Small & Large Intestines
advertisement

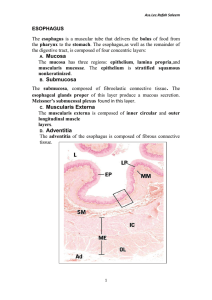
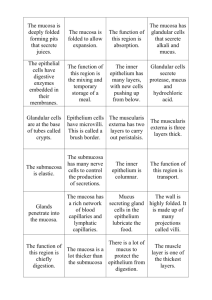
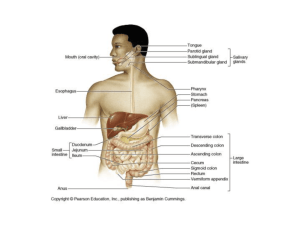
Small & Large Intestines Large Intestine: reabsorption of water and elimination of undigested food and waste Small Intestine: principal site for digestion of food and absorption of the products of digestion 4 Layers of Digestive System Mucosa - Epithelium - Lamina Propria - Muscularis Mucosae Submucosa - Connective tissue, blood vessels, submucosal plexus Muscularis Externa - 2 muscle layers, myenteric plexus Adventitia / Serosa - Loose connective tissue Layer 1: Mucosal Layer Epithelium - enterocytes (with microvilli), - goblet cells, - paneth cells (SI only), - entero-endocrine cells, - M cells Lamina Propria - loose connective tissue - Peyer’s Patches - lacteals Muscularis Mucosae - Boundary b/t mucosa and submucosa - 2 layers of smooth muscle Layer 2: Submucosa & Layer 3: Muscularis Externae Submucosa: • Connective Tissue • Blood vessels • Submucosal (Meissner’s) Plexus • (Brunner’s glands in duodenum) Muscularis Externae: • 2 smooth muscle layers • Myenteric (Auerbach’s) Plexus b/t muscle layers Myenteric Plexus Submucosal Plexus Layer 4: Adventitia/Serosa Loose connective tissue Plicae Circularis vs Villi Both are present in the small intestine as specializations to maximize absorptive surface area Plicae Circularis: circular folds w/in a core of submucosa. Contains many villi. Villus: finger-like mucosal projections w/in a core of lamina propria Cells of Mucosal Epithelium: Enterocytes • Absorptive Cells • Columnar cells with basal nuclei • Microvilli on apical surface • Digestive enzymes in microvilli glycocalyx (breakdown sugars & proteins) • Junctional complexes and terminal web Cells of Mucosal Epithelium: Enterocytes Terminal bar Microvilli Cells of Mucosal Epithelium: Enterocytes • Junctional complexes and terminal web Terminal Bar Cells of Mucosal Epithelium: Goblet Cells • Produce mucus • Interspersed among enterocytes • Appear empty because mucus is washed out in slide preparation • (more goblet cells in colon than SI) Cells of Mucosal Epithelium in SI: Paneth Cells • Located in Crypts of Lieberkuhn (bases of glands of SI b/t villi) • Secrete lysozymes • Basophilic base, eosinophilic granules at apex • Regulate bacterial flora of gut Cells of Mucosal Epithelium in SI: Paneth Cells • Located in Crypts of Lieberkuhn (base of glands of SI b/t villi) • Basophilic base, eosinophilic granules at apex Cells of Mucosal Epithelium: Enteroendocrine Cells • Secrete Hormones – GIP, CCK, Secretin • Seen with silver stain • (Also in stomach) Features of Mucosal Lamina Propria in SI Lamina Propria: loose cellular connective tissue Contains: 1. 2. Peyer’s Patches: lymph nodules and immune cells Lacteals: endotheliallined lymphatic channels w/in villi that uptake lipid droplets Features of Mucosal Muscularis Mucosae in SI • Boundary b/t mucosa and submucosa • Composed of two thin layers of smooth muscle Duodenum Characterized by submucosal Brunner’s Glands (protect duodenum by neutralizing stomach acid) Duodenum vs Jejunum and Ileum Submucosal Brunner’s Glands No Brunner’s Glands Large Intestine • Function: Reabsorbs water and electrolytes and eliminates undigested food and waste Large vs Small Intestine Similarities • Same Layers – – – – Mucosa Submucosa Muscularis Externa Adventitia/Serosa Same Epithelial Cells -Enterocytes -Goblet cells -Enteroendocrine cells -M cells BUT Differences • Large Intestine has NO plicae circularis and NO villi • • Large Intestine has MORE GOBLET cells • NO PANETH cells in LI Large vs Small Intestine Junction: Rectum and Anal Canal Rectum -simple columnar epithelium with goblet cells -glands Recto-Anal Junction -stratified columnar/ cuboidal epithelium -No glands Recto-Anal Junction -stratified columnar/cuboidal epithelium - as move toward anus, more stratified squamous - at perineum, stratified squamous epithelia is keratinized Anal Transition Zone Stratified Columnar/Cuboidal Anal Stratified Squamous Epithelium Hemorrhagic Vessels These vessels are in the submucosa of the anal canal. When dilated, they are internal hemorrhoids. Hemorrhagic vessel Question 1 The organ shown : a. Digests carbohydrates and proteins b. Contains paneth cells c. Reabsorbs water d. Conjugates bile Question 2 Villi are present in both images: True or False Question 3 Which sequence is in the correct oral to rectum/anal order? B A D C