GENERAL CHEMISTY CHAPTER 9 Practice Assessment
advertisement

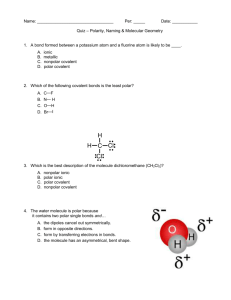
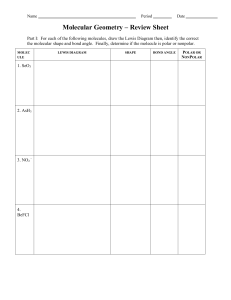
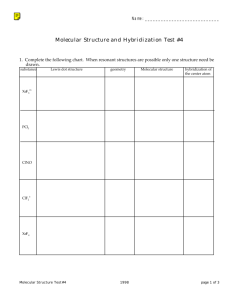
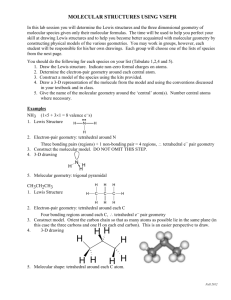
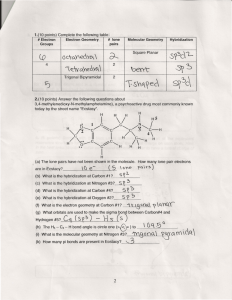
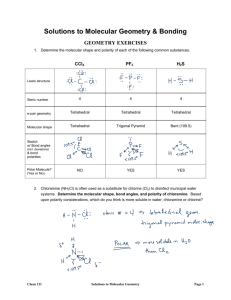
GENERAL CHEMISTY CHAPTER 9 Practice Assessment 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Calculate the Δ EN for the following bonds and classify the bonds as ionic, non-polar covalent, or polar covalent: C–P, Ba–N, Pd–Cl, Ge–Se. Describe AND explain the trends in electronegativity within a group and a period on the periodic table. Do you expect CaO or CaN to have a higher melting point? Why? Ammonia, NH3, has 4 pairs of electrons around the central nitrogen atom, but it is not classified as a tetrahedral geometry. State the molecular shape/geometry of ammonia, and explain why the tetrahedral geometry has become distorted. Draw the Lewis Dot Diagram for water. Include the correct location of the partial charges on the molecule. State the molecular shape/geometry of water. Why does water exhibit strong surface tension, and an ability to dissolve many other compounds? When we compare the geometry of methane, CH4, to methyl chloride, CH3Cl, we see that they are both tetrahedral. Which molecule would you expect to have the higher boiling point, and why? Draw the Lewis Dot Diagram for the molecule CH2O. State the molecular shape(s)/geometry of this molecule. Is the molecule polar or non-polar? How do you know? Draw Lewis Dot Diagrams for the following molecules/ions and state the molecular shape/geometry of each: N31- , Cl2S, SeO2 Compare and contrast the physical properties of non-polar covalent, polar covalent and ionic compounds. Use examples to supplement your answer.