KIN 211 Chapter 3: Digestion
advertisement

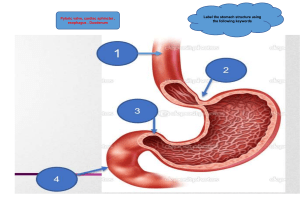
KIN 211 Chapter 3: Digestion Carbohydrates Digestion of carbohydrate begins in the mouth, with the secretion of the enzyme salivary amylase from the serous cells of the salivary gland. This enzyme breaks starch and glycogen into disaccharides. Carbohydrates The salivary glands are grouped into three categories: the parotid gland, submandibular glands, and sublingual, all located near the mouth. As the food is swallowed, it moves into the esophagus (a straight collapsible tube), which essentially provides a passageway from the pharynx to the stomach. Carbohydrates The Peristalsis is responsible for pushing the food into the next organ. Cardiac Sphincter The bolus passes through the cardiac sphincter, into the first section of the stomach. Regions of the Stomach The stomach is divided into several regions: the cardiac region, body region, fundic region, and pyloric region. Stomach The stomach works to mix and churn the food, which aids in further digestion of carbohydrates. At this point, the bolus is converted into a semifluid paste of bolus and gastric juices called chyme. Chyme through Pyloric Sphincter The chyme then travels through the pyloric sphincter into the first section of the small intestines.