molecular polarity Review Sheetpdf

MOLEC
ULE
1. SeO
3
Name Period Date
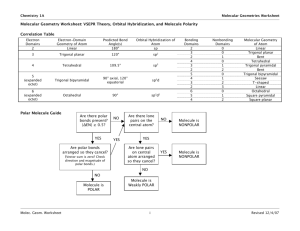
Molecular Geometry – Review Sheet
Part I: For each of the following molecules, draw the Lewis Diagram then, identify the correct the molecular shape and bond angle. Finally, determine if the molecule is polar or nonpolar.
LEWIS DIAGRAM SHAPE BOND ANGLE
P
OLAR OR
N
ON
P
OLAR
2. AsH
3
3. NO
2
-
4.
BeFCl
MOLECULE
5. SiH
2
Br
2
6. SeH
7. PF
8. SCl
5
6
2
LEWIS DIAGRAM SHAPE BOND ANGLE P OLAR OR
N ON P OLAR
Predicting Molecular Geometry
Part II : In each case, predict the approximate bond angle(s) , around the central atom (Note: It is helpful to first sketch the Lewis stucture!)
Molecule or Ion
(1) OF
2
(2) H
2
CO
(a) No. of valence e
- ‘s
(3) NO
2
+
(4) BF
3
(5) SbF
3
I
2
(b) Lewis structure
(c) Approximate bond angle(s)
(d) Polar or non-polar molecule?
(e) Molecular Geometry name
(f) Electronic Geometry
Ion: always polar!
______________________________________________________________________________
Part II cont .: For each of the molecules below fill in the indicated items in the chart. The central atoms are underlined.
Molecule (1) SO
2
(2) HBF
2
(3) XeF
4
(4) CH
2
Cl
2
(5) NF
3
(a) No. of valence e
- ‘s
(b) Lewis structure
(c) Approximate bond angle(s)
(d) Polar or non-polar molecule?
(e) Geometry name
(f) Electronic geometry
List the molecular geometry shape names for the molecules which will always be polar…regardless of the atoms bonding to the central atom:
2)
Part III : For each of the following pairs of compounds, determine which is most polar based on their Lewis structures and the atoms involved in the molecule.
1) methyl chloride (CHCl
3
) or methyl bromide (CHBr
3
) water or hydrogen sulfide (H
2
S)
3)
4) hydrochloric acid (HCl) or hydroiodic acid (HI) bromoacetylene (C
2
HBr) or chloroacetylene (C
2
HCl)
5) carbon tetrachloride (CCl
4
) or xeon tetrachloride (XeCl
3
F)
Part IV : Draw all resonance structures for the following molecules and use formal charges to determine the most stable choice between structures.
(a) SCN
-
(b) SO
3
Part V : Bond Energy
Calculate the change in enthalpy for the following reaction. See POGIL for average bond energy values.
H
2
+ N
2
NH
3