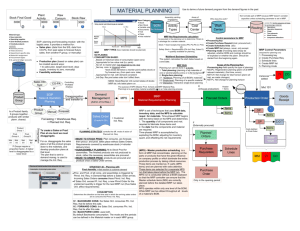
MRP & CRP: Explosion Calculus & Capacity Planning
advertisement

The Explosion Calculus n MRP processing at one level: Gross requirements at one level of product structure are translated into production schedule (planned order release) at that level. n Explosion into lower levels: Planned Order Release (POR) quantities at one level of product structure are translated into gross requirements at lower levels. 1 MRP – Example n You are producing skateboards, and each consists of one unit of board, and two units of subassembly of roller-set. Roller-sets are produced inside the plant, and consist of two components rollers and axles. Prepare the MRP tables of all items. 2 1 Skateboard assembly Material Inventory 3 Product Structure / Bill-of-matreial (BOM) Item A: Skateboard Material Inventory Item B: Board Item C: Roller-set Item D: Roller Item E: Axle 4 2 Bill of Material (BOM) Parent of B and C A Level 0 Components of A B[1] C[2] Level 1 D[2] 2 units of C, and 1 unit of B to make 1 unit of A E[1] Level 2 2 units of D, and 1 unit of E to make 1 unit of C 5 Master Production Schedule Week A D 1 2 3 Item Lead time (weeks) 4 5 6 50 7 40 A 1 8 9 10 80 60 B 2 C 1 D 3 E 2 6 3 Inventory Master Parts File Item A Current inventory levels 10 Lot size L4L Material Inventory B C 20 50 100 L4L Work-in-process Inventory D 30 200 E 20 150 Finished good Inventory 7 Open Orders Data Scheduled Receipts (Due Dates) ITEM / WEEKS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 A B 20 C 90 D 40 E 8 9 8 4 MRP table for item A WEEKS 1 2 3 4 5 GR SR PIB 10 10 10 10 10 NR PR POR 40 6 7 50 8 9 10 80 0 0 40 40 0 0 0 80 80 80 9 MRP table for item B WEEKS 1 2 GR SR PIB NR 3 4 5 6 40 20 20 20 40 40 0 0 7 8 9 80 0 0 20 80 100 PR POR 100 10 5 MRP table for item C WEEKS 1 2 3 4 5 GR 80 SR 90 PIB 50 140 140 140 60 NR PR POR 6 7 8 9 160 60 60 60 0 100 100 100 11 MRP table for item D WEEKS 1 GR SR PIB NR PR POR 2 3 4 40 5 6 7 8 9 260 40 30 30 70 30 30 30 30 170 170 230 400 400 12 6 MRP table for item E WEEKS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 GR SR PIB NR PR POR 8 9 100 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 70 70 80 150 150 13 MRP Outputs Planned Orders (Release Dates) ITEM / WEEKS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 A 40 B 100 C D E 8 9 80 100 400 150 14 7 Capacity Requirement Planning to validate MRP Planned Order Quantity Released at a given period may exceed the available capacity at that period. n Therefore POR quantities must be valid for shop capacity. n 15 Example for CRP Item : Week POR C 1 0 2 3 4 5 60 20 150 0 Processing time = 0.3 hours /unit Item: D Week 1 2 3 4 5 POR 70 30 50 100 120 Processing time = 0.25 hours /unit They are produced in the same workstation: runs 8 hours /day and 5 days /week. 16 8 Capacity Requirements Week POR (C) Process time POR (D) Process time Capacity Req. Capacity Excess capacity Capacity shortage 1 0 0.3 70 0.25 17.5 40 22.5 0 40 – 17.5 = 22.5 hours 2 60 0.3 30 0.25 25.5 40 14.5 0 3 20 0.3 50 0.25 18.5 40 21.5 0 4 150 0.3 100 0.25 70 40 0 30 5 0 0.3 120 0.25 30 40 10 0 6 0 0.3 0 0.25 0 40 40 0 0 x 0.3 + 70 x 0.3 = 17.5 hours 17 CRP Capacity Req. Capacity 17.5 40 25.5 40 18.5 40 70 40 30 40 0 40 18 9 Shifting lot to previous periods with excess capacity 19 Splitting lot into two or more periods 20 10