Endocrine System Review Packet: Glands, Hormones, & Cases
advertisement
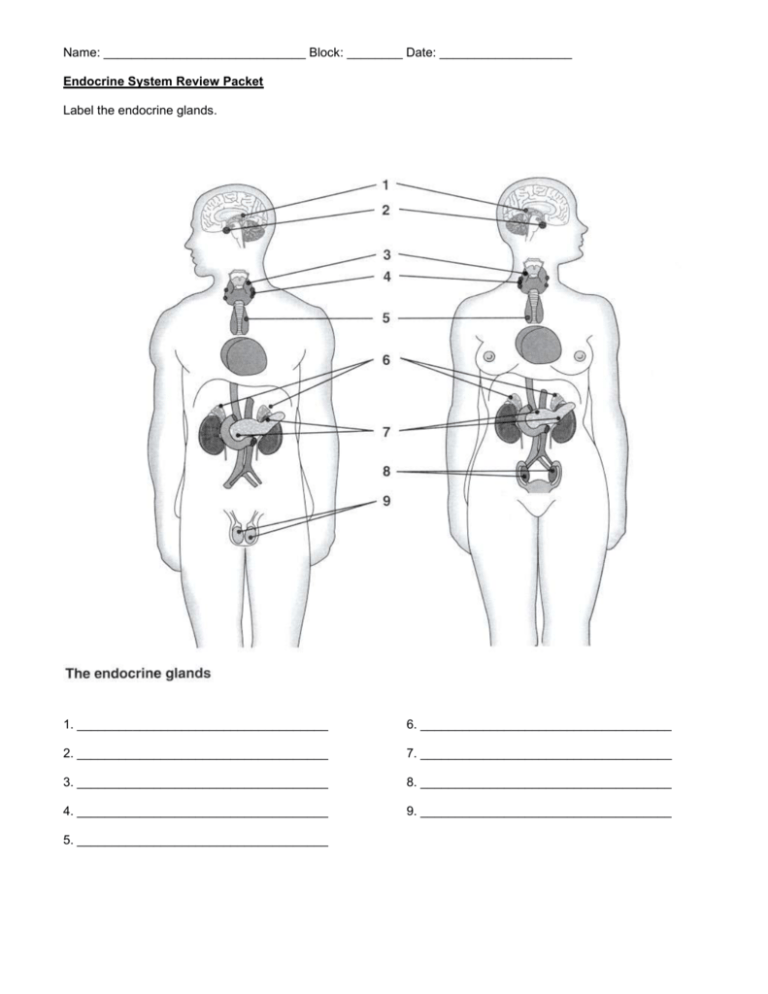
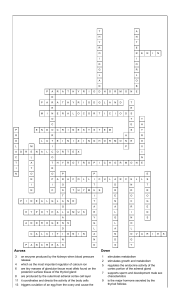
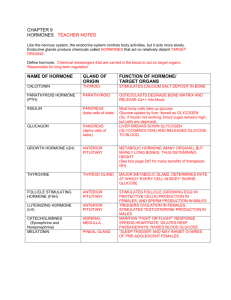
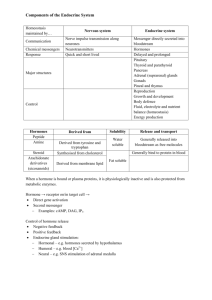
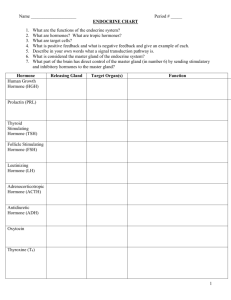
Name: _____________________________ Block: ________ Date: ___________________ Endocrine System Review Packet Label the endocrine glands. 1. ____________________________________ 6. ____________________________________ 2. ____________________________________ 7. ____________________________________ 3. ____________________________________ 8. ____________________________________ 4. ____________________________________ 9. ____________________________________ 5. ____________________________________ Endocrine Organs and Their Hormones Directions: Indicate the major organ or organ part producing and/or releasing each of the hormones by writing it next to the hormone listed. Endocrine Organs/Organs: Adrenal cortex Thyroid Posterior pituitary Thymus Ovaries Pancreas Stomach Parathyroids Pineal Heart Testes Adrenal medulla Anterior pituitary Small intestine _______________________ 1. ACTH _______________________ 13. TSH _______________________ 2. ADH _______________________ 14. Progesterone _______________________ 3. Oxytocin _______________________ 15. Insulin _______________________ 4. Cortisone _______________________ 16. Secretin _______________________ 5. Estrogen _______________________ 17. Thymosin _______________________ 6. FSH _______________________ 18. Prolactin _______________________ 7. Glucagon _______________________ 19. Testosterone _______________________ 8. Epinephrine _______________________ 20. Melatonin _______________________ 9. Calcitonin _______________________ 21. Thyroxine _______________________ 10. PTH _______________________ 22. Gastrin _______________________ 11. Growth Hormone _______________________ 23. Aldosterone _______________________ 12. Atrial Natriuretic Peptide _______________________ 24. Leutinizing Hormone Hormones and Their Effects Directions: On the line provided, write the name of the hormone that matches the function. ______________________ 1. Basal metabolic hormone ______________________ 2. Necessary for the development of T-lymphocytes ______________________ 3. Maintains blood calcium levels; released when blood calcium levels drop ______________________ 4. Protects the body during long-term stressful situations ______________________ 5. Stimulates the production and maturation of gametes ______________________ 6. Enables glucose to be taken up by body cells ______________________ 7. Initiates the maturation of the male reproductive organs ______________________ 8. Released by the posterior pituitary to regulate water balance ______________________ 9. Responsible for the development of a female’s secondary sex characteristics ______________________ 10. Triggers ovulation in females and the release of other female sex hormones ______________________ 11. Vital in maintaining blood sodium levels ______________________ 12. Stimulates production of milk in breast; secretion increased by nursing ______________________ 13. Helps regulate the sleep-wake cycle ______________________ 14. Stimulates mitosis of bone and muscle cells ______________________ 15. Causes uterine contractions; secretion regulated through positive feedback ______________________ 16. Stimulates calcium being deposited into bone; important for skeletal growth in childhood ______________________ 17. The antagonist of insulin; raises blood glucose levels ______________________ 18. Main hormone that aids in the “fight or flight” response Label the diagram below with the following terms: capillary, hormone (x3), non-target cell, receptor (x2), secreting cell, target cell Case Studies Kelly is exhibiting neuromuscular irritability, tetany (tingling noted around the mouth and in her feet), dry skin and fingernails, more prone to cavities (you suspect weak tooth enamel). Her blood work is normal, except hypocalcemia is noted. She is treated with supplemental calcium and vitamin D. Hormone/Gland Problem: Autumn, age 30, has had noticeable weight gain resulting in purple striae (stretch marks) along the abdomen. She has increased deposits of adipose tissue in the face (moon face), the shoulders (hump), neck and trunk. She states that when she cuts herself, it takes “forever” to heal. She complains of an irregular heartbeat as well. A physical exam indicates hypertension. Her blood work reveals hypernatremia, hypokalemia, and hyperglycemia. A urine test reveals glucosuria. Hormone/Gland Problem: Timothy, 6 months old, is brought to the doctor. The parents, who were thrilled with their “good baby” are now concerned something is wrong. The child’s tongue protrudes from his mouth and jaundice is present. The child is generally inactive and sleeps excessively. The child’s skin is cold to the touch. Hormone/Gland Problem: Jerome, age 17, is complaining of frequent urination, fatigue, dry mouth, dizziness, polydipsia (extreme thirst), and a craving for cold water. He is hospitalized to record his fluid intake and output to obtain lab values. In a 24-hour period, he voided 7 liters of dilute urine and drank 8.5 liters of fluid. His blood pressure was an average of 72/36. Hormone/Gland Problem: