Digestive System: Anatomy, Functions, and Histology
advertisement

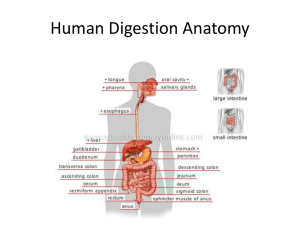
The Digestive System Functions of the Digestive System Digestion – break down of food into monomers Absorption – movement of digestive end products into the body Organs of the Digestive System mouth throat esophagus stomach small intestines large intestines rectum anus Accessory Organs teeth tongue salivary glands liver pancreas gallbladder Activities of the Digestive System Digestion Absorption of monomers into the blood or lymph Movement – – – – Ingestion Mastication Deglutition (swallowing) Peristalsis Secretion – exocrine secretions - digestive enzymes and associated fluid – endocrine secretions - hormones to regulate digestion (released from stomach and sm. intestines) Storage and elimination Oral Cavity Esophagus Wall Mucosa – Epithelium – Connective Tissue (lamina propria) – Smooth muscle Submucosa – Connective Tissue submucosal plexus Muscle Layers – Circular – Longitudinal myenteric plexus Serosa Stomach Functions Chyme* storage Protein digestion Mechanical breakdown Limited absorption Acid kills pathogens *chyme is the name for food once it is mixed with stomach acid/juices Stomach Lower esophageal sphincter (LES) Cardia Fundus Body Pylorus Pyloric sphincter Lower esophageal sphincter (LES) also known as cardiac sphincter or cardioesphageal sphincter The Stomach Rugae Rugae are large folds of the stomach wall that allow it to expand when filled with food. Stomach can hold 1 gallon of food. Stomach Lining Features Three muscle layers: Innermost is the oblique layer Simple columnar epithelium Gastric pits: deep convolutions of epithelial layer ending in gastric glands that are lined with specialized cells that secrete enzymes, acid, and hormones. Stomach Lining Gastric Pit / Gastric Gland Pyloric Region stomach duodenum pyloric sphincter The duodenum is the first section of the small intestines Small Intestines Functions Digestion – Carbohydrate – Protein – Fats Absorption Small Intestines 1 inch wide & divided into 3 sections duodenum – First 10 inches – Pancreatic juices and bile enter here jejunum – 8 feet long (approximately) ileum – 12 feet long (approximately) Common bile and pancreatic duct common bile duct pancreas pancreatic duct hepatopancreatic ampulla duodenum Duodenum, Pancreas, Gall Bladder Duodenum Histology Plicae circularis Also known as circular folds Folds of mucosa and submucosa Duodenum Histology Mucosa - Villi Submucosa Musclular layer Serosa Villi - ileum Villi are microscopic folds of intestinal lining Simple columnar epithelium Goblet cell is marked Microvilli – human jejunum Microvilli are folds of the cell membrane How many cells do you see in this photo? Large Intestines Functions Absorption – Water – Vitamins – Minerals Storage & Elimination of fecal matter Large Intestine Ileocecal valve Cecum Colon – Ascending – Transverse – Descending – sigmoid Rectum Anus (anal canal) Pancreas pancreas pancreatic duct Functions of Pancreas Exocrine – pancreatic acini – Digestive enzymes produced by acinar cells – Bicarbonate produced by epithelial cells that line the ducts Endocrine – Insulin – Glucagon – pancreatic islets Pancreas Histology (sheep) liver –posterior view caudate lobe left lobe quadrate lobe gallbladder right lobe Liver Lobule gallbladder bile flows from liver via right and left hepatic ducts Bile backs up from common bile duct and fills up gallbladder cystic duct common bile duct