The Elements of Group 18 (8A, VIII, VIIIA) The Noble Gases Noble
advertisement

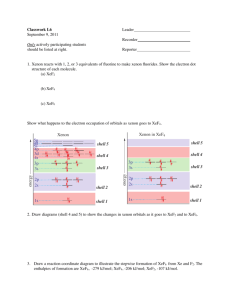
Noble Gases - Properties The Elements of Group 18 (8A, VIII, VIIIA) The Noble Gases He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn Valence electron configuration: ns2np6 Occurrence Properties and Uses Air is the only source of most noble gases: 0.000524% He (5.2 ppm) 0.001818% Ne 0.934% Ar 1 ppm Kr 0.05 ppm Xe He from natural gas up to 8% He by volume. Pure elements isolated by fractionation Electric discharge lamps. Lasers and flashlamps. Inert atmosphere chemistry. Metallurgy and semiconductors. Superconducting magnets. NMR, MRI, particle accelerators. Blimps An MRI image of a head. Group 18: The Noble Gases Noble Gases “Electron-rich”: Lewis base properties? Gas-phase PA He 178 kJ/mol Ne 199 Ar 369 Kr 424 Xe 499 H2O 690 NH3 853 PA (proton affinity) = -∆ ∆H for B + H+ → BH+ Long thought to be chemically inert, called the Inert Gases Pauling (1930s) predicted reactivity of xenon to form oxide and fluoride compounds. Early 1960s: observation that O2 reacted with PtF6 to give O2PtF (really O2+ PtF6-) Xe same ionization energy and size as O2 Synthesis of XePtF6 Subsequently XeF2, XeF4, XeOF2, XeF6, XeO3, XeO4 and H4XeO6 Xenon Compounds Crystals of xenon tetrafluoride under magnification. All xenon compounds are strong oxidizing agents: XeF2(aq) + 2 H+(aq) + 2 e- → Xe(g) + 2 HF(aq) E° = +2.64 V Intermolecular Attractions in XeF2, XeF4 Enthalpy Diagram for formation of XeF2 • Xe does not react directly with O2 or Cl2 • No other noble gases combine directly with F2 Electron group geometries for XeF2, XeF4, XeF6 Periodic Trends in Bonding Metallic character decreases from left to right across the table. capped trigonal prism capped octahedron pentagonal bipyramid