Sep 2511:19 AM 1. Draw Lewis structures for five isomers of
advertisement

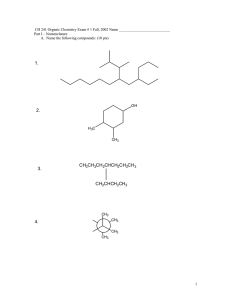
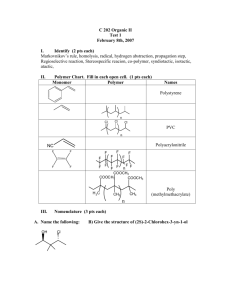
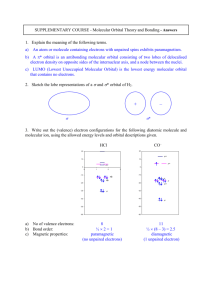
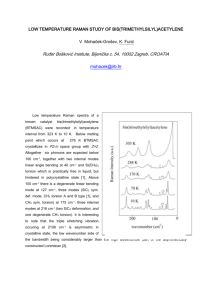
1. Draw Lewis structures for five isomers of C7H12O. At least one of your structures should contain an alkyne, one a ketone, and one an alcohol. (15 pts) Sep 25­11:19 AM 2. Dr. Murata and his group recently reported the isolation and structural elucidation of the following dinopodic acid from Clinopodium chinense var. parviflorum. (see Carroll, et. al. *J. of Nat. Prod., 2009, 72, 1379). This and other compounds isolated from the plant were shown to be Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Inhibitors. Label and name (eg: alkyne) each of the functional groups present in this molecule. (10 pts) Sep 25­11:19 AM 1 3. Provide the IUPAC names for a.-d. and/or draw the structures for e.-f. Choose five. (20 pts) 7­bromo­2­methyl­6­(1­methylethyl)nonane or 7­bromo­2­methyl­6­iso­propylnonane trans­8­chloro­5­ethyl­3­octene 6­fluoro­3­propyl­1­heptyne 5­butyl­3­methylcyclooctene Sep 25­11:20 AM 4. Explain which functional groups are present in the following compounds based on their IR spectra. (10 pts) This is a carboxylic acid. The strong stretch at 1700 cm­1 indicates (screams) carbonyl (C=O). The broad messy region (2500­3500 cm­1) overlying the C­H stretching band at 3000 cm­1 indicates an O­H of a carboxylic acid. The O­H of an alcohol would be more centered at 3200 cm­1 and be a distinct band. This spectrum is indicative of a primary amine. The double band at around 3200 cm­ 1 indicates an NH2 group. There is no C=O stretching band at 1700 cm­1 so we know it is not an amide. There is a band around 1600 cm­1 which could be a C=C stretching band so it could be an alkene, but this isn't clear. Sep 25­11:22 AM 2 5. Draw a Lewis structure (no need to depict every possible isomer) for the following formulas. Use vectors to indicate the direction of the dipole for all polar bonds. (15 pts) a. C4H6O b. C2H7N c. C2H4F2 Sep 25­11:22 AM Choose the one best answer for the next ten questions. (30 pts) 6. What are the formal charges of each nitrogen (from left to right)? a. b. c. d. e. -1 , +1, 0 +1, -1, 0 0, +1, -1 -1, 0, +1 +1, +1, 0 7. Which of the following IR bands would you NOT expect to find in caffeine a. 3400 cm-1 b. 1710 cm-1 c. 1650 cm-1 d. 3100 cm-1 e. 2950 cm-1 Sep 25­11:23 AM 3 8. Which structural isomer of CH3NO is most stable? 9. a. b. c. d. e. f. 10. a. b. c. d. e. The term “degenerate orbital” means that the energy of an orbital the same as another orbital the energy of an orbital doesn’t generate enough energy the energy of an orbital is less than the next orbital to keep the electron around the nucleus the orbital is not a true orbital for electron density C and D The intermolecular interaction between molecules of CH3CH2OH include ion-dipole hydrogen bonding dipole-dipole B, C A, B, and C Sep 25­11:24 AM 11. Which of the following MUST be name according to the E/Z system? 12. What is the type of bond and which orbital overlap to form the indicated bond in propene? a. b. c. d. e. 13. σ Csp3 + Csp3 σ Csp3 + Csp2 σ Csp2 + Csp2 π Csp2 + Csp2 σ Csp3 + Csp Which structures represent isomers? Sep 25­11:27 AM 4 14. Which compound would have the highest boiling point? a. CH3­CH2F b. CH3­CH2OCH3 c. d. CH3­CH2CH2­CH3 e. CH3­CH2CH2­NH2 15. Which of the following compounds is an amide? Sep 25­11:29 AM 5