World History Middle Ages Test Review
advertisement
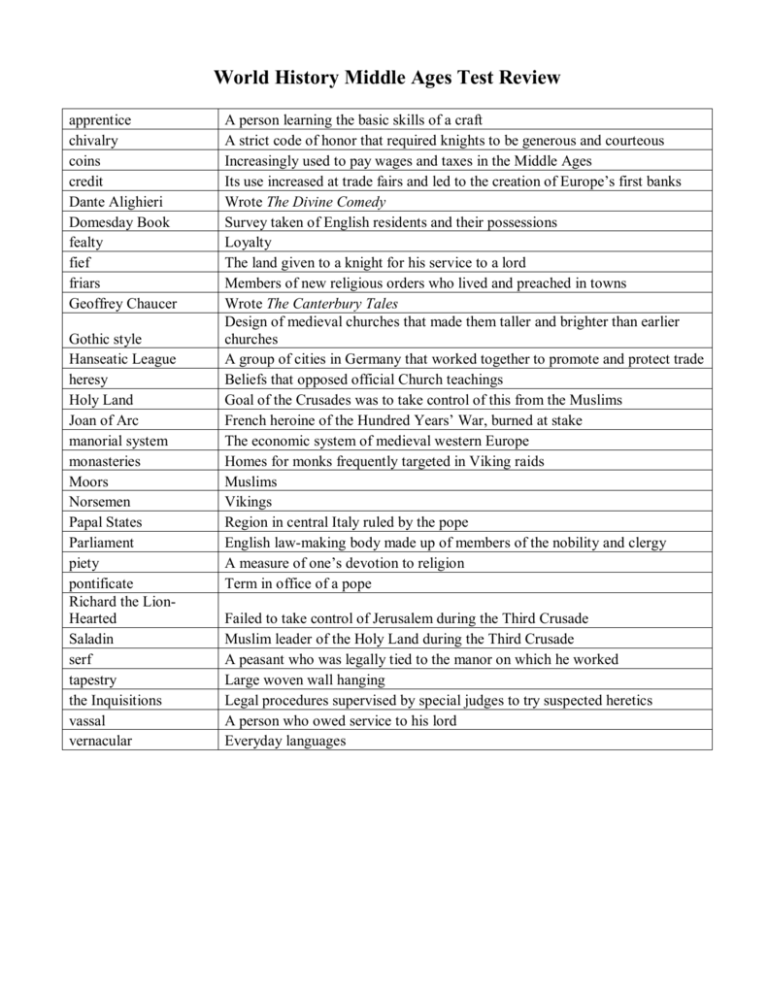
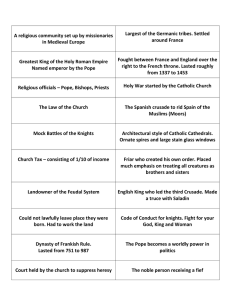
World History Middle Ages Test Review apprentice chivalry coins credit Dante Alighieri Domesday Book fealty fief friars Geoffrey Chaucer Gothic style Hanseatic League heresy Holy Land Joan of Arc manorial system monasteries Moors Norsemen Papal States Parliament piety pontificate Richard the LionHearted Saladin serf tapestry the Inquisitions vassal vernacular A person learning the basic skills of a craft A strict code of honor that required knights to be generous and courteous Increasingly used to pay wages and taxes in the Middle Ages Its use increased at trade fairs and led to the creation of Europe’s first banks Wrote The Divine Comedy Survey taken of English residents and their possessions Loyalty The land given to a knight for his service to a lord Members of new religious orders who lived and preached in towns Wrote The Canterbury Tales Design of medieval churches that made them taller and brighter than earlier churches A group of cities in Germany that worked together to promote and protect trade Beliefs that opposed official Church teachings Goal of the Crusades was to take control of this from the Muslims French heroine of the Hundred Years’ War, burned at stake The economic system of medieval western Europe Homes for monks frequently targeted in Viking raids Muslims Vikings Region in central Italy ruled by the pope English law-making body made up of members of the nobility and clergy A measure of one’s devotion to religion Term in office of a pope Failed to take control of Jerusalem during the Third Crusade Muslim leader of the Holy Land during the Third Crusade A peasant who was legally tied to the manor on which he worked Large woven wall hanging Legal procedures supervised by special judges to try suspected heretics A person who owed service to his lord Everyday languages Castles were built for what particular purpose? Defense How did Charlemagne ensure that his counts remained loyal and did their jobs well? By setting up a system of rewards and punishments administered by inspectors What advance in engineering made this type of architecture possible? The flying buttress What caused the collapse of the medieval manor system? The Black Death What is another name for the plague that devastated Europe in the mid-1300s? The Black Death What was the art of illumination? decorating written manuscripts with pictures or designs What was the goal of the First Crusade? To take Jerusalem and the Holy Land away from the Muslims. What were two main effects of the Crusades? European kings gained more political power and relations between religious groups became more strained. Why did Europe become a feudal society? Europeans needed to defend themselves against constant raids and invasions. Why did merchants asked the king for special charters? Merchants did not want to pay fees to feudal lords. Why did the pope have such great influence in the Middle Ages? Nearly everyone in Europe was Christian. Why did Vikings begin raiding northern Europe? Viking farmers could not grow enough food.