Problems 11-14
advertisement

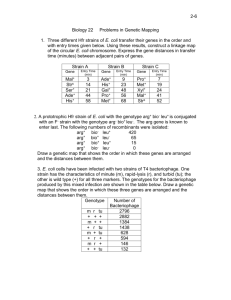
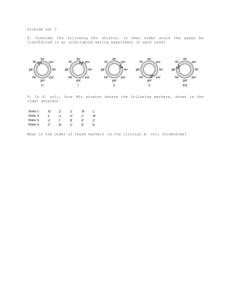
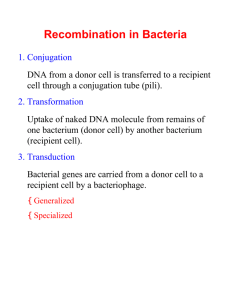
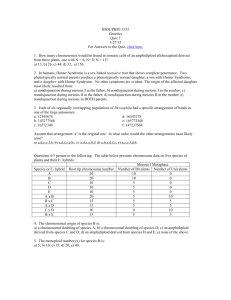
BS 50—Genetics and Genomics Week of Nov 14 Additional Practice Problems for Section Problem 1 (16pts) A bacterial geneticist hopes to map genes a through g by means of interrupted-mating experiments using three Hfr strains designated X, Y, and Z. In all crosses the Hfr parent is wild-type for each gene and is streptomycin sensitive, whereas the recipient F– strain is multiply mutant and streptomycin resistant. a) How does an Hfr strain differ from an F+ strain? b) Why does it matter that the Hfr is streptomycin sensitive while the F– strain is streptomycin resistant? c) From the data in the accompanying table, showing times of entry in minutes, deduce the genetic map of the markers a through g. Write the genes in correct order and between adjacent pairs of genes write the distance in minutes. Time of entry Hfr a X Y 21 Z 10 b c 12 26 d 7 4 e f 5 20 g 15 16 2. (20 points) You are studying the Lac operon in E. coli by making use of partial diploids in which the F' factor contains a copy of the entire Lac operon plus the LacI gene. You start with an F- strain containing a certain unknown genotype for the Lac operon and the LacI gene. You have three different F' derivatives, called F'#1, F'#2 and F'#3, each carrying a different set of lac mutations. By mating between the F' strains and the F-, you create three partial diploids. Their phenotypes for LacZ (beta-galactosidase), LacY (permease) and LacA (trans-acetylase) are: F genotype beta-galactosidase F- / F'#1 inducible F- / F'#2 constitutive F- / F'#3 null You find that the F'#3 is lacI - permease constitutive constitutive constitutive trans-acetylase inducible null constitutive lacOC lacZ -. What is the Lac genotype (for LacI, LacO, LacZ, LacY and LacA) on the Fchromosome? Justify your answers. 3. You are performing a transformation experiment in E. coli. Transforming + + + + donor DNA is from bacteria of the genotype h i j k while recipient - - - - + bacteria are of the genotype h i j k . You select for k bacteria and then + check the k colonies for their genotypes at the h, i, and j genes. You find that + + + + 0% of the k colonies are h , 16% are i , and 68% are j . a. Describe the map of these genes on the bacterial chromosome in as much detail as you can. + + + + - - - - – b. Suppose you perform an Hfr h i j k X F h i j k interrupted mating experiment, taking ten minute interruption timepoints. Which genes would you expect to show transfer during the same time point? Explain your reasoning. 4) You are characterizing a series of Hfr derivatives of a new strain of E. coli, called E. coli veritas. (6 pts) A) Briefly describe how different Hfr derivatives are generated from an F+ strain of E. coli veritas. The F-element integrates by a single crossover event at a region of sequence homology into the bacterial chromosome. Since there are several regions of homology, different Hfr derivatives at diverse locations will be produced. (12 pts) B) In interrupted mating experiments, you find the following results from mating these E. coli veritas Hfr derivatives crossed separately to F– individuals. Genetic marker ade his bio gal phe cys iso tyr mal Earliest interruption time exhibiting transfer of marker (minutes) HfrZ HfrY HfrM 42 48 62 79 94 3 22 31 38 42 36 23 6 92 80 63 56 47 94 88 74 58 43 31 15 8 1 Depending upon whether you think the genetic map of E. coli veritas is circular or linear, draw the map of the genetic markers on the circle or straight line below. Include the location of insertion and direction of transfer for each Hfr derivative. 1. (continued) (6 pts) C) After treating the HfrY strain with X-rays, you find that the derivative strain, which you call HfrY-x, shows the following gene transfer when crossed to the standard E. coli veritas F– strain: Earliest interruption time exhibiting transfer of marker (minutes) Genetic marker ade his bio gal phe cys iso tyr mal HfrY-x 42 36 23 6 92 46 63 70 79 How does the HfrY-x chromosome differ from the chromosome of HfrY? (6 pts) D) How would X-rays have caused this change in the E. coli veritas chromosome?