Unit C Practice Problems Chapter 8 1. Draw the lewis structures for
advertisement

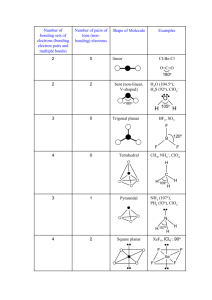
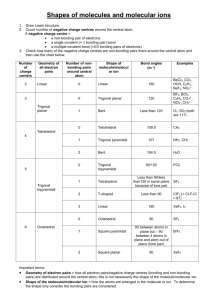
Unit C Practice Problems Chapter 8 1. Draw the lewis structures for the following molecules: a. BeF2 b. SO3 c. CNS1d. NO 2. The correct Lewis symbol for ground state carbon is a) b) c) d) e) 3. Which of the atoms below is least likely to violate the octet rule? a) Be b) P c) S d) B e) F 4. What is the bond order of the C–O bond in acetone? O CH3 C a) 4 b) 1.5 CH3 c) 0.5 d) 1 e) 2 5. Which of the following is the correct Lewis structure for SOCl2? (Consider formal charge) a) d) b) e) c) 6. Which of the following bonds is most polar? a) N – Cl d) Br – Br b) C – N e) S – O c) S – S 7. The molecule BrF3 has how many lone pairs of electrons on the central atom? a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 3 8. Classify the following bonds as either metallic, ionic, covalent, or covalent network: a. Francium Fluoride b. Diamond c. Gold d. Water Chapter 9 1. Use VSEPR theory to predict the shapes of the following molecules: a. BrF5 b. HCN c. BF3 d. SO2 e. SCl2 2. What type of hybridized orbital is used by the central atom of each of the molecules in problem 1? 3. CCl4 is a perfect tetrahedron, but AsCl4 is a distorted tetrahedron. Explain. 4. BeCl2 and TeCl2 are both covalent molecules, yet BeCl2 is linear while TeCl2 is nonlinear (bent). Explain. 5. What types of hybridized orbitals can be formed by elements of the third period that cannot be formed by elements in the second period? 6. Which molecule should have the larger dipole moment, HBr or HI? 7. Which of the following molecules has a dipole moment? a. CCl4 b. H2S c. CO2 d. BCl3 e. Cl2 8. Choose the best answer. For the water molecule: a. The bonds are polar, and the molecule is nonpolar. b. The bonds are nonpolar, and the molecule is polar. c. The bonds are polar, and the molecule is polar. d. The bonds are nonpolar and the molecule is nonpolar. 9. NF3 has a trigonal pyramidal geometry. How many electron pairs are in the valence shell of the central atom? 10. Predict whether the following molecules are polar or nonpolar: SO2, NF3, CS2. 11. Determine the total number of sigma and pi bonds in the molecules CCl2O and CH3CHCHCN. 12. Predict which will exhibit delocalized pi bonding (resonance structures): (SO3)2-, (NH4)+, NO2, (NCS)-, (OCN)-, (I3)- 13. Identify the hybridization of the central atom in the following compounds and ions: CF4, SF4, (PO2F2)-, (SF3)+, (I3)-, (SO4)2-, (BH4)-, (SF5)-, OSF4, ClF3, BCl3, (XeO6)4- 14. Describe the bonding in XeF4 using hybrid orbitals. Remember to consider first the Lewis structure, then the structural pair geometry and molecular shape. 15. Describe the hybridization of each carbon and oxygen atom in acetic acid, CH3CO2H Chapter 25 Name the following: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. CH3CH=CHCH2CH3 7. CH3(CH2)4CH(CH3)2 8. (CH3)2CHC≡CCH3 9. The following structures all have the same molecular formula: C6H14. Which of these structures represent the same molecule? Draw the following molecules: 1. 2-methylbutane 2. 2,3,3,3-tetramethylpentane 3. 5-methyl-1-hexyne 4. 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene 5. 3-ethyl-2,3-dimethyloctane Unit C Practice Problems Answers Chapter 8 1. a: b: c: d: 2. a 3. e 4. e 5. b 6. a 7. c 8. a: ionic; b: covalent network; c: metallic; d: covalent Chapter 9 1. a. Square pyramidal, b. Linear, c. Trigonal Planar, d. Bent, e. Bent 2. a. sp3d2, b. sp, c. sp2, d. sp2, e. sp3 3. CCl4 has four electron pairs about the central C atom, while AsCl4 has 5 pairs about the As atom with only 4 Cl atoms attached. The extra pair of unshared electrons in AsCl4 prevents it from forming a tetrahedron. 4. There are two electron pairs in the valence shell of Be in BeCl2, but there are four pairs in the valence shell of Te in TeCl2. These four pairs are at the corners of a tetrahedron. When two Cl atoms bond to a Te atom via two of the pairs, the Cl-Te-Cl bond angle is 109.5 degrees. 5. sp3d and sp3d2 6. HBr because of the bond polarity. Br is more electronegative than I is. 7. b only 8. c 9. Four 10. Polar, Polar, Nonpolar 11. CCl2O - 3 sigma, 1 pi; CH3CHCHCN - 9 sigma, 3 pi 12. No, No, Yes, Yes, Yes, No 13. sp3 (tetrahedral) sp3d (trigonal bipyramidal) sp3 (tetrahedral) sp3 (tetrahedral) sp3d (trigonal bipyramidal) sp3 (tetrahedral) sp3 (tetrahedral) sp3d2 (octahedral) sp3d (trigonal bipyramidal) sp3d (trigonal bipyramidal) sp2 (trigonal planar) sp3d2 (octahedral) 14. Xe atom uses sp3d2 hybridization (octahedral, square planar) 15. single-bonded C is sp3 (tetrahedral), double-bonded C is sp2 (trigonal planar) single-bonded O is sp3 (tetrahedral, bent), double-bonded O is sp2 (trigonal planar) Chapter 25 Name the following molecules: 1. 3,5-dimethyl 2-hexene 2. 2,2,3-triimethylpentane 3. 4-methyloctane 4. 6-ethyl-2,5,6-trimethyloctane 5. 5-ethyl-2-methyl-3-heptyne 6. 2-pentene 7. 2-methylheptane 8. 4-methyl-2-pentyne 9. A&B Draw the following molecules: 1. 2-methylbutane 2. 2,3,3,3-tetramethylpentane 3. 5-methyl-1-hexyne 4. 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene 5. 3-ethyl-2,3-dimethyloctane