Aspirin Synthesis: Reaction, HPLC, & Recrystallization
advertisement
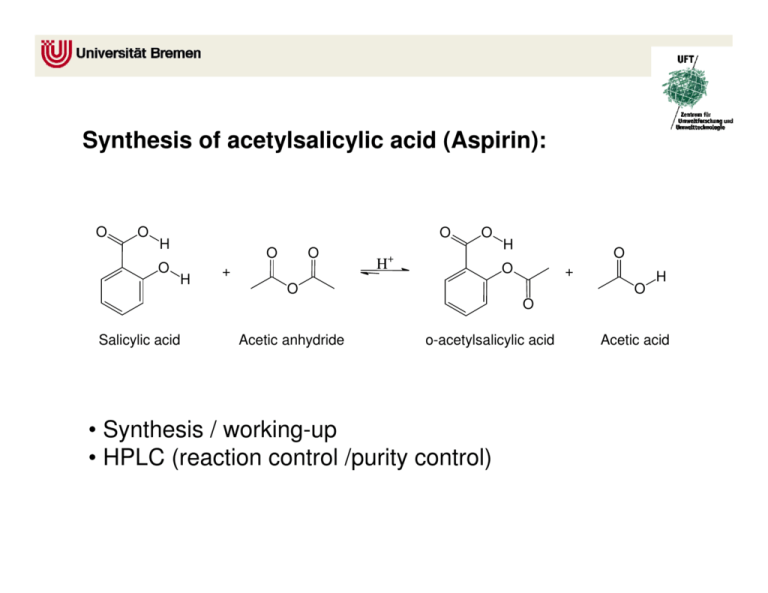
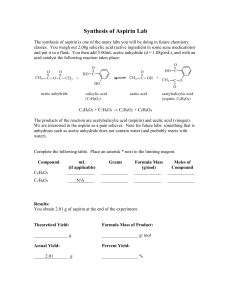
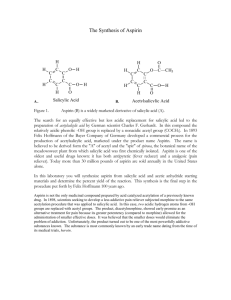
Synthesis of acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin): O O O H O O H O + H O + H O O + O O H O Salicylic acid Acetic anhydride o-acetylsalicylic acid • Synthesis / working-up • HPLC (reaction control /purity control) Acetic acid Experimental arrangement: Mechanism of the reaction: • addition-elimination- mechanism electrophilic carbon low electron density O O H O δO H + δ+ O O + O O H O H O + O lone pair nucleophile high electron density O H 1. step: Activation of the electrophile • increase in reactivity 2. Step: Addition reaction 3. Step: Elimination reaction Reaction control: • using the HPLC to follow the course of the reaction • take a sample every 20 minutes (before and after the additon of sulphuric acid) • stop the reaction when no further formation of the acetylic salicylic acid is observable Working-up: Recrystallisation • Recrystallisation is a fundamental technique used to purify solid compounds Recrystallisation is based on the principles of solubility: • compounds tend to be more soluble in hot solvents than they are in cold liquids • if a saturated hot solution is allowed to cool, the solute is no longer soluble in the solvent and forms crystals of pure compound • impurities are excluded from the growing crystals and the pure solid crystals can be separated from the dissolved impurities by filtration Characterisation: • HPLC • melting point determination Melting point determination: • the determination of melting points is one of the oldest identification • fast and simple tool • changes from a solid to a liquid state • pure crystalline substances have a clear, sharply defined melting point • a pure substance melts at a precisely defined temperature, characteristic of every crystalline substance • to obtain a first impression of the purity of a substance • small quantities of impurities change the melting point Determination of the yield: • you started with 0,05 mol Salicylic acid and acetic anhydride • if you have a yield of 100% you should obtain 0.05 mol aspirin • 0.05 mol * molecular weight of aspirin = X g • balance out your dried product • calculate your aspirin yield in % Sources of risk: Acetic anhydride: Sources of risk: Acetic anhydride: R10 Flammable R20/21 Harmful by inhalation and in contact with skin R34 Causes burns Salicylic acid: Salicylic acid: R22 Harmful if swallowed R41 Risk of serious damage to eyes Sulphuric acid: R35 Causes severe burn Sulphuric acid: R35 Causes severe burn