Naming Binary Covalent Compounds WS
advertisement

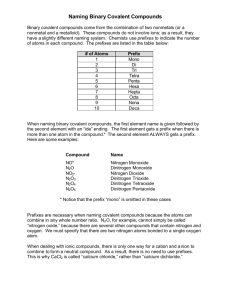
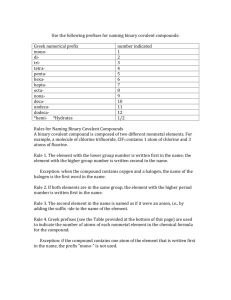
Name_______________________________Period__________Date__________ Naming Binary Covalent Compounds Binary covalent compounds come from the combination of two nonmetals (or a nonmetal and a metalloid). These compounds do not involve ions; as a result, they have a slightly different naming system. Chemists use prefixes to indicate the number of atoms in each compound. Number Greek Prefix (Memorize) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 When naming binary covalent compounds, the first element name is given followed by the second element with an “ide” ending. The first element gets a prefix when there is more than one atom in the compound (NO mono on first element listed*). The second element ALWAYS gets a prefix. Binary Covalent Compound Name Binary Covalent Compound Formula *Nitrogen Monoxide N2O *NO2 Dinitrogen Trioxide Dinitrogen Tetraoxide N2O5 Prefixes are necessary when naming covalent compounds because the atoms can combine in any whole number ratio. N2O, for example, cannot simply be called “nitrogen oxide,” because there are several other compounds that contain nitrogen and oxygen. We must specify that there are two nitrogen atoms bonded to a single oxygen atom. When dealing with ionic compounds, there is only one way for a cation and anion to combine to form a neutral compound. As a result, there is no need to use prefixes. This is why CaCl2 is called “calcium chloride,” rather than “calcium dichloride.” Ionic Compound Name (NO GREEK) Ionic Compound Formula Lithium nitride Lithium oxide Barium fluoride Barium phosphide Compare and contrast the naming rules for Binary Ionic and Binary Covalent compounds. Record below: Write the formulas for the following covalent compounds 1. antimony tribromide ______________________________ 2. chlorine dioxide _________________________________ 3. iodine pentafluoride ______________________________ 4. ammonia ______________________________________ 5. phosphorus triiodide ______________________________ Write the names for the following covalent compounds: 6. SeF6 _________________________________ 7. Si2Br6 ________________________________ 8. SCl4 _________________________________ 9. CH4 _________________________________ 10. NF3 ________________________________