Plant Hormones: Synthesis and Function Summary
advertisement

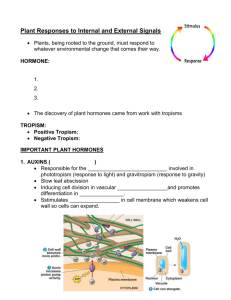
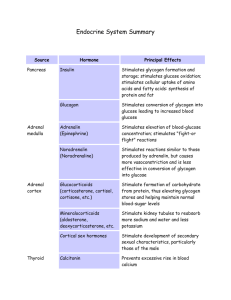
Plant Hormone Where They are Synthesized and Found Plant Hormones Function • • Stimulates cell elongation Stimulates cell division along with CK Along with CK, suppresses lateral bud growth when supplied from apical buds (Apical Dominance) Induces new root formation Involved in phototropism and gravitropism • • • • • • Stimulates cell division along with auxin Stimulates cell broadening Stimulates stomatal opening Promotes chlorophyll synthesis. Promotes unloading of sugars from phloem Delays leaf senescence (aging) • • • Auxin (IAA) This hormone is synthesized in shoot and root meristematic tissue It is synthesized in much greater amounts in the shoots than roots Cytokinin This hormone is synthesized in shoot and root meristematic tissue It is synthesized in much greater amounts in the roots than shoots (CK) Ethylene Ethylene is present in the tissues of ripening fruits, nodes of stems, aging leaves and flowers Abscisic Acid This hormone is produced in stems and leaves. Absicisic acid is found mostly in water-­‐stressed leaves and stems, as well as unripe fruit • • • Stimulates the closing of stomata Inhibits shoot growth Inhibits seed germination • • • • Stimulates stem elongation Inhibits root growth Along with auxin, stimulates fruit growth Ends seed dormancy after imbibition This hormone is produced in the meristems of apical buds and roots, young leaves, and seed embryos Induces seed germination Stimulates flower and leaf senescence (aging) Leaf and fruit abscission (dropping) Stimulates fruit ripening Involved in stress responses o Production of adventitious roots during flooding o Disease and wound resistance (ABA) Gibberellin • • • • •