Joint Articulations Synarthrosis
advertisement

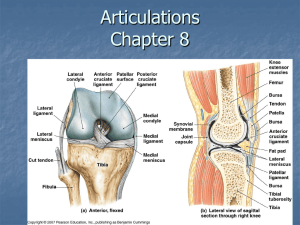
Joint Articulations Synarthrosis • Synarthroses • A junction between bones that is held together by dense irregular connective tissue • Function is to bind bones together and to transmit force from one bone to the next with minimal joint motion • Movement?: • E.g., ____________ ____________ A junction between bones that is formed primarily by fibrocartilage and/or hyaline cartilage. Can have disks or pads between two articulating surfaces Examples: Intervertebral joints (disk), pubic symphysis (disk); First rib & sternum (hyaline cartilage) 1 Diarthroses Joints • Diarthroses = __________ • All ___________ have the following features: 1. Synovial fluid • Provides nutrition and lubrication inside the joint cavity for the… 2. _________________ • Covers the ends of the bones 3. Articular capsule • Connective tissue that encloses the joint • Is composed of 2 distinct layers, internal layer is called… Diarthroses (cont.) 4. _____________ • • Average 3-10 cell layers thick Cells of synovial membrane also manufacture and add hyaluronate and lubricating glycoproteins (i.e., lubricin) to the joint fluid 5. Capsular ligaments • Are a part of the external, or fibrous, layer of the capsule. Thickened regions of the fibrous capsule are these ligaments 6. Blood vessels • Have capillary beds that penetrate as far as the junction of the fibrous capsule and synovial membrane 7. Sensory Nerves • Also supply the fibrous capsule Other parts of synovial joint • __________ • Pads of fibrocartilage which increase congruency and improve force dispersion • Peripheral labrum of fibrocartilage • Deepen the concave member of these joint and support and thicken the attachment of the joint capsule • E.g., : • Fat Pads • Lie between fibrous capsule and the synovial membrane • Synovial plicae • Overlapped pleats of synovial tissue • Increase synovial surface area and allow joint motion without undue tension on the synovial lining 2 Quick Review • 3 Types of Joints: • 2 parts of the articular capsule? Categories of Synovial Joints Gliding Joint (_____) 1) • • Two flat bony surfaces that allow limited gliding motion E.g., _____ joint 2) • • Allows rotational movement around a long axis E.g., rotation of radius and radio-ulnar joint Categories of Synovial Joints 3. Biaxial Ball & Socket joint (__________) • • Joint in where movement occurs in two planes E.g., knee joint 4. Multiaxial Ball & Socket joint (Ball & Socket) • • Permits movement in ______ planes E.g., shoulder and hip joints 3 Categories of Synovial Joints _______ Joints 5) • Permits wide range of movement in only one plane E.g., humeroradial joint & interphalangeal joints • Saddle joint 6) • • Each partner of joint has one surface is concave , the other convex Best example at carpometacarpal joint Stability of Synovial Joints • Stability is defined as resistance to displacement • Structure of joints is related to their function • Highly moveable joints lack stability, i.e, there is an inverse relationship between mobility and stability Factors that affect joint stability 1. _____ of bony structure • Shoulder vs. hip 2. ______________ arrangement • Ligaments are stress resistant tissue that connects bone to bone 3. ___________ arrangement • Increased mobility requires increased contribution by the musculature that crosses the joint 4. Fascia • IT band in knee provides additional support 5. Atmospheric Pressure • Joints act as a vacuum to approximate joint surfaces 4 Joint Motion Osteokinematic Motion • • • • Examples are flexion, extension, abduction, etc. ___________ = ROM exceeds normal anatomic limits ___________ = ROM is less than would be normally permitted by joint Causes of hypomobility include: • • Bony or cartilaginous block Ligament, capsule, or muscle contracture Joint Motion Arthrokinematics • • • Refer to the movement of the joint surfaces ____________________________ are examples of arthrokinematic motion Concave-Convex Rule: • • When a concave surface moves on a stable convex surface, sliding occurs in the same direction as motion of the bony lever When a convex surface moves on a stable concave surface, sliding occurs in the opposite direction as motion of the bony lever 5 Tissues That Form Joints • 4 Primary types of connective tissues: • • • • Dense Irregular Connective Tissue Articular Cartilage Fibrocartilage Bone 6 Dense Irregular Connective Tissue • Anatomic Location: • External fibrous layer of joint capsule • Forms ___________ • Fibers: • High ________ collagen fiber content • Low _______ fiber content • Ground Substance: • Low amount • Purpose: • Restrains unwanted movement between bones • Read last paragraph of section on page _____ Articular Cartilage • Specialized type of hyaline cartilage • No ___________ – a layer of connective tissue that covers most cartilage • ___________ contains _______ and able to repair itself • It is Avascular & ___________ • Very low coefficient of friction • Anatomic Location: • Ends of articulating bones in synovial joints • Fibers: • High __________ collagen fiber • Ground Substance: • High amount • Purpose: • Resists and distributes compressive forces and shear forces Fibrocartilage • Perichondrium is poorly organized and contains small blood vessels located only near the ____________ of the tissue • Nutrition of fibrocartilage in synovial joints is dependent on the synovial fluid • Nutrition of fibrocartilage in amphiarthroses is assisted by the “milking” action of intermittent weight bearing • E.g., Intervertebral disks are insufficiently nourished when the spine is held in fixed postures for extended periods • Anatomic location: • Intervertebral disks; disks within pubic symphasis; Menisci; labrum 7 Fibrocartilage (cont.) • Fibers: • Multidirectional ______ collagen • Ground Substance: • Moderate amount • Function: • Can provide some joint stabilization • Primary function is to provide __________ Closure • What type of joint is between your tooth and mandible? • Which direction do you need mobilize the tibia to increase knee extension? Closure • All synovial joints have these 7 things in common: • What factors affect joint stability? 8 Closure • What is the difference between osteokinematic and arthrokinematic motion? • What are the main differences between dense irregular connective tissue, articular cartilage, and fibrocartilage? 9