File
advertisement
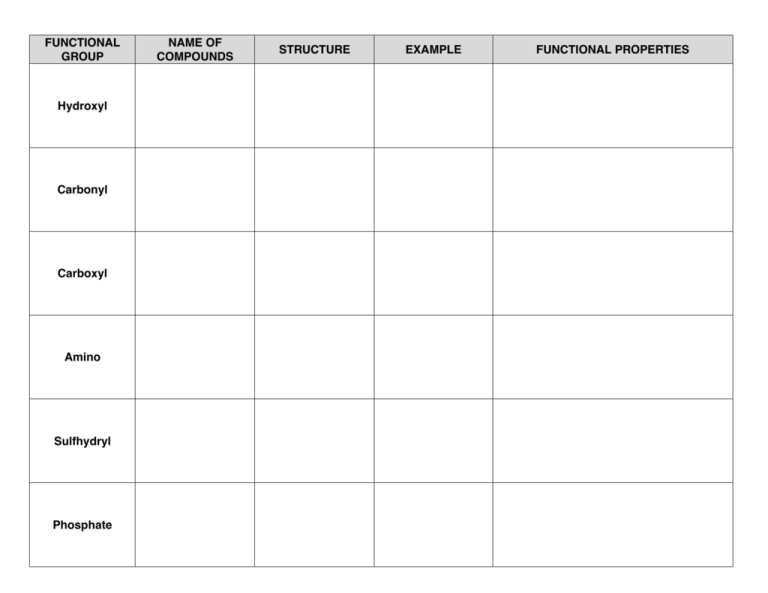
FUNCTIONAL GROUP Hydroxyl Carbonyl Carboxyl Amino Sulfhydryl Phosphate NAME OF COMPOUNDS STRUCTURE EXAMPLE FUNCTIONAL PROPERTIES FUNCTIONAL GROUP NAME OF COMPOUNDS Hydroxyl Alcohols (their specific names ends in –ol ) Carbonyl Ketones Aldehyde STRUCTURE EXAMPLE FUNCTIONAL PROPERTIES ➣is polar as a result of the electronegative oxygen atom drawing electrons toward it ➣attracts water molecules, helping dissolve organic compounds such as sugars ➣A ketone and an aldehyde may be structural isomers with different properties, as in the case for acetone and propanal. ➣Has acidic properties because it is a source of hydrogen ions. ➣The covalent bond between oxygen and hydrogen is so polar that hydrogen ion (H+) tend to dissociate reversibly; for example, Carboxyl Carboxylic acids, or organic acids ➣ Amino Amine Sulfhydryl Thiols Phosphate Organic Phosphates Because it also has a carboxyl group, glycine is both an amine and a carboxylic acid; compounds with both groups are called amino acids. ➣Acts as a base; can pick up a proton from the surrounding solution: ➣ ➣Ionized, with a charge of conditions. + 1, under cellular ➣Two sulfhydryl groups can interact to stabilize protein structure (fig. 5.20) ➣Makes the molecule of which it is a part an anion (negatively charged ion). ➣Can transfer energy between organic molecules FUNCTIONAL GROUP Hydroxyl NAME OF COMPOUNDS STRUCTURE EXAMPLE Draw and name an example Alcohols (their specific names ends in –ol ) FUNCTIONAL PROPERTIES ➣ Use the letters on the next page to designate the correct functional properties for each of the arrows in this column. ➣ Draw both types of structures Ketones Aldehyde ➣ Carbonyl ➣ ➣ ___________ acids, or organic acids ➣ Draw glycine Because it also has a carboxyl group, glycine is both an amine and a carboxylic acid; compounds with both groups are called _____ acids. Draw both types of structures Sulfhydryl Phosphate ➣ Thiols Organic Phosphates Draw and name an example ➣ ➣ ➣ ➣ ➣ AP BIOLOGY Functional Groups Quiz Match these functional properties (by letter) to the functional groups on the chart. This is only a sample. The choices will be reordered on your quiz. ) ➣ B) ➣ A _______ and an ________ may be structural isomers with different properties, as in the case for _______ and ________. (Add the missing words in correct order on the chart. ex. B) ______, _______, ______, _______) C) ➣ This group is polar as a result of the electronegative oxygen atom drawing electrons toward it. D) ➣ The covalent bond between oxygen and hydrogen is so polar that hydrogen ion (H+) tends to dissociate reversibly; for example E) ➣ Makes the molecule of which it is a part an anion (negatively charged ion). F) ➣ G) ➣ Acts as a base; can pick up a proton from the surrounding solution: H) ➣ Has acidic properties because it is a source of hydrogen ions. I) ➣ attracts water molecules, helping dissolve organic compounds such as sugars J) ➣ Can transfer energy between organic molecules K) ➣ Ionized, with a charge of 1, under cellular conditions. L) ➣ Two groups can interact to stabilize protein structure. +