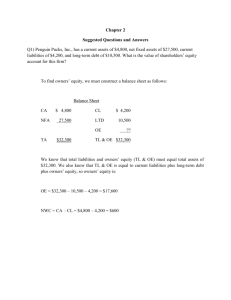
1 FORMULA SHEET Assets (A) – Liabilities (L) = Equity (E) Net
advertisement

1
FORMULA SHEET
Assets (A) – Liabilities (L) = Equity (E)
Net working capital (NWC) = Current assets (CA) – Current liabilities (CL)
Revenues – COGS − Operating expenses = Earnings before interest and taxes = EBIT
EBIT - Interest = Earnings before taxes (EBT)
EBT - Taxes = Earnings after taxes (EAT) or Net income (NI)
Equity (ending) =Equity (beginning) +NI – Dividends + New stock issued – Stock repurchases
Operating cash flow (OCF) = EBIT +Depreciation – Taxes
Net capital spending (NCS) = Net fixed assets (ending) (NFA) –NFA(beginnings) + Depreciation
Change in NWC = NWC (ending) – NWC (beginning). Exclude notes payables from CL.
Cash flow from assets (or free cash flow, FCF) = OCF – NCS – Change in NWC
FCF = Cash to lenders + cash to stockholders
Sources of cash = Uses of cash
Sources: Decrease in assets, increase in liabilities, profits
Uses: Increase in assets, decrease in liabilities, losses, and dividends
Liquidity ratios:
Current ratio (CR) = Current assets (CA) / Current liabilities (CL)
Quick ratio (QR) = (CA – Inventories) / CL
Cash ratio
= Cash / CL
NWC to Total assets = NWC / A
Debt ratios:
Total debt ratio = LIAB / TA = (TA – EQ) / TA
Debt-equity ratio = LIAB / EQ = TA / EQ -1
Equity multiplier = TA / EQ
Long-term debt ratio = Long-term debt / (Long-term debt + equity)
Times interest earned ratio (TIE) = EBIT / Interest
Cash coverage ratio = (EBIT + Depreciation) / Interest
Turnover ratios:
Inventory turnover (IT) = CGS / Inventory
Days’ sales in inventory = 365 / IT
Receivables turnover = Sales / Accounts receivable (AR)
Days’ sales in receivables (or collection period, CP) = 365 / Receivables turnover
NWC turnover = Sales / NWC
Fixed asset turnover = Sales / Net fixed assets
Total asset turnover (TAT) = Sales / Total assets
Profitability ratios:
Profit margin = Net Income / Sales
Return on assets (ROA) = NI / A
Return on equity (ROE) = NI / E
Du Pont equation : ROE = (NI / Sales) (Sales / Total assets) (Total assets / Equity)
ROE = (Profit margin)(Total asset turnover)(Equity multiplier)
Market ratios:
Price earnings multiple (ratio) = Market price per share / Earnings per share
Market-to-book ratio = Market value per share / Book value per share
2
Financial Planning
Internal growth rate = ROA x b / (1- ROA x b)
Sustainable growth rate = ROE x b / (1- ROE x b)
where ROA= return on assets, ROE= return on equity, b= retention ratio
EFN = g x (A – OCL) – PM x S x b x (1+g)
where g =projected growth in sales, A=assets, OCL=operational current assets, PM=profit margin
Raising Capital
Value of a right = PRO – PX = ( PRO – PS ) / (N + 1)
where PRO = the rights-on price, PX = ex-rights price, PS = the subscription price
and N is the number of rights needed to buy one new share at the subscription price
Time Value of Money
PV = FVt /(1+r)t
PV=present value, FV=future value, r=interest rate, t=number of periods
FVAt = A x [(1+r)t -1 ] / r
PVA = A x [1 – (1+r)-t ] / r
C= cash amount, FVAt = future value of an annuity of C dollars per period, PVA=present value of an annuity of C
dollars per period, r=interest rate, t=number of periods.
PV= C / r the perpetuity value
EAR = [1 + (Quoted rate/m)]m -1
EAR=effective annual rate, m= the number of times the interest is compounded per year.
Quoted rate is sometimes called APR (annual percentage rate)
Bonds
P = C x {1 – [1/ (1+r)t ] } / r + 1,000 / (1+r)t
P=current price of bond, C=coupon payments per period, t= the number of coupon payments, r= yield-to-maturity
per period
Fisher effect
(1+R) = (1+r) x (1+h)
R= the nominal rate, r=the real rate, h= the rate of inflation
Stocks
Constant growth case
P0 = D0 x (1+g) / (R – g) = D1 / (R – g) and
R= D1 / P0 + g
P0= value of a share of stock, D0 current dividends per share, D1=next year’s dividends per share
R= required return by shareholders, g= the rate of growth of dividends (earnings and share prices)
Operating cash flow (OCF)
OCF= Net income + Depreciation = EBIT – Taxes + Depreciation
OCF= Sales – Costs – Taxes
OCF= (Sales – Costs) (1- T) + Depreciation x T
where T is the corporate tax rate
3
Break-Even and Degree of Operating Leverage (DOL)
Accounting break-even quantity = (FC + D) / (P – v)
Cash break-even quantity = FC/ (P – v)
Financial break quantity is the quantity that makes the net present value zero.
FC=fixed costs, P=price per unit, v=variable cost per unit
Q =quantity
DOL = 1 + FC / OCF = (P – v) x Q / [(P – v) x Q –FC]
The Security Market Line (SML)
E(Ri) = Rf + [Rm – Rf] x Betai
Cost of Capital
WACC = (E/V) x RE + (P/V) x RP + (D/V) x RD x ( (1 – TC)
WACC=the weighted average cost of capital, RE =cost of equity, RP =cost of preferred stock, RD =before-tax cost
of debt, TC =corporate tax rate..
V= E+P+D
Dollar return
Pt+1 – Pt + Dt
Percent Return
(Pt+1 – Pt + Dt)/Pt
Mean Return
_
X = (R1 + R2 + R3)/3 o r ∑Ri / n
E(R) = Rµ = P1R1 + P2R2 + P3R3 or ∑PiRi
Geometric Mean
[(1 + r1)(1 + r2)(1 + r3)]1/3 or Π(1 + ri)1/ n
Variance
_
_
_
_
Var = [(R1 – X)2 + (R2 – X)2 + (R3 – X)]2/2 or ∑(Ri – X)2/n-1
σ2 = P1(R1 - Rµ)2 + P2(R2 - Rµ)2 + P3(R3 - Rµ)2 or ∑ Pi(Ri - Rµ)2