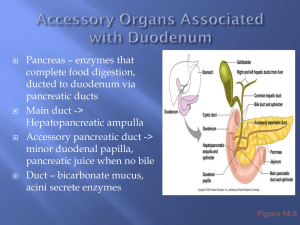
Functions: 1. Production of bile- (breaks down lipids) and stores bile
advertisement

Functions: 1. Production of bile- (breaks down lipids) and stores bile in the gall bladder. 2. Removes extra nutrients from the blood and stores them (glucose is stored as glycogen) 3. Stores iron and some vitamins 4. Breaks down “poisons” and detoxifies them to be excreted in urine. 5. Removes and breaks down bacteria and old RBC’s. Gross anatomy: •Largest visceral organ •Has 4 lobes; divided into lobules. •Lesser omentum anchors the liver to the stomach. •Gets its blood supply from the hepatic artery; blood drains away from the liver by the hepatic portal vein. Gross anatomy: •Bile is produced by the liver and collects in ducts which lead to the hepatic duct. •This fuses with the cystic duct from the gall bladder and together form the common bile duct which empties into the duodenum. •On the way, if it’s not needed, bile can back up into the cystic duct and on into the gall bladder to be stored. Gross anatomy: •Bile is 97% water and 3% salts. It’s made from cholesterol and is the main way we excrete extra cholesterol. Too much fat in the diet will sometimes cause cholesterol to come out of solution and deposit as crystals in the gall bladder, causing gall stones. •Function: to emulsify fat globules- that is to break them apart into smaller globules that can be suspended in the watery intestinal juices. This also greatly increases the surface area so the lipid (fat) molecules can be broken down by the pancreatic enzyme, lipase. •Lipase digests lipids Three types of Lipids: •Neutral fats (fats and oils) •Phospholipids •Steroids Their 4 main properties include: •Non-polar •Insoluble in water (can’t dissolve) •Soluble in alcohol •Made of C,H, and O (phospholipids also include P) NEUTRAL FATS: •Also called fats and oils; Make up adipose tissue Fatty acid Fatty acid Fatty acid FUNCTIONS: Neutral fats are used for: 1. Fuel: can be converted to sugars; It’s main function is to store energy (stores 2X the energy as carbohydrates) 2. Padding: for organs, ex.-kidneys 3. Insulation: which helps maintain body temp. 4. Transport: helps the body dissolve and transport fat-soluable vitamins that are insoluble in water. Oil droplets can be pushed along in the blood stream by blood pressure and vitamins “ride” the oil droplet. Neutral Lipids come in two forms: Saturated and Unsaturated Saturated Lipids: absorbed by LDL •TYPES OF BONDS: Contain fatty acids with all carbons attached by single bonds. (the max. number of hydrogens are bonded to each carbon) •PROPERTIES: solid at room temperature; ex-fats. •HEALTH RELATIONSHIP: Have been linked to buildup of fatty plaque in arteries and contribute to hardening of the arteries (athroschlerosis) and the development of type II diabetes. Unsaturated Fats: absorbed by HDL •TYPE OF BONDS: Contain fatty acids with one or more than one carbon to carbon double bond so they don’t have as many hydrogens. •One double bond = monounsaturated •More than one double bond= polyunsaturated • PROPERTIES: Are liquid at room temperature ex-oils (plant fat) •Release energy when the carbon to hydrogen bonds are broken •HEALTH RELATIONSHIP: Are less likely to cause plaque buildup, some research suggests it reduces arterial plaque Phospholipids: •Function: Make up cell membranes. Steroids: (not anabolic steroids) •Health effects: Too much in the blood stream can lead to arthrosclerosis •Example: cholesterol •Makes vitamin D, steroid hormones and bile salts •Found in and gives structure to the cell membrane Microscopically, they have no capillary network. Instead it is made up of microscopic lobules which contain the cells that produce bile and within them are sinusoids (tiny spaces) Sinusoids are lined with Kupffer cells which phagocytize and break down old RBC’s and bacteria. Bilirubin is a breakdown product of hemoglobin from RBC disassembly. It gives bile its yellowish color as seen in feces. If too many RBC’s are being destroyed, or the liver malfunctions (as with cirrhosis or hepatitis), bilirubin build up in the system causes us to turn yellow = jaundice. •The body’s major producer of digestive enzymes. •Is located below the stomach, nestled in the curve of the duodenum. •Is an exocrine gland (produces enzymes) and also a endocrine gland produces hormones. • Exocrine part has digestive functions. Units are acini (clusters of cells that make pancreatic juices) • Ducts leading from acini secrete sodium bicarbonate to help neutralize pH of liquid coming from the stomach. • All small ducts throughout the pancreas merge into 1 big ductthe pancreatic duct. • This combines with the common bile duct just before both empty into the duodenum close to the pyloric valve. The pancreas participates in digestion of all 3 major biochemical nutrients and nucleic acids (DNA/RNA). This takes place where the pancreatic duct dumps pancreatic juices into the duodenum (upper small intestine). Carbohydrates- Amylase Proteins- Protease Lipids- Lipase Nucleic Acids (RNA/DNA)- Nuclease The pancreatic enzymes are activated in the duodenum by the enzyme enteropeptidase. This is so the pancreas doesn’t digest itself! Hepatic duct Cystic duct duodenum