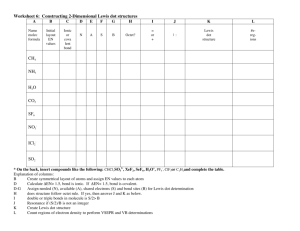
Unit 8: Drawing Molecules

Unit 8: Drawing Molecules
Objectives
Topic 1: Lewis Dot Diagrams & Ionic Bonding
1. Draw a Lewis dot diagram of any representative element.
2. Draw a Lewis dot diagram of any ionic compound.
A Lewis structure is a structural representation of a molecule where dots are used to show electron position around atoms and lines or dot pairs represent covalent bonds between atoms
Lewis Dot & Ionic Bonds
a.k.a. Lewis structures
Steps to drawing Lewis dot diagrams
1. Count up the # of valence e . (same as family # for A group)
2. Write the symbol for the element.
3. For each valence e , put a dot around the symbol.
4. Put one dot on each of the 4 sides of the symbol until each side has one dot, then double up.
Example: Phosphorus 5
P
Lewis Dot & Ionic Bonds
For each element, draw the Lewis dot diagram.
Aluminum Al
Potassium
Xenon
K
Xe
Lewis Dot & Ionic Bonds
In ionic compounds, the cation gives electron(s) to the anion.
Aluminum nitride Al N
This transfer makes the cation positively charged and the anion negatively charged.
These ions then associate with each other.
Al 3+ N 3-
Lewis Dot Diagram
Lewis Dot & Ionic Bonds
Steps to drawing Lewis dot diagrams
1. Write the formula (if not given).
2. Put the oddball ion in the middle.
3. Arrange the other ions around it.
4. Surround the anions with electrons (2 on each side).
Example: Indium chloride
Cl In 3+ Cl -
Cl -
InCl
3
Lewis Dot & Ionic Bonds
For each ionic compound, draw the Lewis dot diagram.
Calcium oxide Ca 2+ O 2-
Iron(II) chloride
Potassium sulfide
Cl -
Fe 2+ Cl -
K + S 2-
K +
Objectives
Topic 2: Lewis Dot Diagrams & Covalent Bonding
1. List the diatomic elements
2. Draw Lewis dot diagrams for molecules
ChemThink
Due 1/9 & 1/10
Ionic Bonding – Tutorial & Question Set
Ionic Formulas – Tutaorial & Question Set
Due 1/15 & 1/16
Covalent Bonding – Tutorial & Question Set
Molecular Shapes – Tutorial & Question Set
Types of Bonds
Covalent Bonding - True Molecules
Nitrogen
Water
Ammonia
Diatomic
Molecule
Diatomic Elements
There are 7 gases that never exist as single atoms.
Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine & Iodine
He H H H
Bonding
In ionic compounds, the e are given from one atom to the other.
In covalent compounds, the e are shared between the two atoms.
When each atom donates 1 e , they form a single bond.
Bonds are represented by lines between the atoms.
Electrons that don’t bond are called lone pairs and are represented by dots.
Example: Iodine
Lone pair
Now each atom has 8
I I
Single bond
Bonding
Steps for drawing molecules
1. Determine which atom goes in the middle a) Never hydrogen b) Oddball in formula c) Fewest valence electrons
2. Arrange letters
3. Add up total valence electrons
4. Bond up to the central atom
5. Subtract two electrons for each bond
6. Count how many each atom still needs
7. If need = have, put lone pairs on picture
If need > have, draw another bond
and repeat 5-7
Example: NH
3
0
2
H N H
N : 5 x 1 = 5
H : 1 x 3 = 3
8 bonds : -2 x 3 = -6
0 need = 2, have = 2
2
0
H
Bonding - practice
For each molecule, draw its Lewis structure.
Lewis structure: a model of a covalent molecule that shows all of the valence electrons
1. Two shared electrons make a single covalent bond,
four make a double bond, etc.
2. unshared pairs: pairs of un-bonded valence electrons
3. Each atom needs a full outer shell, i.e., 8 electrons.
Exception: H needs 2 electrons
Bonding - practice
For each molecule, draw its Lewis structure.
Hydrogen sulfide
H S H
H
2
O
2
H O O H
Carbon tetrachloride
Cl
Cl C
Cl
Cl
Multiple bonds
If each atom contributes 2 e to share, they form a double bond.
Example : carbon disulfide
S C S
Need: 8 Have: 8
When need > have, draw another bond
C = 4 x 1 = 4
S = 6 x 2 = 12
16
2 bonds x -2 = -4
12
1 bond x -2 = -2
10
1 bond x -2 = -2
8
Multiple bonds
If each atom contributes 3 e to share, they form a triple bond.
Example : nitrogen
N
Need: 4 Have: 4
N
N = 5 x 2 = 10
1 bond x -2 = -2
8
1 bond x -2 = -2
6
1 bond x -2 = -2
4
Multiple bonds
Only certain elements can make multiple bonds.
Carbon, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus & Sulfur are the only 5 that usually make multiple bonds. (Si may on occasion)
How do you know if they will?
If one of these is in the center of the molecule and… if it is attached to another one of these and… if the central atom doesn’t have enough electrons… make a double (or triple) bond
COCl
2
Multiple bonds - example
6
Cl C O
Cl
6
C = 4 x 1 = 4
O = 6 x 1 = 6
Cl = 7 x 2 = 14
24
3 bonds x -2 = -6
18
1bond x -2 = -2
16
Multiple bonds - practice
For each compound, draw the Lewis dot structure.
Sulfur dioxide O S O
Hydrocyanic acid
C
2
H
4
N C H
H
C
H
C
H
H
Sulfur trioxide
Mixed Practice
O S
O
O
Tellurium dichloride
Cl Te
Cl
Dinitrogen dioxide
O N N O
O N N O
A Word about the CA
There are two ways to draw these. Dots between elements represent bonds
O S
O
O
O S O
O
Cl Te
Cl
Cl Te Cl
Objectives
Topic 3: Molecular Structure – VSEPR Theory
1. Identify the shape of molecules based on the # of their bonding partners and lone pairs.
Activating Prior Knowledge
What charge does an electron have?
What do two negative charges do?
Bond Angle
In a molecule, each atom is surrounded by a negatively charged electron cloud.
When atoms bond, their clouds overlap
However, e try to stay as far away from each other as possible.
This is called the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory.
Therefore, atoms in a molecule arrange themselves in 3D space to have the maximum bond angles.
Bond Angle
Name
Linear
Linear
Bent
Bent
Trigonal
2
2
3
planar
Pyramidal 3
Tetrahedral 4
# bonding # lone example partners pairs molecule
1
2
N/A
0
F F O
1
2
0
1
0
O
F
S
F
B
H
O
F
H
C
H
H
H
H
N
H
C
O
H
O
H
The Geometry Song
If you’re linear, your partners are one
Or two but your lone pairs are none
Tetra’s the prefix for 4
So four partners, no more
Bent’s two partners, two lone pairs or one
If you’re planar your partners are three
That’s why it’s called trigonal you see
Your lone pairs are none,
‘Cause if they were one
Pyramidal your name would be
Geometry
Steps for determining geometry
1. Draw molecule
2. Count number of bonding partners and number of lone pairs on central atom
3. Reference chart to find geometry
Example: sulfur dichloride
Cl S
Cl
2 bonding partners
2 lone pairs
Bent
Bond Angle - Practice
For each molecule, determine the molecular structure.
HCN
PI
3 linear pyramidal
SiH
4 tetrahedral