Viscera of the GI system and Abdomen
advertisement
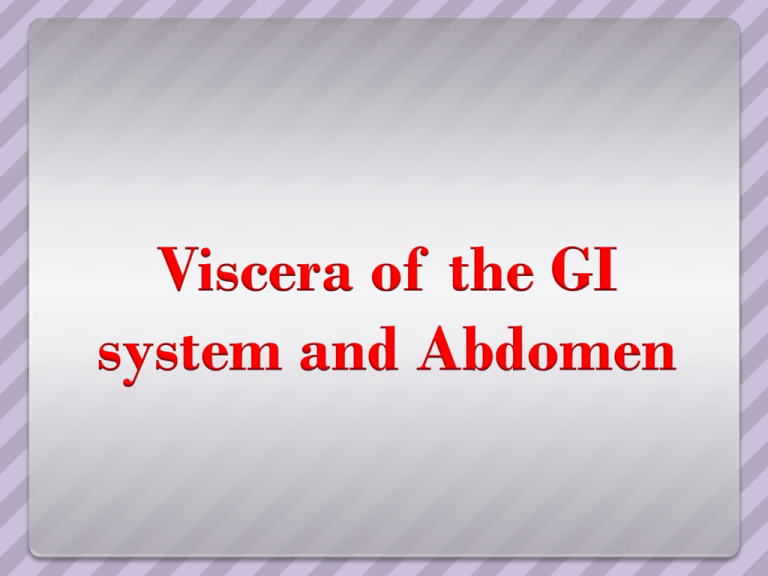
Spleen Spleen is an ovoid, purplish, delicate, vascular mass about the size and shape of one’s fist. It is covered with fibroelastic capsule on which it is entirely sorrounded by peritonium except at the hilum Located at the left upper quadrant or L. hypochondrium. Most delicate organ and vulnerable organ,even though it is protected by the lower thoracic ribs. Although it is a mobile organ, it does not descend below the costal region It rests on the left colic fexure Functions of spleen Prenatally it was a hematopoitic organ, In adults it functions as a site of Lymphocyte proliferation, Removing/destroying expended RBCs and platelets Recycling iron Blood Resorvoir storing RBCs and platelets It is sorrounded anteriorly by stomach Posteriorly, left part of diaphragm,ribs 9-11 Inferiorly, left colic flexure Medially, left kidney connected to the posterior wall of greater curvature of stomach by gastrospleenic ligament Left kidney by splenorenal ligament Spleenic artery, the largest branch of celiac trunk which inturn divides into 5 branches to supply the spleen. Severe blows on the left side, Fracturing the ribs, Blunt trauma to the abdomen causing an increase in intraabdominal pressure May cause the rupture of thin capsule and peritonium disrupting its soft parenchyma. Spleenomegaly may result because of spleenic disease or hypertension. Repair of a ruptured spleen is difficult. So sub-total or total splenectomy is performed to prevent profuse bleeding and in cases of severe untreatable spleenomegaly In adults, spleen is not a vital organ liver Largest gland After skin, largest single organ. It occupies the R. hypochondrium and it extends into epigastric region and also the L. hypochondrium. Functions of liver In the late fetus, it serves as a hematopoietic organ. In adults, Production and secretion of bile Filtration of blood removing bacteria, metabolizing various foreign substances and detoxifying Stores glycogen The liver L. & R. lobes by falciform ligament R.lobe quadrate lobe and a caudate lobe by the presence of gallbladder,fissure of ligamentum teres and inferior vena cava in the groove. These are functional lobes which have separate R. & L. branches of hepatic artery, portal vein and the hepaic ducts Porta hepatis, hilum of liver opens on the posteroinferior surface and lies between the caudate and quadrae lobes Liver has dual blood supply. The hepatic artery brings oxygenated blood to the liver and the portal vein brings venous blood rich in products of digestion. The liver is made up of liver lobules. The central vein of each lobule is a tributary of the sinusoids. In spaces between lobules are portal canals, which contains the brances of hepatic artery, portal vein and a tributary of bile duct. The hepatic artery and portal venal blood passes thru sinusoids, which are ultimately drained into central vein. Interlobar tributaries of the bile ducts, situated in the portal canals receive bile from canaliculi R.hepaic duct drains from R.lobe and L.hepatic duct from L., caudate and quadrate lobes R. and L. ducts emerge thru the porta hepatis and join into common hepatic duct which joins with the cystic duct from the gall bladder to form the bile duct The bile duct enters into the descending duodenum thru the hepatopancreat ic ampulla (ampulla of vater) which is guarded by sphinchter of oddi. Gall Bladder Gall bladder is a pear-shaped sac lying on the undersurface of liver. Gall bladder stores and concenterates bile When digestion does not happen, the sphincter of oddi remains closed and the bile accumulates in the gall bladder. The fatty foods entry into duodenum stimulates the contraction of the gall bladder and relaxation of sphincter of oddi which causes the emptying of bile. Cystic artery, a branch of R. hepatic artery supplies the gall bladder Pancreas Pancreas is an elongated gland that lies in the epigastrium and the left upper quadrant. Pancreas is both an exocrine and endocrine glandular function Exocrine gland secretes pepsin and other enzymes which hydrolyzes proteins Endocrine gland secretes insulin and glucagon which plays a key role in carbohydrate metabolism. The hepatic duct joins with the bile duct and opens into the ampulla of vater. The splenic and the superior and inferior pancreaticoduodenal arteries supply the pancreas.