Plant Responses to Internal and External Signals Plants, being
advertisement

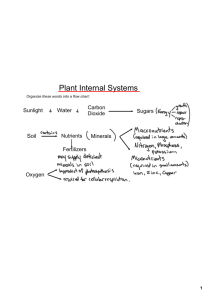
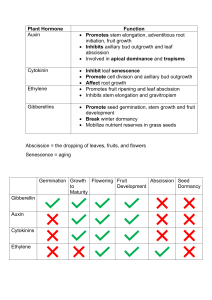
Plant Responses to Internal and External Signals Plants, being rooted to the ground, must respond to whatever environmental change that comes their way. HORMONE: 1. 2. 3. The discovery of plant hormones came from work with tropisms TROPISM: Positive Tropism: Negative Tropism: IMPORTANT PLANT HORMONES 1. AUXINS ( ) Responsible for the ___________________________ involved in phototropism (response to light) and gravitropism (response to gravity) Slow leaf abscission Inducing cell division in vascular _________________and promotes differentiation in _______________. Sstimulates _________________ in cell membrane which weakens cell wall so cells can expand. PHOTOTROPISM: o positive = _______________________; negative = ____________ ________________ o Differential rate of elongation Shoot bends towards light due to asymmetrical distribution of auxins Light stimulates movement of auxin to dark side so cells on dark side elongate faster than cells on light side. GRAVITROPISM: o Roots grow down and shoots grow up THIGOMOTROPISM: o Vines curl around supports (example of ____________________) o Do Mimosa plants show negative thigomotropism? 2. CYTOKININS ( ) Produced in actively growing tissues such as _______, __________ and __________ Works together with auxin Plays an important role in cell division, growth and differentiation by ___________________________________________________ Stimulates germination Delays senescence (_______________________________________) 3. GIBBERELLINS ( ) Promotes seed/bud germination, leaf growth Stimulates ____________________ _____________________________ Stimulates stem elongation Untreated Treated Many “dwarf” varieties don’t have working gibberellins Stimulates _________________________ Delays _____________________ (aging of leaves and fruits) Gibberellins are used commercially in the spraying of Thompson seedless grapes Aleurone Endosperm -amylase Sugar GA Water GA cotyledon Germination of a Seed 4. ABSCISIC ACID (ABA) ( ) Often antagonistic to other hormones Slows growth and promotes ________________________ Seed dormancy has great survival value because __________________ _________________________________________________________ LEAF ABSCISSION: _______________________________________ o Prevents deciduous trees from desiccation (drying out) during winter when roots cannot absorb water from frozen ground o Shortening days and cooler temperatures cause ABA levels to spike, which signals the closing of _______________ in leaves 5. ETHYLENE GAS ( ) Controls senescence (aging) by playing a role in __________________ (programmed cell death) in leaves and flowers _________________________________________ Example of _________________________ – ethylene triggers ripening; ripening triggers more ethylene production o Why should put fruit in a paper bag to ripen “One bad apple spoils the whole bunch”