Material Planning Process
advertisement
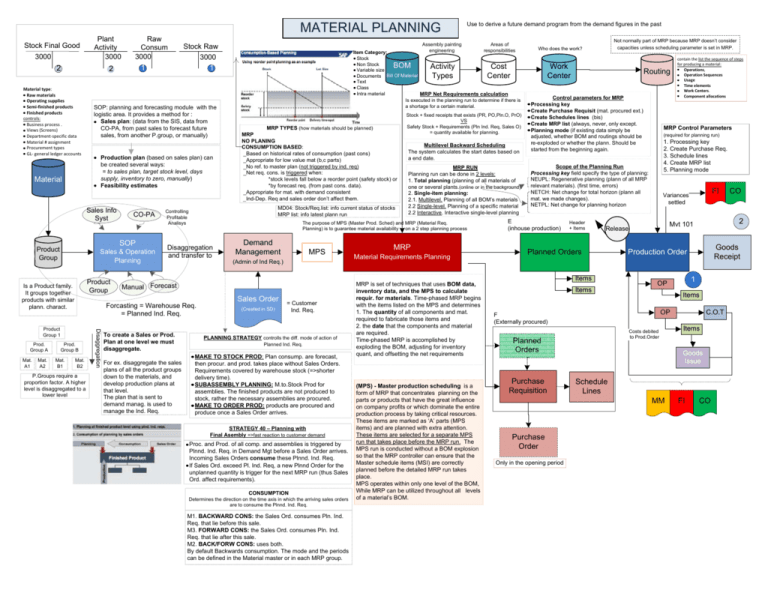
MATERIAL PLANNING Stock Final Good 3000 Plant Activity 3000 2 Production plan (based on sales plan) can be created several ways: = to sales plan, target stock level, days supply, inventory to zero, manually) Feasibility estimates Sales Info Syst SOP Product Group Sales & Operation Planning Product Group Is a Product family. It groups together products with similar plann. charact. Mat. B1 Mat. B2 P.Groups require a proportion factor. A higher level is disaggregated to a lower level Disaggregation Mat. A2 Prod. Group B MRP TYPES (how materials should be planned) MRP NO PLANING CONSUMPTION BASED: _Based on historical rates of consumption (past cons) _Appropriate for low value mat (b,c parts) _No ref. to master plan (not triggered by ind. req) _Net req. cons. is triggered when: *stock levels fall below a reorder point (safety stock) or *by forecast req. (from past cons. data). _Appropriate for mat. with demand consistent _Ind-Dep. Req and sales order don’t affect them. MD04: Stock/Req.list: info current status of stocks MRP list: info latest plann run Controlling Profitable Analisys Activity Types Multilevel Backward Scheduling The system calculates the start dates based on a end date. MRP RUN Planning run can be done in 2 levels: 1. Total planning (planning of all materials of one or several plants.(online or in the background). 2. Single-item planning: 2.1. Multilevel. Planning of all BOM’s materials 2.2 Single-level. Planning of a specific material 2.2 Interactive. Interactive single-level planning Disaggregation and transfer to Demand Management MPS (Admin of Ind Req.) MRP Material Requirements Planning Not normally part of MRP because MRP doesn’t consider capacities unless scheduling parameter is set in MRP. Who does the work? Cost Center Stock + fixed receipts that exists (PR, PO,Pln.O, PrO) VS Safety Stock + Requirements (Pln Ind. Req, Sales O) = quantity available for planning. The purpose of MPS (Master Prod. Sched) and MRP (Material Req. Planning) is to guarantee material availability on a 2 step planning process Work Center Routing Control parameters for MRP Processing key Create Purchase Requisit (mat. procured ext.) Create Schedules lines (bis) Create MRP list (always, never, only except. Planning mode (if existing data simply be adjusted, whether BOM and routings should be re-exploded or whether the plann. Should be started from the beginning again. E (inhouse production) Header + Items To create a Sales or Prod. Plan at one level we must disaggregate. For ex. disaggregate the sales plans of all the product groups down to the materials, and develop production plans at that level. The plan that is sent to demand manag. is used to manage the Ind. Req. Sales Order (Created in SD) = Customer Ind. Req. PLANNING STRATEGY controlls the diff. mode of action of Planned Ind. Req. MAKE TO STOCK PROD: Plan consump. are forecast, then procur. and prod. takes place without Sales Orders. Requirements covered by warehouse stock (=>shorter delivery time). SUBASSEMBLY PLANNING: M.to.Stock Prod for assemblies. The finished products are not produced to stock, rather the necessary assemblies are procured. MAKE TO ORDER PROD: products are procured and produce once a Sales Order arrives. STRATEGY 40 – Planning with Final Asembly =>fast reaction to customer demand Proc. and Prod. of all comp. and assemblies is triggered by Plnnd. Ind. Req. in Demand Mgt before a Sales Order arrives. Incoming Sales Orders consume these Plnnd. Ind. Req. If Sales Ord. exceed Pl. Ind. Req, a new Plnnd Order for the unplanned quantity is trigger for the next MRP run (thus Sales Ord. affect requirements). CONSUMPTION Determines the direction on the time axis in which the arriving sales orders are to consume the Plnnd. Ind. Req. M1. BACKWARD CONS: the Sales Ord. consumes Pln. Ind. Req. that lie before this sale. M3. FORWARD CONS: the Sales Ord. consumes Pln. Ind. Req. that lie after this sale. M2. BACK/FORW CONS: uses both. By default Backwards consumption. The mode and the periods can be defined in the Material master or in each MRP group. MRP is set of techniques that uses BOM data, inventory data, and the MPS to calculate requir. for materials. Time-phased MRP begins with the items listed on the MPS and determines 1. The quantity of all components and mat. required to fabricate those items and 2. the date that the components and material are required. Time-phased MRP is accomplished by exploding the BOM, adjusting for inventory quant, and offsetting the net requirements (MPS) - Master production scheduling is a form of MRP that concentrates planning on the parts or products that have the great influence on company profits or which dominate the entire production process by taking critical resources. These items are marked as ‘A’ parts (MPS items) and are planned with extra attention. These items are selected for a separate MPS run that takes place before the MRP run. The MPS run is conducted without a BOM explosion so that the MRP controller can ensure that the Master schedule items (MSI) are correctly planned before the detailed MRP run takes place. MPS operates within only one level of the BOM, While MRP can be utilized throughout all levels of a material’s BOM. (required for planning run) 1. Processing key 2. Create Purchase Req. 3. Schedule lines 4. Create MRP list 5. Planning mode Items Items Costs debited to Prod.Order C.O.T Items Goods Issue Schedule Lines MM Only in the opening period 1 OP Planned Orders Purchase Order Goods Receipt Production Order OP FI CO 2 Mvt 101 F (Externally procured) Purchase Requisition FI Variances settled Release Planned Orders contain the list the sequence of steps for producing a material: Operations, Operation Sequences Usage Time elements Work Centers. Component allocations MRP Control Parameters Scope of the Planning Run Processing key field specify the type of planning: NEUPL: Regenerative planning (plann of all MRP relevant materials). (first time, errors) NETCH: Net change for total horizon (plann all mat. we made changes). NETPL: Net change for planning horizon Items Manual Forecast Forcasting = Warehouse Req. = Planned Ind. Req. Product Group 1 Mat. A1 CO-PA BOM 1 SOP: planning and forecasting module with the logistic area. It provides a method for : Sales plan: (data from the SIS, data from CO-PA, from past sales to forecast future sales, from another P.group, or manually) Material Assembly painting Areas of engineering responsibilities Item Category: Stock Non Stock Variable size Documents Bill Of Material Text Class Intra material MRP Net Requirements calculation Is executed in the planning run to determine if there is a shortage for a certain material. Stock Raw 3000 1 2 Material type: Raw materials Operating supplies Semi-finished products Finished products controls: Business process . Views (Screens) Department-specific data Material # assignment Procurement types GL- general ledger accounts Prod. Group A Raw Consum 3000 Use to derive a future demand program from the demand figures in the past CO