Functional Analysis Quiz
advertisement

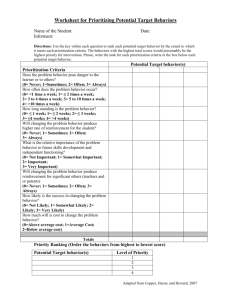
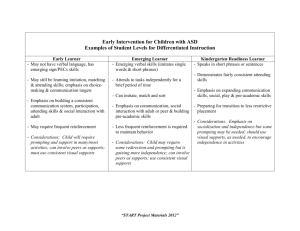
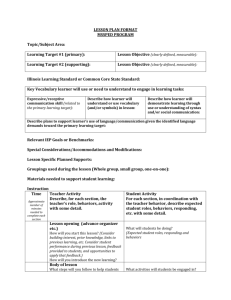
Name: ____________________ Date: ____________ Score: __(out of 22 points)__ Assessing and Reducing Problem Behavior 1. A __functional__ __assessment_is a set of procedures to identify the causes of maladaptive or socially inappropriate behavior and reduce it through teaching replacement behavior instead of suppressing it through punishment. 2. When conducting a functional assessment, the causes of problem behaviors are sought in the immediate ___environment___ and the ___learning___ ___history_____ of the individual and are not based upon intrapsychic variables or psychodynamic processes. 3. Treatments derived from a functional assessment are classified by the ___function___ and not by the form of maladaptive behavior. 4. What is the problem with developing treatments based upon the form (topography) of the problem behavior? ___the same topography may be emitted for various reasons; therefore, treatment by topography may effectively reduce (extinguish) the PB in some cases, but in other cases treatment by topography may actually strengthen (reinforce) the PB_________________ The four major functions of problem behavior are: 5. _____SMPR________________________________________ 6. _____SMNR________________________________________ 7. _____APR__________________________________________ 8. _____ANR_________________________________________ 1 9. The self-stimulatory sensations that are produced by one’s own interaction with the environment have been maintained by a history of ___________ APR ______________. 10. The function of behavior where the behavior is more likely to occur after something is delivered by another person is called _______ SMPR __________________. 11. _________ SMNR _________________is the function of behavior maintained by the withdrawal of something that is aversive, by another person, after a behavior occurs, thereby making that behavior more likely to occur again under similar conditions. 12. A descriptive analysis that describes what occurred just prior to and just after a problem behavior can be as accurate as a formal functional analysis in determining the functions of problem behavior. True False 13. Why is it important to topographically define problem behaviors? ___so as to ensure what’s being measured can be objectively observed and consistently measured across observes; for consistency in treatment and data recording____________ ________________________________________________________________________ The three general procedures to reduce problem behavior are: 14. _____ Eliminate the MO _____________________________ 15. _____ EXT ________________________________________ 16. _____ Differential Reinforcement ______________________ 17. A problem behavior is maintained by a history of socially mediated negative reinforcement. How should you respond when this problem behavior occurs in order to terminate this behavior’s reinforcement contingency, thereby extinguishing the problem behavior? ___maintain the demand; no longer remove the demand; implement escape extinction; prompt compliance with the demand; or any other acceptable response_______________ 2 18. If the function of problem behavior is socially mediated negative reinforcement, why would the use of “time out” as a consequence for that behavior NOT be recommended? ___because time out would actually reinforce the problem behavior given the function is SMNR__________________________________________________________________ 19. When the learner engages in problem behavior because it is his/her form of requesting and you have determined that the answer is “yes, the learner can have this reinforcer” you should implement the __count and mand___________ protocol. 20. If the learner has a history of engaging in problem behavior when he has been denied access to a reinforcer, implement the ______accepting no_______ protocol. 21. The two procedures recommended to reduce self-stimulatory problem behaviors (i.e., those evoked by the antecedent “automatic reinforcement is high in value) are ___stim as a reinforcer____________ and _____RIRD_______________. 22. Why might it be recommended to teach a functional equivalent for problem behavior maintained by socially mediated negative reinforcement (i.e., escape from demands)? ___in cases when the learner engages in very intense self-injurious, aggressive, or otherwise destructive problem behaviors and it would therefore be unsafe or impractical to implement escape extinction (e.g., because of the learner’s size/strength)___________ 3