Behavior Analysis - the science that studies environmental events
advertisement

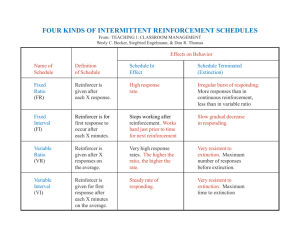
BEHV 2300 – Midterm Review By Stephen Smetana Unit 1 - Introduction to Behavior Analysis Behaviorism - the philosophy that informs the science that studies environmental events and behavior Behavior Analysis - the science that studies environmental events and behavior Applied Behavior Analysis - the application of the science to socially significant problems Private Events - An event that no other person can observe Principle of Public Events - Using public events to explain behavior Skinner Environmental Events 4 Attitudes of Science BEHV 2300 – Midterm Review By Stephen Smetana UNIT 2 – Basic Concepts Behavior - A statement that specifies exactly what behavior to observe Response Operant - behavior is behavior that is affected by its consequences during an organism’s lifetime Respondent - behavior is behavior that is elicited by antecedent stimuli Behavioral Definition Objective - refers to behavior that can be observed - enviornmental not private events o e.g. not ‘angry’ but ‘aggression towards….” Clear - reliable and unambiguous o e.g. can someone else paraphrase it? Complete - details what should be included and excluded o e.g. includes kicking and punching people, excludes aggression toward property Approaches to observing Self-report - Reporting on your own behavior - After the fact recording – relying on memory Direct observation - Watching what happens -Immediate recording Antecedents: (stimuli) - Environmental events that precede behavior in time. Consequences: (stimuli) - Environmental events that follow behavior in time. 3-term contingency ABC Diagram algorithm BEHV 2300 – Midterm Review By Stephen Smetana Saw Recorded UNIT 3 - Measurement & Visual Analysis Key Words Measurement Dimensions of Behavior Frequency – count/number Rate – count per unit of time Duration – length of time Magnitude - amplitude, intensity, or force of a response Trend - Which way is the data path moving: Up (upward) BEHV 2300 – Midterm Review By Stephen Smetana Down (downward) Stable Range - the highest and lowest data points (subtract one from the other) Data point - is a dot on the graph that shows the ‘value’ of the recorded data Data path - is the line that connects the data points Divided conditions – Do the points overlap? Stable conditions - Are the data points moving closer to the data points in adjacent conditions? Convincing differences – The data must be Divided and Stable Causation - did the intervention change the behavior? Are there other environmental events that may have produced behavior change? UNIT 4 - Positive Reinforcement Key Terms Positive Reinforcement – procedure Positive Reinforcer – event Follows Increases Unknown Event Procedure BEHV 2300 – Midterm Review By Stephen Smetana UNIT 5 - Reinforcer Effectiveness Key Terms Deprivation/deprived <===> Satiation/Satiated Immediacy <===> Within a minute Size <===> Worthwhile Contingency <===> if and only if None (when none of the principles are violated) Unknown Keys to DISC Deprivation Immediacy Size Contingency Hasn’t had it in a long time Never gets Can’t get enough Was important Loved Really enjoyed Right after Immediately While Only gets when Never gets it at any other time If and only if UNIT 6 - Negative Reinforcement Key Words Negative Reinforcement – procedure Negative Reinforcer – event Escape <===> Terminates Avoidance <===>Prevents BEHV 2300 – Midterm Review By Stephen Smetana Format Example UNIT 7 – Extinction of Everyday Behaviors Extinction – Procedure in which an event that follows a behavior is stopped and the rate of the behavior decreases. Extinction Burst – A temporary increase in the rate of responding as soon as the extinction procedure begins. (Reinforcer is stopped) BEHV 2300 – Midterm Review By Stephen Smetana Extinction induced Variability - When the behavior no longer results in reinforcement, the organism may emit other behavior. Extinguished Unknown