Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry Guidelines
advertisement
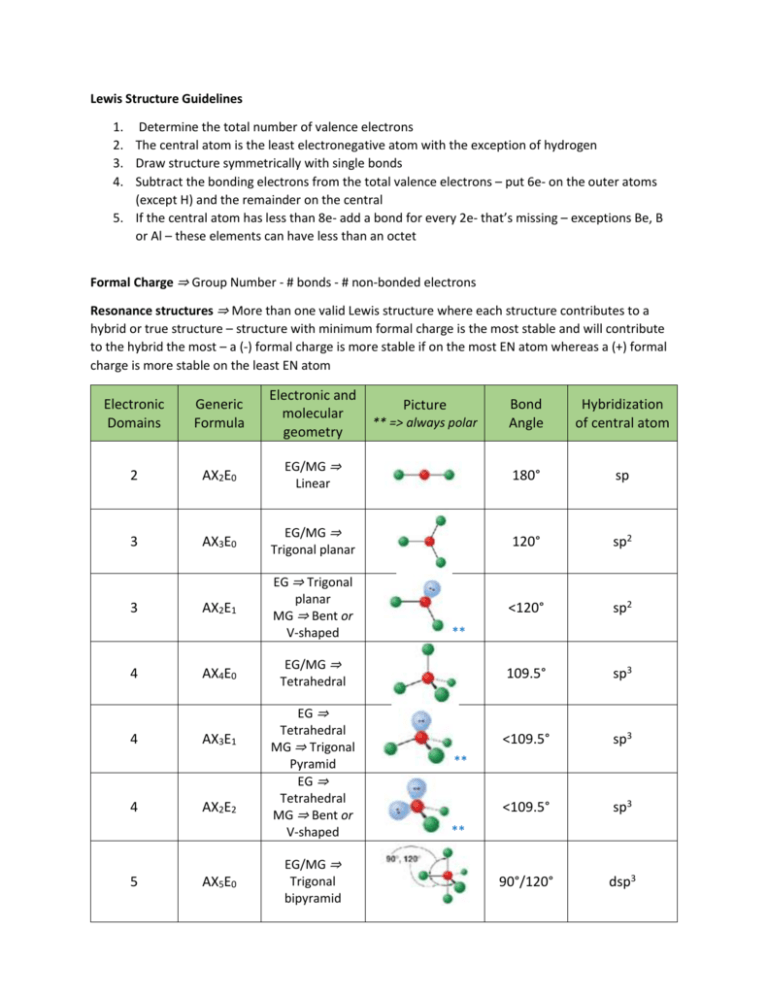
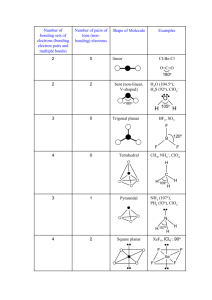
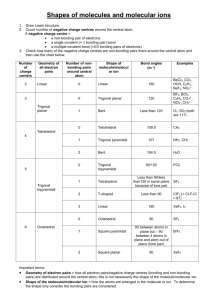
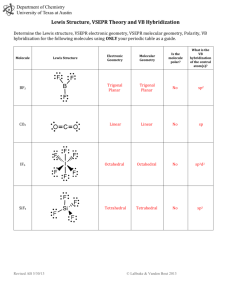
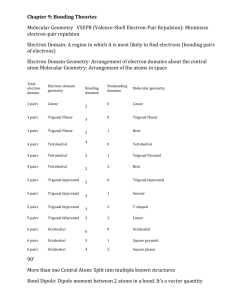
Lewis Structure Guidelines 1. Determine the total number of valence electrons 2. The central atom is the least electronegative atom with the exception of hydrogen 3. Draw structure symmetrically with single bonds 4. Subtract the bonding electrons from the total valence electrons – put 6e- on the outer atoms (except H) and the remainder on the central 5. If the central atom has less than 8e- add a bond for every 2e- that’s missing – exceptions Be, B or Al – these elements can have less than an octet Formal Charge ⇒ Group Number - # bonds - # non-bonded electrons Resonance structures ⇒ More than one valid Lewis structure where each structure contributes to a hybrid or true structure – structure with minimum formal charge is the most stable and will contribute to the hybrid the most – a (-) formal charge is more stable if on the most EN atom whereas a (+) formal charge is more stable on the least EN atom Electronic Domains Generic Formula Electronic and molecular geometry 2 AX2E0 3 3 4 4 4 5 Bond Angle Hybridization of central atom EG/MG ⇒ Linear 180° sp AX3E0 EG/MG ⇒ Trigonal planar 120° sp2 AX2E1 EG ⇒ Trigonal planar MG ⇒ Bent or V-shaped <120° sp2 109.5° sp3 <109.5° sp3 <109.5° sp3 90°/120° dsp3 AX4E0 AX3E1 AX2E2 AX5E0 Picture ** => always polar ** EG/MG ⇒ Tetrahedral EG ⇒ Tetrahedral MG ⇒ Trigonal Pyramid EG ⇒ Tetrahedral MG ⇒ Bent or V-shaped EG/MG ⇒ Trigonal bipyramid ** ** Electronic Domians Generic Formula Electronic and molecular geometry 5 AX4E1 EG ⇒ Trigonal bipyramid MG => See-Saw 5 5 AX3E2 AX2E3 Picture ** => always polar Bond Angle Hybridization of central atom <90°/<120° dsp3 <90° dsp3 180° dsp3 90° d2sp3 <90° d2sp3 90° d2sp3 <90° d2sp3 180° d2sp3 ** EG ⇒ Trigonal bipyramid MG ⇒ T-shaped ** EG ⇒ Trigonal bipyramid MG ⇒ linear 6 6 AX6E0 AX5E1 6 AX4E2 6 AX3E3 6 AX2E4 EG/MG ⇒ Octahedral EG ⇒ Octahedral MG ⇒ Square pyramid EG ⇒ Octahedral MG ⇒ Square planar EG ⇒ Octahedral MG ⇒ T-shaped EG ⇒ Octahedral MG ⇒ linear ** ** Molecular Polarity ⇒ Molecules are polar or have a non-zero dipole moment if there’s an uneven distribution of bonding electrons. Non-polar molecules have no dipole moment due to an even or symmetrical distribution of bonding electrons 1. Are all of the central atoms the same (if more than one) and all of the outer atoms the same? a. no ⇒ it’s polar (has a non-zero dipole moment) b. yes ⇒ keep going 2. Does the central atom have lone pairs? a. no ⇒ non-polar b. yes ⇒ keep going 3. Is the molecular geometry linear or square planar? a. no ⇒ polar b. yes ⇒ non-polar