The Mammalian Digestive System
advertisement

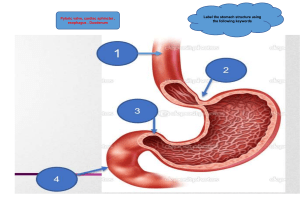
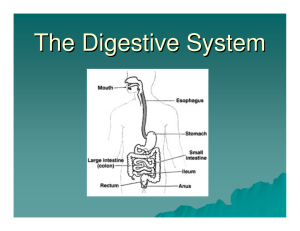
The Human Digestive System The Human Digestive System The digestive system of humans consists of a digestive tract and several accessory organs which work together to help the body gain nutrients from food. The organs form a tract through the body which function to mechanically and chemically digest the food for absorption. The accessory organs assist in the digestion of food into its component nutrients which can then be absorbed. pharynx tongue salivary glands esophagus liver gall bladder common bile duct lower esophageal sphincter stomach pancreas pancreatic duct duodenum pyloric sphincter transverse colon descending colon ascending colon small intestines cecum rectum anus Organ Structure • Oral Cavity • Contains the tongue, which is a large Function • muscle in the mouth that has taste and chewing to break down buds in structures called papillae and taste food Also the location of teeth and exit • point of salivary glands • Esophagus • Long muscular tube leading to the This is mechanical digestion of food • Muscles around the tube push stomach the food bolus down towards Lined with both circular and the stomach longitudinal muscles • Secretes mucin (a lubricant) • Food bolus enters through the lower • • Secretes mucous and acid • Contains folds called rugae • Chyme exits through the pyloric sphincter into the small intestines This movement is known as peristalsis • esophageal sphincter Stomach Tongue and teeth aid in mixing Churning of the stomach helps to mechanically digest food. • Hydrochloric acid aids in chemical breakdown of food. • The enzyme pepsin chemically breaks down protein. Organ Structure • First part of the small intestine after • are released by the pancreas and sphincter • Ducts release secretions here • Consists of the duodenum, the jejunum, and the ileum • Very long tube with many folds gall bladder to help with chemical digestion • Absorption of nutrients through villi and microvilli which provide called villi and microvilli • Muscles move chyme around to mix it with digestive enzymes that chyme moves through the pyloric Duodenum Small Intestines Function increased surface area Connects to the large intestines through the ileocecal valve • Colon Larger diameter and shorter length than small intestine • • breakdown products from Contain bacteria that assist in bacteria digestion Rectum and Anus • Last tube of the digestive tract before exit of waste products through the anal sphincter Absorption of water and • Storage of undigested waste before controlled elimination Organ Structure • Glands located above and Salivary Glands below the oral cavity which release liquids into the mouth through salivary ducts Liver • Large organ located above the stomach • Small sack under the liver that Gall Bladder is connected to the liver and the duodenum through the common bile duct Function • Produces saliva and the enzyme amylase which breaks down some carbohydrates • Produces bile which breaks down globs of fat • Storage of bile before it is release into the duodenum through the bile duct • Located behind the stomach Pancreas and connected to the duodenum through the • Production of enzymes to break down fats and proteins