Carboxylic acids
advertisement

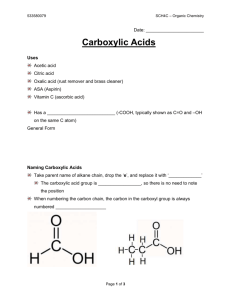
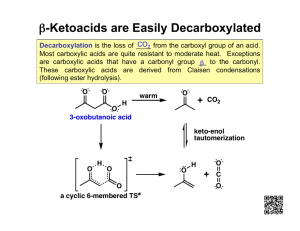
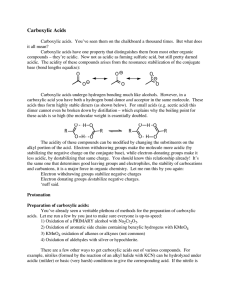
Chapter 16 Carboxylic Acids Various dilute solutions of ethanoic acid A carboxylic acid contains a carboxyl group, which is a carbonyl group (C═O) attached to a hydroxyl group (—OH); the carbon of the carboxyl group is numbered position 1 To write the IUPAC names of a carboxylic acid STEP 1 Replace the e in the alkane name with oic acid. CH4 Methane HCOOH Methanoic acid CH3-CH3 Ethane CH3—COOH Ethanoic acid STEP 2 Locate and name substituents, counting from the carboxyl carbon as carbon 1. Alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) occur naturally in fruit, milk, and sugarcane; they are used in skin care products 2-hydroxyethanoic acid 2-hydroxypropanoic acid 2,3-dihydroxybutanedioic acid 2-hydroxybutanoic acid Benzoic acid is the carboxylic acid that is attached to a benzene ring the –NH2 group is called amino; 4-aminobenzoic acid is an example of an amino acid Some common carboxylic acids used as analgesics Carboxylic acids are strongly polar have two polar groups: hydroxyl (−OH) and the carbonyl (C═O) Carboxylic acids form very strong hydrogen bonds with themselves in the absence of water The smaller carboxylic acids (1-4 carbons) are quite soluble in water Carboxylic acids are weak acids that ionize in water to produce carboxylate ions and hydronium ions A weak acid is an acid that undergoes the reaction shown above to the extent of about 5% but will react completely with stronger bases. For example: C H 3 — C O O H CH3COOH + NaOH CH3COO– Na+ + H2O Esters: HCl + NaOH CH3CO2H + CH3CH2OH NaCl + H2O CH3CO2CH2CH3 + H2O Aspirin is used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation is an ester of salicylic acid and acetic acid Oil of wintergreen is used to soothe sore muscles is an ester of salicylic acid and methanol Naming esters The name of an ester contains the names of the alkyl group from the alcohol the carbon chain from the acid with -ate ending Fats are esters of 1,2,3-trihydroxypropane (glycerol) and a long chain fatty acid O O O CH3(CH2)16 C O CH2O C CH O CH2O C Na+ (CH2)16CH3 CH3(CH2)16 C NaOH CH2OH (CH2)16CH3 HO CH CH2OH The fatty acids are not necessarily all the same; some differ in the number of carbons, some have double bonds in them (unsaturated fats); upon hydrolysis they yield the salt of a fatty acid known as a soap Soaps have a polar end and a non-polar tail and self assemble in water in a spherical fashion with the non-polar ends pointing inward and the polar ends on the outside. The non-polar ends are good for dissolving grease and oil. These small spherical balls are called micelles O -