea; Lycurgean reforms at Sparta beginning of science and philosophy (Presocratics) Pythian, Isthmian, Nemean games inaugurated Peisistratus and sons tyrants of Athens; Peisistratus explans religious festivals Cleisthenes institutes political reforms in Athens (democracy) Ionians revolt era of rationalism and scientists; Hippocrates; advances in medicine; increase in literacy Classical Period Marathon (490-­‐79 Persian Wars) Thermopylae, Artemesium, Salamis, Plataea, Mycale; Persians retreat Delian League established 'First' Peloponnesian War Athenians transfer treasury from Delos to Athens Peloponnesian War trial and execution of Socrates 4th Century 395-­‐87 359 357-­‐55 356 347 340 336 335 323 Rome 4000 1800-­‐1200 1000 800 900-­‐700 700s 700-­‐400 753-­‐510 650-­‐600 580-­‐480 500-­‐287 450 387 396 343-­‐41 341-­‐38 326-­‐304 298-­‐290 280 264-­‐41 237 227 218-­‐201 215-­‐205 198 200-­‐196 c.a 200 rise of rhetores at Athens; economic inequality; stasis throughout Greece Corinthian War accession of Philip II Social War birth of Alexander the Great Ddeath of Plato Athens and Macedon at war invasion of Asia by Philip II Aristotle founds the Lyceum death of Alexander emergence of agriculture Bronze Age first trances of settlements at the site of Rome Phoenicians found Carthage Iron Age introduction of writing to Italy Etruscan and Greek cities at their height in Italy Monarchy (7 kings) construction of the Forum Romanum archaic period Struggle of the Orders Twelve Tables Gauls loot Rome Romans take over Veii First Samnite War Latin War Second Samnite War Third Samnite War Rome issues its first coins First Punic War; Sicily becomes Rome's first colony at the end Roman takeover of Sardinia from Carthage Sardinia-­‐Corsica becomes a province Second Punic War (final defeat at Zama) First Macedonian War two Roman provinces established in Spain Second Macedonian War beginning of historical writing in Rome; Roman elites engage with Greek literature, culture, philosophy, rhetoric 195 186-­‐83 192-­‐89 171-­‐68 168 150s-­‐130s 149-­‐146 133 136-­‐32 121 113-­‐101 107, 104-­‐01 112-­‐05 104-­‐100 91-­‐87 90-­‐89 88 90-­‐85 87 83-­‐82 82-­‐81 73-­‐71 74-­‐63 70 63 60-­‐59 59 58-­‐51 49 48 48-­‐47 44 42 37 31 27 14 CE 37 41 54 64 66-­‐73 68 Cato's consulship Suppression of the cult of Bacchus Rome defeats Antiochus III in the Syrian War Third Macedonian War Polybius comes to Rome as a hostage War with the Lusitanians and Celtiberians Third Punic War, destruction of Carthage, province of Africa capture of Numantia; Tiberius Gracchus tribune; Pergamum bequeathed to Rome First Slave War province of Transalpine Gaul established confrontation with Cimbri and Teutones consulship of Marius; reform of the milirary war with Jugurtha in Numidia Second Slave War in Siciliy Social War citizenship extended throughout Italy Sulla's first march on Rome90-­‐85 war with Mithradates in Asia Minor and Greece Marius and Cinna march on Rome Sulla marches on Rome dictatorship of Sulla; proscriptions slave revolt of Spartacus Lucullus and Pompey resume war with Mithradates earliest amphitheater built in Pompeii consulship of Cicero 'First Triumvirate' (Caesar, Pompey, Crassus) Julius Caesar consul Caesar campaigns in Gaul Caesar crosses the Rubicon Pompey defeated by Caesar at Pharsalus, killed in Egypt Cleopatra declared ruler in Egypt Caesar killed Antony and Octavian defeat Brutus and Cassius at Philippi Second Triumvirate Octavian defeats Antony and Cleopatra at Actium first settlement; Octavian renamed Augustus Augustus dies, succeeded by Tiberiius Tiberius dies, succeeded by Caligula Caligula assassinated, succeeded by Claudius Claudius dies, succeeded by Nero Great Fire of Rome First Jewish Revolt, destruction of the Temple in Jerusalem (70) Nero commits suicide, succeded by Galba Some writers whose works you may encounter: Homer (epic poet, c.a. 750) Hesiod (didactic poet, c.a. 700) Herodotus (Greek historian, mid-­‐fifth century) Thucydides (Greek historian, 460-­‐395) Aeschylus (Greek tragic playwright, 525-­‐456) Sophocles (Greek tragic playwright, 496-­‐405) Euripides (Greek tragic playwright, 480-­‐406) Hippocrates (Greek physician, 460-­‐370) Aristophanes (Greek comic playwright, 446-­‐386) Menander (Greek comic playwright, 342-­‐291) Plautus (Roman comic playwright, 254-­‐184) Cato the Elder (Censor, 234-­‐149) Terence (n. African comic playwright, died 159) Livy (historian, 59-­‐17) Virgil (epic poet, 70-­‐19) Seneca (philosopher, 4 BCE-­‐65 CE) Tacitus (historian, 56CE -­‐117 CE) Plutarch (historian, biographer, essayist, 45 CE-­‐120 CE) Suetonius (historian, biographer, 70 CE-­‐130 CE) Galen (Greek physician, 130 CE-­‐200 CE) Athenaeus (Greek rhetorician, 2-­‐3rd CE)