AP Biology Carbon Compounds ppt

AP Biology: Organic
Compounds
T H E V E R S A T I L I T Y O F C A R B O N - T H E
B U I L D I N G B L O C K S O F L I F E !
Why Carbon Compounds? (Why not another element?
Bonding Properties
4 Covalent Bonds
Endless possibilities!
Living Organisms and Carbon
All life is built on Carbon
75% Water
25% Carbon compounds!
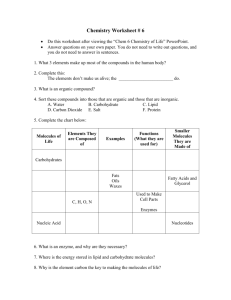
Four Types:
--Carbohydrates
--Lipids
--Proteins
--Nucleic Acids
Hydrocarbons
These are examples of hydrocarbons.
-Hydrophobic
-Stable
-Very little attraction between molecules
-Mostly gases at normal temperatures and pressures
Hydrocarbons Can Grow
Isomers
Molecules with the same elements, but with different physical structures
They have different chemical properties and can affect living systems in different ways.
Form Affects Function
Structural differences create important functional significance
Example:
medicines
L-version active
but not D-version
sometimes with tragic results…
Form Affects Function
Thalidomide
prescribed to pregnant women in 50s & 60s
reduced morning sickness, but…
stereoisomer caused severe birth defects
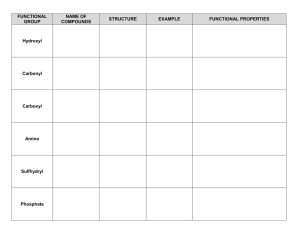
Functional Groups of Carbon Compounds
Parts of organic molecules that are involved in chemical reactions
give organic molecules distinctive properties
hydroxyl
amino carbonyl
carboxyl sulfhydryl phosphate methyl
Effects of Different Functional Groups
Basic structure of male & female hormones is identical
attachment of different functional groups interacts with different targets in the body—produces different effects!
Hydroxyl Group
-OH
Organic compounds with OH groups are called alcohols
Names typically end in “ol” (example: ethanol)
Amino Group
-NH2
Carbon compounds attached to NH2 are called amines
--NH2 acts as a base and can easily pick up H+ ions
Found in amino acids
Carbonyl Group
Carbon double-bonded to oxygen
May be in the middle or at the end of the carbon chain
Carboxyl Group
Carbon is double-bonded to oxygen and singlebonded to a hydroxyl (OH) group.
Compounds with a Carboxyl group (COOH) are acids.
Examples: Amino Acids, Fatty Acids
Sulfhydryl Group
-SH
Carbon compound is bonded to a sulfur-hydrogen group.
Compounds with sulfhydryl groups are called thiols.
Sulfhydryl groups stabilize protein molecules.
Phosphate Group
-PO4
Lots of oxygen=lots of negative charge! (Why?)
Highly reactive group
Transfers energy between organic molecules (ex:
ATP)
Methyl Group
CH3
May be attached to any carbon on a compound.