File
advertisement

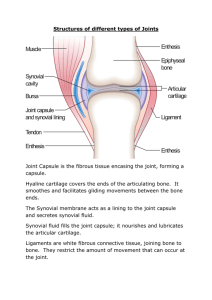
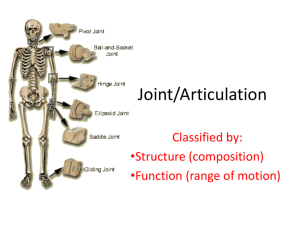
Chapter 8 Joints = Articulations Junctions between bones Bind skeletal system together Make bone growth possible Permit skeleton to change shape during childbirth Enable body to move in response to skeletal muscle contraction Fibrous connective tissue Joints vary considerably in structure & function Classified by movement Synarthroses Amphiarthroses Diarthroses Classified by tissue type used to bind bones Fibrous Cartilaginous Synovial Dense CT (collagenous) Syndesmosis Ex. Tibia/Fibula Suture Ex. Skull Gomphosis Peg/socket Ex. Teeth and jaw Hyaline cartilage connects bones Synchondrosis Bands of cartilage join bones Primary cartilaginous joint ▪ Ex. Epiphyseal plate ▪ Ex. 1st rib and manubrium Symphysis Hyaline cartilage attached to fibrocartilage Secondary cartilaginous joint Most joints Functions Resist wear Minimize shock Minimize friction Diarthrotic Ex. Knee Components: Articular cartilage Joint capsule ▪ Reinforced by ligaments ▪ Dense CT encasing joint ▪ Synovial membrane ▪ Synovial fluid Meniscus Fibrocartilage Projects into joint cavity Cushion Distribute body weight Bursa Sac of synovial fluid Located between skin and bony projection Cushion tendon over bone or another tendon Ball and socket rotational Condyloid No rotation Gliding Hinge Flexion, extension Pivot Rotation Saddle Two plane motion Rotation Move part around axis Circumduction End follows circular path Supination/Pronation Abduction/Adduction Flexion/Extension Hyperextension Protraction/retraction Elevation/depression Eversion/inversion Related to changes in collagen structure Fibrous Accumulate bone matrix Stiffen or fuse Cartilaginous Loss of water and calcium Loss of elasticity Stiffening Synovial Circulation slows Collagen shortens and stiffens Lost elasticity, range of motion Rotator cuff 4 muscles Tendons and fibrous joint capsule Reinforce joint Support joint Why do you suppose that shoulder joints are relatively easily dislocated? Cruciate ligaments Anterior (ACL) Posterior (PCL) Collateral ligaments Lateral (LCL) Medial (MCL) Menisci Medial Lateral Tendons Quadriceps Patella Knee surgery Femur Arthroscopic Scissors to remove tear Tibia Torn meniscus Due to injury, infection, wear/tear Sprains Tearing/overstretching CT (cartilage, ligaments, or tendons) ▪ Ex. Inverting ankle ▪ Sprain due to stretching lateral ligaments RICE Bursitis Inflammation of bursa ▪ Repetitive motion, excessive pressure Rest, ice, NSAIDs, cortisone Arthritis Inflamed, swollen, painful joints Rheumatoid ▪ Autoimmune disorder ▪ Most painful form ▪ Inflammation, thickening of synovium, softening of bone/cartilage, ossification in/of joint Osteoarthritis ▪ Degenerative disorder ▪ Most common type ▪ Articular cartilage weakens, disintegrates Chapter Assessments 2-8, 12-17, 20, 23, 26-29, 31 Integrative Assessments 1-5