Organic Chemistry Chapter 1
advertisement

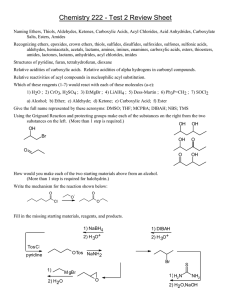
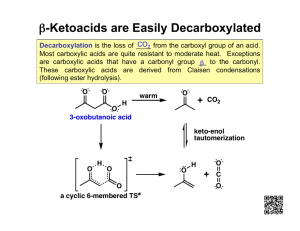
Organic Chemistry Chapter 10 Part II Carboxylic Acids Derivatives other than Ester Nanoplasmonic Research Group Activated Acyl Compounds - Focus on leaving group - • Acyl Halides Carboxylic acids with thionyl chloride or phosphorus pentachloride • Acid Anhydrides Carbonylation of methylacetate or dehydration of carboxylic acids Acyl halides can react with.. • Water to form a carboxylic acid • Alcohol to form an ester • Amine to form an amide Acid anhydrides can react with.. • Water to form a carboxylic acid • Alcohol to form an ester • Amine to form an amide “The point is acid anhydride is more reactive than ester, but less reactive than acyl halide toward nucleophile” The least reactive carboxylic acid derivative - Amide - • The reaction of a carboxylic acid with an amine • Planar geometry!!: rotation around the CN bond is restricted due to resonance • High boiling point The Claisen Condensation (I) • Carbon-carbon bond forming reaction that occurs between two esters or one ester and another carbonyl compound in the presence of a strong base • At least one of the reagents must be enolizable • The base used must not interfere with the reaction (nonnucleophilic!!!!) The Claisen Condensation (II) Summary (Reaction of Acid Derivatives) The Claisen Condensation (II)