Reinforcement Quiz
advertisement

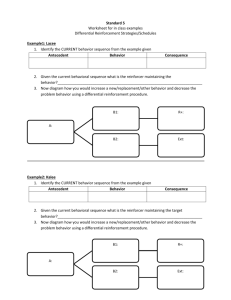
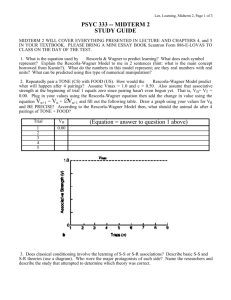
Name: ___________________ Date: ____________ Score: __(out of 20 points)__ Reinforcement 1. Skinner developed an apparatus commonly referred to as a/an ____operant chamber or Skinner Box______ and a recording device called a ____cumulative record(er)_________ to measure the change in response rates of rats and pigeons. 2. Reinforcement is defined as presenting a _consequence_______ following a behavior which _increases_____ the future frequency or rate of the behavior. 3. A _____reinforcer_____ is the consequence that follows a behavior and increases the future probability of the occurrence of that behavior. 4. A __positive reinforcer________ is a stimulus that is presented after a behavior and increases the future frequency of that behavior while a ___negative reinforcer_________ is a stimulus that is removed following a behavior and increases the future frequency of that behavior. 5. Both positive and negative reinforcers ___increase___________ the future probability of the occurrence of the behavior they immediately follow. 6. Negative reinforcers, like positive reinforcers, increase behavior, but a negative reinforcer is something that is ___removed or taken away______, instead of presented, after a behavior. 7. The instructor allows Linda to end the work session when she completes a task and Linda completes tasks more often. Ending the work session is a ___negative reinforcer_____. 1 8. The instructor gives praise to Robert every time he greets her and he greets her more often. Praise is a ___positive reinforcer________. 9. The instructor gives Linda candy every time she completes a task and Linda completes tasks more often. Candy is a __positive reinforcer_____. 10. William nags the instructor for some candy, the instructor finally gives William candy, and then William stops nagging. As a result, the instructor is more likely to give in to William nagging in the future. Stopping the nagging is a __negative reinforcer________ for the instructor. 11. As a result of the above situation, William nags more frequently for candy. Candy is a __positive reinforcer_________ for William’s nagging. 12. Escape from pain, food, self-stimulation, water, sleep, and sex are examples of ___primary or unconditioned____ reinforcers. 13. A _secondary or conditioned or learned reinforcer_ is any event that, although originally neutral, derives its reinforcing properties through pairing with a primary reinforcer or with an already-established reinforcer. 14. In a sense, some reinforcers are learned through experience. Examples of _secondary or learned or conditioned reinforcers_ include toys, praise, car rides, tokens, or money. 15. The reinforcement of every occurrence of a response occurs on a _continuous______ schedule of reinforcement. 16. During a/an __intermittent schedule__ schedule of reinforcement, reinforcement of some, but not all, occurrences of a response is given. 17. A _Fixed Ratio (FR)___ is a schedule of reinforcement in which the reinforcer follows a predetermined number of responses. 2 18. A _Variable Ratio (VR)_is a schedule of reinforcement in which the reinforcer follows a different number of responses each time such that over time a specific average number of responses are reinforced. 19. A _Fixed Interval (FI)_ is a schedule of reinforcement in which the reinforcer follows the first pre-specified response after a pre-specified amount of time has elapsed. 20. A _Variable Interval (VI)_ is a schedule of reinforcement in which the reinforcer follows the first pre-specified response after different intervals of time have elapsed such that over time a specific average interval is maintained. 3


![Reinforcement and Motivation [Compatibility Mode]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008925113_1-f5c766bb58c7f58b529c7a2527652f66-300x300.png)