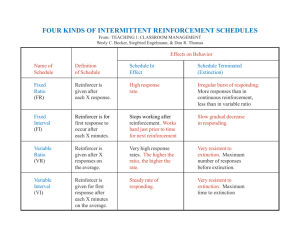
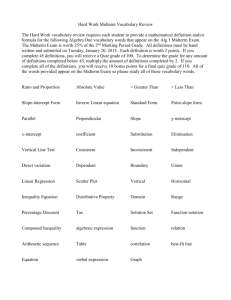
PSYC 333 -- MIDTERM 2 STUDY GUIDE (Equation = answer to
advertisement
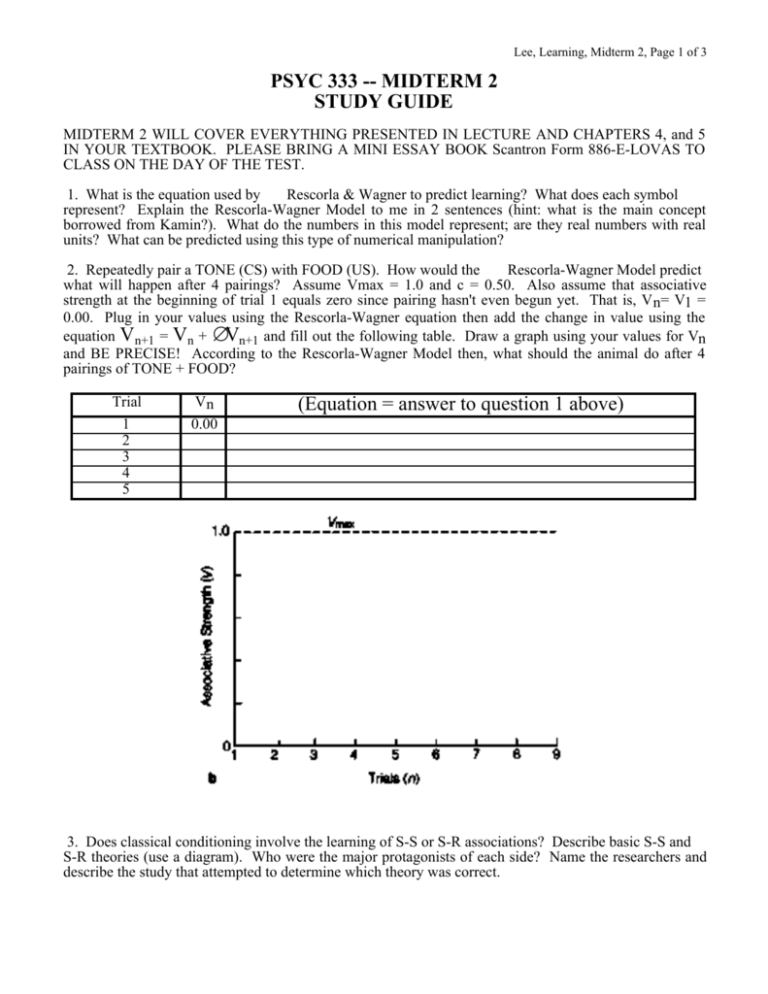
Lee, Learning, Midterm 2, Page 1 of 3 PSYC 333 -- MIDTERM 2 STUDY GUIDE MIDTERM 2 WILL COVER EVERYTHING PRESENTED IN LECTURE AND CHAPTERS 4, and 5 IN YOUR TEXTBOOK. PLEASE BRING A MINI ESSAY BOOK Scantron Form 886-E-LOVAS TO CLASS ON THE DAY OF THE TEST. 1. What is the equation used by Rescorla & Wagner to predict learning? What does each symbol represent? Explain the Rescorla-Wagner Model to me in 2 sentences (hint: what is the main concept borrowed from Kamin?). What do the numbers in this model represent; are they real numbers with real units? What can be predicted using this type of numerical manipulation? 2. Repeatedly pair a TONE (CS) with FOOD (US). How would the Rescorla-Wagner Model predict what will happen after 4 pairings? Assume Vmax = 1.0 and c = 0.50. Also assume that associative strength at the beginning of trial 1 equals zero since pairing hasn't even begun yet. That is, V n= V1 = 0.00. Plug in your values using the Rescorla-Wagner equation then add the change in value using the equation V n+1 = Vn + ∆Vn+1 and fill out the following table. Draw a graph using your values for Vn and BE PRECISE! According to the Rescorla-Wagner Model then, what should the animal do after 4 pairings of TONE + FOOD? Trial 1 2 3 4 5 Vn 0.00 (Equation = answer to question 1 above) 3. Does classical conditioning involve the learning of S-S or S-R associations? Describe basic S-S and S-R theories (use a diagram). Who were the major protagonists of each side? Name the researchers and describe the study that attempted to determine which theory was correct. Lee, Learning, Midterm 2, Page 2 of 3 4. What is the difference between expectation and substitution accounts of conditioning (REMEMBER - THIS IS NOT THE SAME THING AS S-S AND S-R THEORIES!)? What evidence supports each interpretation? Be able to describe and discuss the studies by Jenkins & Moore (1973), Hearst & Jenkins (1974), and Capaldi, Holvancik & Friedman (1976). How did the study by Timberlake, Wahl, & King (1982) lead to the acceptance of both models? 5. Describe Timberlake's behavior system approach to conditioning. Include a discussion of how this system would predict the response a hungry rat would make to 1) a small rolling ball; and 2) another rat. 6. Fill in the blanks. 7. Describe Thorndike's puzzle box experiment and results. What aspect of his results led him to conclude that his animals learned through "trial and error"? Why did Kohler think that "Thorndike's box was stupid?" Describe the experiments by Kohler that challenged Thorndike's results. How did Kohler interpret these results? 8. Describe 4 types of mazes used in research on learning. Be able to draw them, discuss what the animal does in each, and talk a bit about the data that each would produce. 9. Give the definition of 6 basic schedules of reinforcement. Draw a cumulative graph that illustrates the characteristic pattern of responding for each of the 4 partial schedules. Label your graphs carefully! State which schedule leads to "superstitious behavior" and explain why. 10. What is the difference between a FIXED INTERVAL and a FIXED TIME schedule of reinforcement? Describe each in EXCRUTIATING DETAIL!!!!!!! What type(s) of behaviors result from each? Lee, Learning, Midterm 2, Page 3 of 3 11. What is the partial reinforcement extinction effect (PRE)? Describe the study by Lewis & Duncan (1956) that illustrates the effect of the PRE on the human propensity to gamble. 12. By keeping a careful record of your own behavior for 2 weeks, you find out that you spend the following amounts of time doing the following behaviors: BEHAVIOR WATCHING T.V. STUDYING VISITING FRIENDS CHORES HOURS / DAY 2.5 1.0 3.0 0.5 Explain how you could use this information and the Premack Principle to increase the amount of time you spend studying. Under what set of circumstances is the Premack Principle wrong? Describe Timberlake & Allison's idea of a "bliss point". 13. What are contrast effects? Describe in detail the study by Crespi (1942) that led to the "Crespi Effect". Be sure to graph the results and label your graphs carefully! Does the reinforcer affect learning or motivation? How can you tell? 14. You conducted an experiment to investigate the effect of time-of-day on performance by training 4 groups of rats on a Morris Water Maze Task. First, describe the apparatus and the task. Second, your results are as follows: What is your independent variable? What is your dependent Time-of-Day Latency (sec) variable? Do you have a control group? If so, which group is it? 8am 100 Graph and INTERPRET your 12noon 70 results. That is, do not tell me 4pm 30 what the graph looks like, tell me 8pm 10 specifically what effect Time-ofDay has on performance in rats. 15. Be able to define and give, where appropriate, an example of each of the following terms. independent variable dependent variable subject expectations placebo effects experimenter expectations Rescorla-Wagner Model latent inhibition S-S Theory S-R Theory stimulus devaluation stimulus substitution expectation Two-Level Hypothesis behavior system approach releasing stimuli puzzle box Law of Effect reinforcer reinforcement insight learning latency shaping continuous reinforcement (CRF) partial reinforcement fixed interval schedule (FI) variable interval schedule (VI) fixed ratio schedule (FR) variable ratio schedule (VR) fixed interval scallop fixed time schedule superstitious behavior partial reinforcement effect (PRE) primary reinforcer secondary reinforcer social reinforcer Premack Principle bliss point Response Deprivation Hypothesis free-operant magazine training drive incentive positive contrast negative contrast Yerkes-Dodson Law stimulus control generalization discrimination shaping learning performance