CH 241 Organic Chemistry Exam # 1 Fall, 2002 Name... Part I – Nomenclature
advertisement

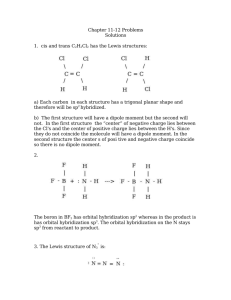
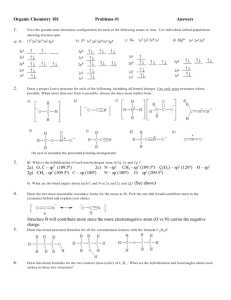
CH 241 Organic Chemistry Exam # 1 Fall, 2002 Name ___________________________ Part I – Nomenclature A. Name the following compounds: (10 pts) 1. OH 2. H 3C CH3 3. CH3CH2CH2CHCH2CH2CH3 CH3CHCH2CH3 CH3 CH3 4. CH3 CH3 1 5. N H Cl B. Write the structure of each of the following compounds: (10 pts) 1. Cyclohexylmethylamine. 2. 2-Methoxypropane 3. Sec-butyl isobutyl ether 4. 3-methyl—5-(1,2-dimethylpropyl)decane 5. 4,4-diethylheptane Part II. Bonding (20 pts) 1. Explain the valence-shell electron-pair repulsion (VSEPR) model and how it is used to describe the shape of a molecule. 2 2. Draw the Lewis structure and describe the hybridization and the shape of a methyl cation (a carbocation) and a methyl anion (a carbanion) 3. Which of the following molecules would you expect to have a dipole moment of zero? Explain your answer. a. CH3CH3 b. NH3 c. BF3 d. CH2Br2 4. Explain why ethanol has a higher boiling point than dimethyl ether. Be sure to include the definition of a boiling point in your explanation. Part III. Acids and Bases (25 pts) A. Given: CH3OH (methanol) pKa = 15.5, H2O (water) pKa = 15.7, CH4 (methane) pKa = 50, CH3COOH (acetic acid) pKa = 4.8 1. List the above compounds in order of increasing acid strength. 2. Which is the stronger base OH or CH3O ? 3 3. Write the structure of the conjugate base of methane. 4. Write the structure of the conjugate acid of methanol. 5. CH3 COOH + CH3O- CH3 COO- + CH3 OH Are the reactants or products favored for the above reaction? Explain your answer. Part IV. Conformation (25 pts) 1. Using the Newman projection, show the most stable conformer of 3-methylhexane, considering rotation about the C3 and C4 bond. 2. Draw the perspective formula of the anti and gauche conformation of butane., considering rotation around the C-2 and C-3 bond. 3. Explain why cyclohexane is such an unusual stable cycloalkane. 4. Draw the most stable chair conformation of ethyl cyclohexane. 4 5. The equilibrium constant for the conversion of axial to equatorial form of cyclohexanol is about 5 at room temperature. Calculate the % of the equatorial conformer of cyclohexanol at room temperature. Keq ~5 Axial Equatorial Multiple Choice Questions (10 pts) 1. What is the formal charge on N in HNO2? a. b. c. d. e. -1 +1 0 +2 -2 2. What is the hybridization of the N atom in HCN? a. b. c. d. e. sp p s sp3 sp2 3. Which of the following compounds is not a cis-disubstituted cyclohexane. a. b. c. d. e. 1,3-disubstituted: two axial substituents 1,3-disubstituted: two equatorial substituents 1,4-disubstituted: one axial and one equatorial substituent 1,3-disubstituted: one axial and one equatorial substituent 1,2-disubstituted: one axial and one equatorial substituent 4. What atomic orbitals are used to form the C-O bond in an alcohol? a. b. c. d. an sp3 orbital of C and an sp2 orbital of O a p orbital of C and a p orbital of O an sp3 orbital of C and an sp orbital of O an sp3 orbital of C and an sp3 orbital of O 5 e. an sp3 orbital of C and a p orbital of O 6