Chemistry Exam Answer Key - R/S, Chirality, SN1/SN2
advertisement

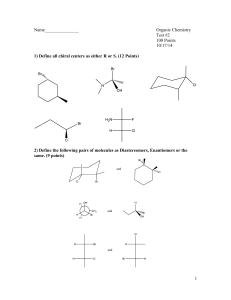
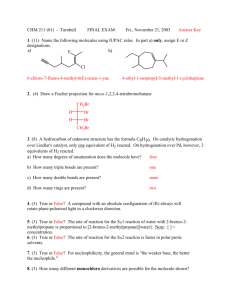
CHEMISTRY 211 - Turnbull ANSWER KEY Name . Hold . Answer all 18 questions (150 pts). *1. (14) Designate either R or S to each of the following molecules. You must show the priorities (#1 = highest) of all 4 attached groups (in each case) to receive full credit. O NH 2 a) b) 3 O 2 1 Cl (R) (R) 4 Br HN 1 Cl 3 4 *2. (7.5) Place an asterisk (*) at each of the chiral centers (if any) in each of the molecules shown. a) * b) Br c) HO * * O * N * H 2N *3. (3) True or False? The rate of reaction for an SN1 reaction is faster in polar, aprotic solvents. *4. (3) True or False? For leaving group ability, the general trend is: "a better leaving group is a weaker base." *5. (4) Which of the following compounds is never chiral? More than one answer is possible. a) 1,2-dichlorobutane b) 1,3-dichlorobutane c) 1,4-dichlorobutane d) 2,3-dichlorobutane *6. (15) True or False? (Circle your choice). a) Secondary carbocations are less stable than tertiary carbocations b) In an SN2 reaction of (R)-2-bromopentane, the product must have the (S) configuration c) OH2 is a better nucleophile than NH3 d) OH2 is a better leaving group than HO— e) In an SN2 reaction of (S)-2-bromopentane, doubling its concentration and not that of the nucleophile would double the rate of reaction f) The SN1 reaction generally proceeds fastest where there is the least steric hindrance to the attack of the nucleophile T or F T or F T or F T or F T or F T or F *7. (6) In the following reaction, how many different mono-chloro products could be obtained? Draw one of them. Cl Cl2 5 mono Cl light *8. (6) Name the following molecule using a systematic method. Cl F 6 5 4 3 2 4-chloro-2-fluoro-2-methylhexane 1 *9. (26) In each of the following reactions reactants or products are missing. Fill in the blanks with the appropriate molecules. If more than one step is involved, indicate this by using 1)......; 2)........ If more than one product could be formed, show only the major product(s). Where appropriate, draw the stereochemistry of the product(s). a) PBr3 1) Li b) c) 2) CuBr 3) CH3Br Br OH PBr3 OH Br NBS + light Br Br d) 1) NaNH2 2) Br *10. (9) For each pair indicated below, indicate by yes or no whether or not they represent resonance forms. a) HO HO • Yes • No b) • Yes • No c) • Yes • No *11. (14) Indicate whether each of the following enantiomers has the R or S configuration. 3 CH3 a) 2 b) OH 1 HOH2C H4 3 2CH(CH3)2 H3CH2C CH3 4 c) 3 2 CH2CH3 R d) H H4 H3C 1 CH2Br S Br 1 1 Cl 4H S H2 CH3 3 CH3 R *12. (11) Assign R or S configuration to one of the chiral centers in the following molecule. Additionally, answer the questions to the right of the molecule. HO H CH2OH R H R • Could any of the stereoisomers of this molecule be meso? Yes X No OH CH2OH • The mirror image of the molecule shown would be (choose one): enantiomer ; meso; diastereomer; identical • Is the molecule shown chiral? Yes X No *13. (2.5) Water has pKa = 15.74 and ammonia has pKa ~ 35. Which compound has the weaker conjugate base? Water *14. (6) Fill in the blanks: An alkyne where the triple bond is not at the end of the chain is called a(n) internal alkyne. Unlike alkenes or alkanes, a hydrogen attached to a carbon of the triple bond can be abstracted using a base, the conjugate acid of which is weaker approximate pKa of an alkyne proton is resultant anion is 25 (stronger / weaker) than the alkyne. The and it is more acidic than an alkene because the (more / less) stable than that from the alkene. more *15. (12) For each of the following pairs, circle all of the statements to their right which are correct. • constitutional isomers • enantiomers • identical • meso • stereoisomers • diastereomers a) NH2 OH H2N CH2OH and FCH2 CH3 F b) CH3 CH2NH2 H OH HO H HO H • constitutional isomers • enantiomers • identical • meso • stereoisomers • diastereomers CH2OH and H OH H OH H OH CH2NH2 CH2OH *16. (3) A molecule with three chiral centers has the possibility of existing as __8__ (a #) stereoisomers? *17. (3) Structures X and Y are stereoisomers. They are not superimposable and are not mirror images of one another. What best describes the relationship between these molecules? a) constitutional isomers b) enantiomers c) diastereomers d) conformers *18. (5) In the following reaction, indicate with an aterisk (*) any chiral centers in the product and state whether the product would be optically active or inactive. + H-Cl * Cl inactive since goes through planar carbocation