Biochemistry (Inorganic) and Nature of Science Review WS
advertisement
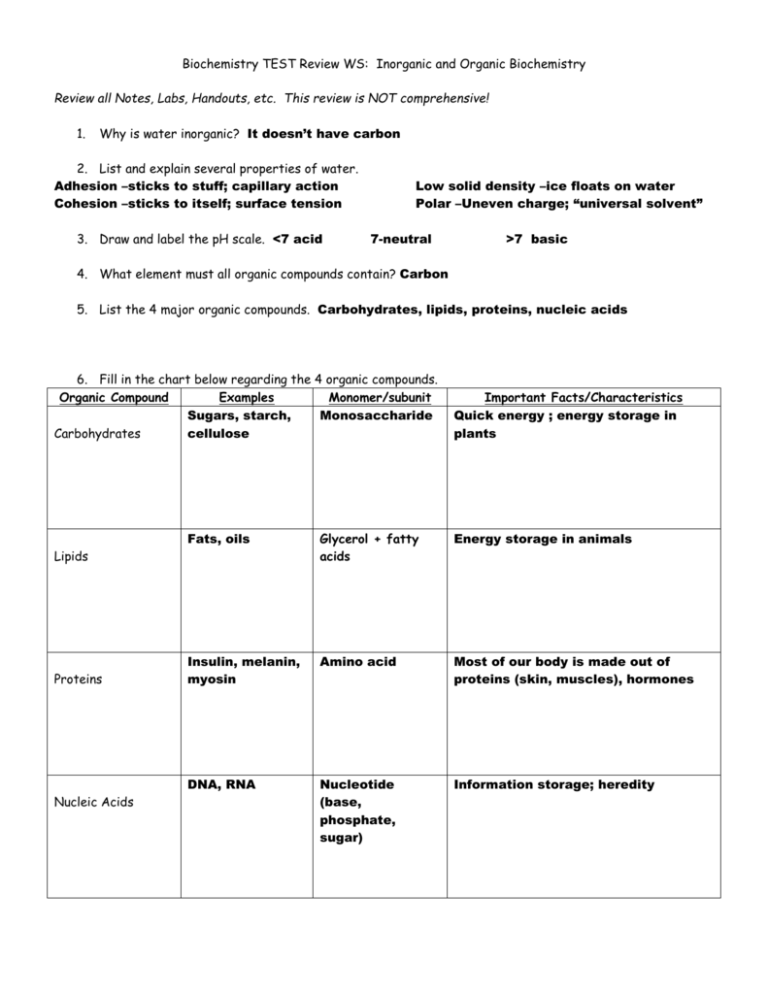
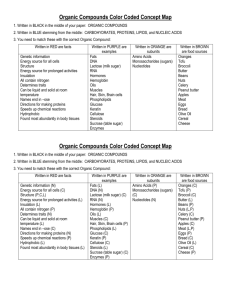
Biochemistry TEST Review WS: Inorganic and Organic Biochemistry Review all Notes, Labs, Handouts, etc. This review is NOT comprehensive! 1. Why is water inorganic? It doesn’t have carbon 2. List and explain several properties of water. Adhesion –sticks to stuff; capillary action Cohesion –sticks to itself; surface tension 3. Draw and label the pH scale. <7 acid Low solid density –ice floats on water Polar –Uneven charge; “universal solvent” 7-neutral >7 basic 4. What element must all organic compounds contain? Carbon 5. List the 4 major organic compounds. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids 6. Fill in the chart below regarding the 4 organic compounds. Organic Compound Examples Monomer/subunit Sugars, starch, Monosaccharide Carbohydrates cellulose Fats, oils Glycerol + fatty acids Energy storage in animals Insulin, melanin, myosin Amino acid Most of our body is made out of proteins (skin, muscles), hormones DNA, RNA Nucleotide (base, phosphate, sugar) Information storage; heredity Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Important Facts/Characteristics Quick energy ; energy storage in plants 7. Which of the 3 organic compounds that are consumed for food stores the most energy (hint: which contains the most Calories/gram)? lipids 8. Sketch the lipid bilayer of a cell membrane. 9. Differentiate between the three major polysaccharides (starch, glycogen, and cellulose) in terms of which organisms store them and where they are stored. Also, indicate which of the three CANNOT be digested by humans. Starch is used by plants to store energy; cellulose is used in plants for structural support, and cannot be digested by humans (wood). Glycogen is used as an energy deposit in the liver of animals. 10. Which of the 4 major organic compounds is made up of nucleotides? Nucleic Acids List the three parts of a nucleotide: Sugar, Base, phoshpate 11. What is the difference between DNA and RNA in terms of sugar that each contains as well as function? DNA has deoxyribose and contains the genetic code; RNA has ribose and helps translate that code into proteins 12. Contrast saturated and unsaturated fats in terms of chemical structure (which only has single bonds between carbons, which has some double bonds), state of matter at room temperature (solid vs. liquid), from what type of organisms these are made (plant vs. animal), and example for each. Saturated Unsaturated From animals No double bonds Solid at room temperature from plants Double bonds Liquid at room temperature 13. List the organic compound type that best fits the following chemical compounds. Lipid Nucleic acid protein carbohydrate