T H E U N I V E R S I T Y O F S Y D N E Y
advertisement
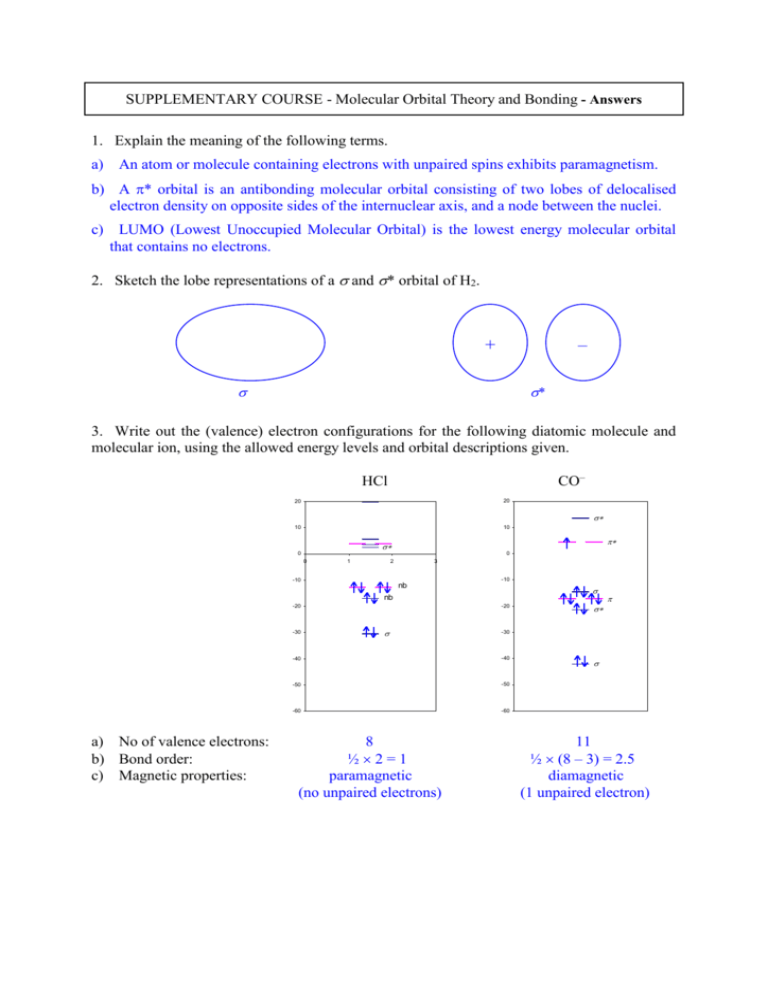
SUPPLEMENTARY COURSE - Molecular Orbital Theory and Bonding - Answers 1. Explain the meaning of the following terms. a) An atom or molecule containing electrons with unpaired spins exhibits paramagnetism. b) A * orbital is an antibonding molecular orbital consisting of two lobes of delocalised electron density on opposite sides of the internuclear axis, and a node between the nuclei. c) LUMO (Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital) is the lowest energy molecular orbital that contains no electrons. 2. Sketch the lobe representations of a and * orbital of H2. – + * 3. Write out the (valence) electron configurations for the following diatomic molecule and molecular ion, using the allowed energy levels and orbital descriptions given. CO– HCl 20 20 10 10 0 0 0 1 2 3 -10 -10 nb nb -20 -20 -30 a) No of valence electrons: b) Bond order: c) Magnetic properties: -30 -40 -40 -50 -50 -60 -60 8 ½2=1 paramagnetic (no unpaired electrons) 11 ½ (8 – 3) = 2.5 diamagnetic (1 unpaired electron) 4. A quantum calculation of the energy levels of ozone (O3) gives the (approximate) energies of the HOMO as –13.85 eV and the LUMO as –8.23 eV. a) Estimate the expected longest electronic absorbance wavelength of O3 from these values. E = -8.23-(-13.85) = 5.62 eV or 5.62 1.602 10–19 J = 9.0 10–19 J = hc/E = 6.626 10–34 J s 3.00 108 m s–1 / 9.0 10–19 J = 2.21 10–7 m = 221 nm b) Is this in the range of UV-A, -B or -C? UV-C (The photochemistry of O3 is actually more complicated than this, and it does absorb in the UV-B range as well.) 5. Explain the meaning of the following terms. a) An n-type semiconductor is a doped material containing additives that can donate electrons from their valence shells into the conductance band of the main component. b) The conductance band is a set or band of closely spaced molecular orbitals in a solid. It is empty in insulators and separated from lower energy levels (valence band) by a band gap. In conductors the conductance and valence bands overlap. c) The Madelung constant is the factor that determines the effect of packing of atoms, or their geometrical arrangement, on the total potential energy of an ionic crystal lattice. 6. On the basis of ionic radii, predict whether NaBr will have the same crystal structure as NaCl or CsCl. From lecture notes the ionic radii are: Na+ (0.102nm), Br– (0.196 nm), Cl– (0.181 nm). The radius ratio, r+/r–, for NaBr (0.520) is smaller than for NaCl (0.563), suggesting that Na+ can more easily fit into the octahedral interstices of the NaCl structure. There is no need to form the CsCl structure. 7. Sketch a unit cell (one complete cube) of an fcc lattice. simple cubic body-centred cubic face-centred cubic 8. CdS is a semiconductor that absorbs in wavelengths below about 470 nm. Calculate its band gap in joules. What colour do you expect it to be? E = hc/ = 6.626 10–34 J s 3.00 108 m s–1 / 470 10–9 m = 4.23 10–19 J (= 4.23 10–19 / 1.602 10–19 = 2.60 eV) It’s yellow











