Basics
advertisement

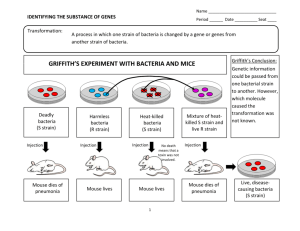
Grey-all bacteria Red- E. coli Common Complex media TY (per liter): 6 gr casein (hydrolyzed milk protein) 3 gr yeast extract .4 gr CaCl2 LB (per liter): 10 gr casein 5 gr yeast extract 10 gr NaCl These are cheap, easy to make and support high rates of growth. However, what is in the media, exactly, is unknown. For example, how much methionine is in 10 ml of LB? M9 minimal medium For one liter Na2HPO4 KH2PO4 MgSO4 NaCl NH4Cl CaCl2 KCl Carbon source 12.8g 3g 0.5 0.5g 1g 0.015 gr .185 4 gr Amino acids, vitamins, bases, etc. can be added as needed. Lab WT vs Real WT Sinorhizobium meliloti-”WT” Rm1021 after 30 years found to be a mutant in expR. Sinorhizobium meliloti strain Rm8530. Sam as Rm1021, but expR is fixed. It no longer forms single colonies because the goop together due to lot of exopolysaccharide being made. Phenotype/Genotype •Phenotype: observable properties (Trp+, Trp–) •Genotype: genetic composition (trp-, met+) •Allele: different forms of a gene. Different alleles are given numbers: (trpA1, trpA3) •Different genes that give the same general phenotype when mutated are given the same name with different alphabetical designations: (trpA, trpB). S. meliloti trpA region Different mutations combine letters and numbers. For e.g. a strain may be (trpA1, trpA2, trpB3, accD). Meaning it has 2 mutations in trpA and one in trpB and accD. Deciphering a genotype E. coli strain JM107 (lac-proAB) thi gyrA96 endA1 hsdR17(rK– mK+) relA1 supE44 –/F´ traD36 proAB+ lacIqZM15 (lac-proAB): deleted for the genes from lac to proAB thi: can’t make thiamine gyrA96: a specific mutation in the gyrase A gene endA1: a specific mutation in the endA (endonuclease) gene relA1: a specific mutation in the relA gene supE44: a specific mutation that suppresses nonsense mutations – : no bacteriophage lambda F´ : has a plasmid called the F plasmid which carries other E. coli genes (that’s what the prime after the the F means). This F’ carries traD26, the proAB genes (fixes the proAB) and a special lacI gene called lacIQ and a lacZ deletion: ZM15 Deciphering genotypes continued E. coli strain HB101 (gpt-proA)62 leuB6 supE44 ara-14 galK2 lacY1 (mcrC-mrr) rpsL20(Strr) xyl-5 mtl-1 recA13 What carbon source(s) can strain HB101not grow on? What amino acid(s) would you need to add to minimal medium to allow growth? Why are leuB62 and ara-14 written as they are? What does Strr mean? Is this the strain’s genotype or phenotype? The NEB catalog, or the GeneticStockCenter at Yale (or similar) is very helpful in deciphering genotypes NEB strains NEB E. coli mutations Penicillin enrichment to help find auxotrophs Killing by penicillin From Fitzgerald and Williams 1975 Results of penicillin enrichment From Fitzgerald and Williams 1975